|
Vizier (Ebla)
Vizier ( or ), is the title used by modern scholars to indicate the head of the administration in the first Eblaite kingdom. The title holder held the highest position after the king and controlled the army. During the reign of king Isar-Damu, the office of vizier became hereditary. Title and responsibilities Vizier is a rendering presented by Alfonso Archi to indicate the second in command official of Ebla, whose native title was probably "head of the administration" (lugal sa-za). Eblaite viziers' authority was of such importance that they were thought of as kings during the earliest stages of deciphering the tablets of Ebla, as the names of actual monarchs rarely appeared in administrative tablets. Aside from heading the administration, the vizier was in command of the kingdom's trade, army and acted as the head of provincial governors. History The title was not created until after the period of king Igrish-Halam (fl c. 2360 BC), but high officials were already prominent dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
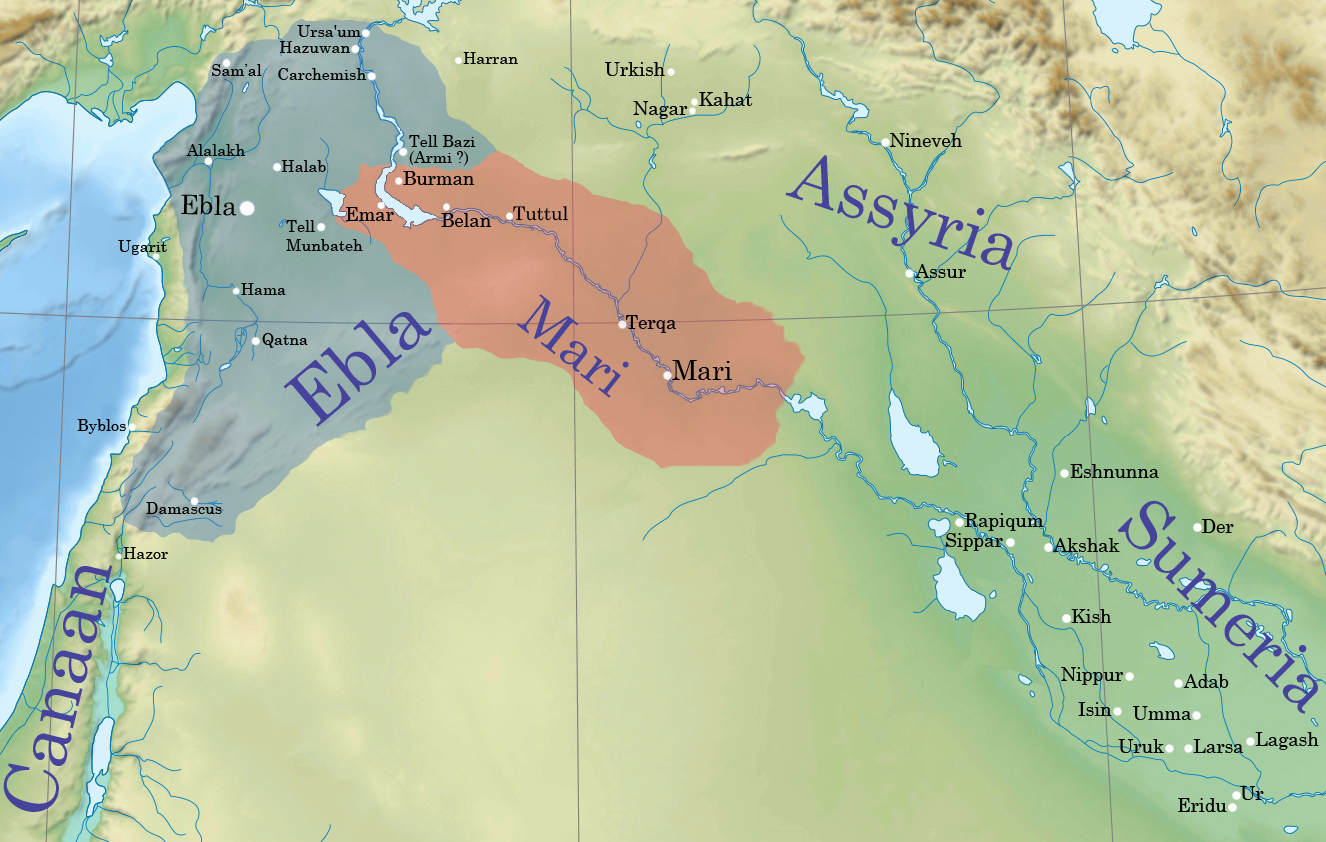
Ebla
Ebla (Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', , modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a Tell (archaeology), tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was an important center throughout the and in the first half of the Its discovery proved the Levant was a center of ancient, centralized civilization equal to Ancient Egypt, Egypt and Mesopotamia and ruled out the view that the latter two were the only important centers in the Ancient Near East, Near East during the Early Bronze Age. The first Eblaite kingdom has been described as the first recorded world power. Starting as a small settlement in the Early Bronze Age ( ), Ebla developed into a trading empire and later into an expansionist power that imposed its hegemony over much of northern and eastern Syria. Ebla was destroyed during the It was then rebuilt and was mentioned in the records of the Third Dynasty of Ur. The second Ebla w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibbi-Sipish
Ibbi-Sipish or Ibbi-Zikir (died 2300 BC) was the vizier of Ebla for king Ishar-Damu for 17 years. He was the son of his predecessor, Ibrium, who had been Ishar-Damu's vizier for 15 years. Ibbi-Sipish visited cities abroad, such as Kish. He also concluded a treaty with Armi. It is further known from one tablet that Ibbi-Sipish vanquished king Hida'ar of Mari, Ebla's main rival in the region, in the 32nd year of Ishar-Damu's reign. However, Ebla's destruction was to come only three years later, presumably at the hands of the Akkadian ruler Sargon the Great Sargon of Akkad (; ; died 2279 BC), also known as Sargon the Great, was the first ruler of the Akkadian Empire, known for his conquests of the Sumerian city-states in the 24th to 23rd centuries BC.The date of the reign of Sargon is highly unc .... Until 1985, the consensus of scholars had been that Ibbi-Sipish, Ibrium, and Ibrium's predecessor Ar-ennum, had all been reigning monarchs in Ebla; consequently, it was ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibrium
Ibrium (died 2322 BC), also spelt Ebrium, was the vizier of Ebla for king Irkab-Damu and his successor Isar-Damu. Ibrium is attested to have campaigned against the city of Abarsal during the time of vizier Arrukum. He took office after Arrukum during the last two years of Irkab-Damu's reign and continued to hold office during the reign of Isar-Damu. Ibrium kept his position for around 20 years and was succeeded by his son Ibbi-Sipish, thus establishing a parallel dynasty of viziers next to the royal family. Ibrium waged a war against Armi in his ninth year as vizier. The Ebla tablets mention that the battle happened near a town called Batin (a location possibly located in modern northeastern Aleppo Aleppo is a city in Syria, which serves as the capital of the Aleppo Governorate, the most populous Governorates of Syria, governorate of Syria. With an estimated population of 2,098,000 residents it is Syria's largest city by urban area, and ...), and that a messenger arr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irkab-Damu
Irkab-Damu () was king ( Malikum) of the first Eblaite kingdom, whose era saw Ebla's turning into the dominant power in the Levant. During his reign, the vizier started to acquire an important role in running the affair of the state and the military. Irkab-Damu's reign is also noted for the wide diplomatic relations between Ebla and the surrounding kingdoms. Reign Irkab-Damu succeeded king Igrish-Halam, whose reign was characterized by an Eblaite weakness, and tribute paying to the kingdom of Mari with whom Ebla fought a long war. Irkab-Damu started his reign by concluding a peace and trading treaty with Abarsal (probably located along the Euphrates river east of Ebla), one of the first recorded treaties in history. Ebla paid tribute to Mari during Irkab-Damu's first years on the throne. A letter from king Enna-Dagan of Mari was discovered at Ebla, and was used by the Mariote monarch as a tool to assert Mari's authority, as it contained a historic telling of the victories wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Between Ebla And Abarsal
The Treaty between Ebla and Abarsal is a diplomatic treaty that was concluded between the Early Bronze Age city-states of Ebla and Abarsal. It was signed around 2350 BC, and may be the earliest recorded diplomatic treaty in human history. While the geographical location of Ebla is clear, the historians have so far not been able to identify the exact location of Abarsal. Among several hypotheses, Giovanni Pettinato prefers to see Abarsal as the future city of Assur, the capital of Assyria. However, the text indicates that it is a state bordering or close to Ebla with which it shares a common border. Dating and chronology The tablet containing the treaty was found in the archives of Ebla that survived the fire of the royal palace. Despite the difficulties encountered during the restoration of the cuneiform tablets, it was possible to date this treaty around the year 2350 BC, thanks to prosopographic studies of its writing. This treaty was probably written at the time of King Irk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isar-Damu
Isar-Damu (died 2305 BC), was the king ( Malikum) of the first Eblaite kingdom. Isar-Damu fought a long war with Mari which ended in Eblaite victory; he was probably the last king of the first kingdom. Reign Isar-Damu succeeded his father Irkab-Damu as a young child; his mother, Dusigu, seems to have taken advantage of her position as her husbands favorite wife and her probable familial relation to the powerful vizier Ibrium in order to elevate her son to the throne, despite him being one of Irkab-Damu's youngest sons. The first years of Isar-Damus's reign were dominated by his mother and the vizier; texts from Ebla show that Isar-Damu's name appeared on official documents after that of his mother. Ibrium was the commander of the army and he conducted multiple campaigns against rebellious vassal-rulers or neighboring kingdoms. Isar-Damu concluded an alliance with Nagar and the relations progressed toward a dynastic marriage between princess Tagrish-Damu, Isar-Damu's daught ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tir (official)
Tir, tir or TIR may refer to: * The modern Persian name for the Zoroastrian god Tishtrya * Tir (month), of the Iranian calendar * Tir (god), of ancient Armenia * Tabar, Iran, a village in North Khorasan Province * Old English spelling of the Norse god Týr * Tir (demon), son of Iblis *''Tir'', a 2010 album by Cerys Matthews Abbreviations * Total internal reflection * Tigrinya language, ISO 639 code * Tirupati Airport, IATA code * Translocated intimin receptor, used by ''E. coli'' * TIR Convention, (''Transports Internationaux Routiers'', International Road Transport) * Toll-Interleukin receptor * Total indicator reading in metrology Other * Tir McDohl, in the video game ''Suikoden'' * INS ''Tir'', various ships of the Indian navy See also *Tira (other) *Tir Planitia, a large basin on Mercury *Tír na nÓg In Irish mythology, Tír na nÓg ( , ; ) or Tír na hÓige ('Land of Youth') is one of the names for the Celtic Otherworld, or perhaps for a part of it. Tír ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darmiya (Vizier)
Darmiya or Darma is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken in the Darma Valley, Dharchula Tehsil, Pithoragarh District of the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is one of the fifteen tribes, as stated in ''The Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Uttar Pradesh Order, 1967'' (C.O. 78) in clause (1) of Article 342 of the Constitution of India. Majorly it is called Bhotia; Bhotia is the broad term used in Himalayan region: several communities and languages are considered under this term. This tribal language is the member of west Tibeto-Burman language family in the Himalayan region of Uttarakhand. It is related to Rangas, Rongpo, Chaudangsi, and Byangsi. Alternate names for this language include Darma, Darma Lwo, Darma-Lwo, Darmani, Saukas, and Shaukas. Information about the language was first published in Grierson's ''Linguistic Survey of India'', and it has been studied by Krishnamurti, Cristina Wills, K. Srikumar, Kavita Rastogi, Ashish Kumar Pandey and Vishnu Singh. Darmiya language has 34 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |