|
Vesical Nervous Plexus
The vesical nervous plexus arises from the forepart of the pelvic plexus. The nerves composing it are numerous, and contain a large proportion of spinal nerve fibers. They accompany the vesicle arteries, and are distributed to the sides and fundus of the bladder. Numerous filaments also pass to the seminal vesicles and vas deferens; those accompanying the vas deferens join, on the spermatic cord The spermatic cord is the cord-like structure in males formed by the vas deferens (''ductus deferens'') and surrounding tissue that runs from the deep inguinal ring down to each testicle. Its serosal covering, the tunica vaginalis, is an exten ..., with branches from the spermatic plexus. Additional images File:Gray838.png, The right sympathetic chain and its connections with the thoracic, abdominal, and pelvic plexuses. References External links {{Authority control Nerve plexus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sympathetic Trunk
The sympathetic trunk (sympathetic chain, gangliated cord) is a paired bundle of nerve fibers that run from the base of the skull to the coccyx. It is a major component of the sympathetic nervous system. Structure The sympathetic trunk lies just lateral to the vertebral bodies for the entire length of the vertebral column. It interacts with the anterior rami of spinal nerves by way of rami communicantes. The sympathetic trunk permits preganglionic fibers of the sympathetic nervous system to ascend to spinal levels superior to T1 and descend to spinal levels inferior to L2/3.Greenstein B., Greenstein A. (2002): Color atlas of neuroscience – Neuroanatomy and neurophysiology. Thieme, Stuttgart – New York, . The superior end of it is continued upward through the carotid canal into the skull, and forms a plexus on the internal carotid artery; the inferior part travels in front of the coccyx, where it converges with the other trunk at a structure known as the ganglion impar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
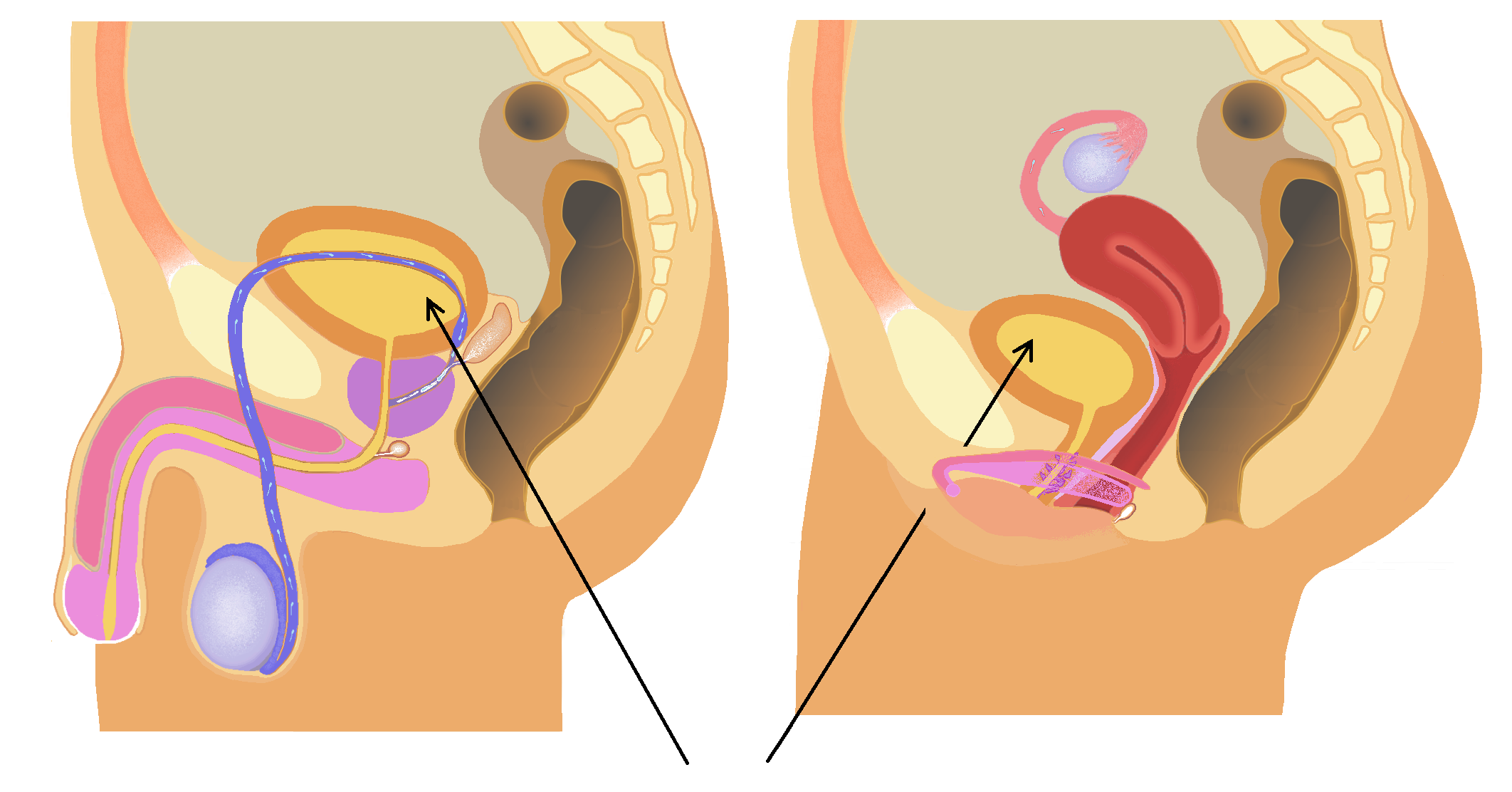
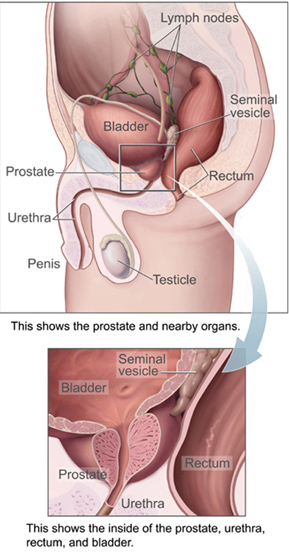
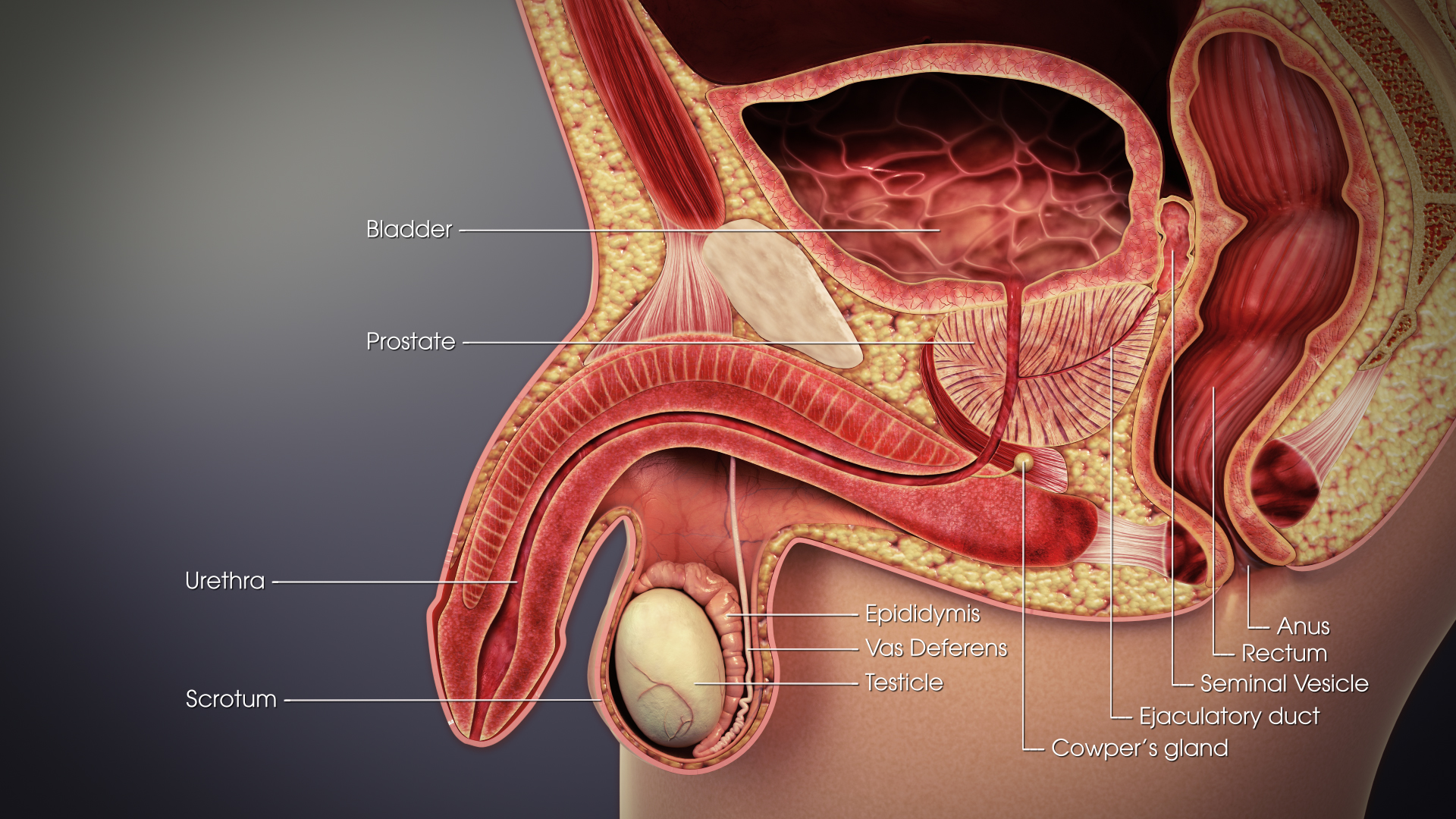
Urinary Bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. The typical adult human bladder will hold between 300 and (10 and ) before the urge to empty occurs, but can hold considerably more. The Latin phrase for "urinary bladder" is ''vesica urinaria'', and the term ''vesical'' or prefix ''vesico-'' appear in connection with associated structures such as vesical veins. The modern Latin word for "bladder" – ''cystis'' – appears in associated terms such as cystitis (inflammation of the bladder). Structure In humans, the bladder is a hollow muscular organ situated at the base of the pelvis. In gross anatomy, the bladder can be divided into a broad (base), a body, an apex, and a neck. The apex (also called the vertex) is directed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvic Plexus
The pelvis (: pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of an anatomical trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis or pelvic skeleton). The pelvic region of the trunk includes the bony pelvis, the pelvic cavity (the space enclosed by the bony pelvis), the pelvic floor, below the pelvic cavity, and the perineum, below the pelvic floor. The pelvic skeleton is formed in the area of the back, by the sacrum and the coccyx and anteriorly and to the left and right sides, by a pair of hip bones. The two hip bones connect the spine with the lower limbs. They are attached to the sacrum posteriorly, connected to each other anteriorly, and joined with the two femurs at the hip joints. The gap enclosed by the bony pelvis, called the pelvic cavity, is the section of the body underneath the abdomen and mainly consists of the reproductive organs and the rectum, while the pelvic floor at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Nerve
A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries Motor neuron, motor, Sensory neuron, sensory, and Autonomic nervous system, autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into the corresponding cervical vertebrae, cervical, thoracic vertebrae, thoracic, lumbar vertebrae, lumbar, sacral vertebrae, sacral and coccygeal vertebrae, coccygeal regions of the spine. There are eight pairs of cervical nerves, twelve pairs of thoracic nerves, five pairs of lumbar nerves, five pairs of sacral nerves, and one pair of coccygeal nerves. The spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system. Structure Each spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, formed from the combination of nerve root axon, fibers from its Dorsal root of spinal nerve, dorsal and Ventral root of spinal nerve, ventral roots. The dorsal root is the afferent nerve fiber, afferent sensory root and carries sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vesicle Arteries
Vesical arteries are variable in number. They supply the bladder and terminal ureter. The two most prominent are the superior vesical artery and the inferior vesical artery. The superior vesical artery comes off of the internal iliac artery and sometimes the umbilical artery. The inferior vesical artery comes off of the internal iliac artery. The inferior vesical artery is a pelvic branch of the internal iliac artery in men; and in women it branches from the vaginal artery. This literature has been reviewed recently with observations of variation in pelvic vascularization and the close relationship between vaginal In mammals and other animals, the vagina (: vaginas or vaginae) is the elastic, muscular reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix (neck of the uterus). The vaginal introit ... and bladder vascularization in women. References Arteries of the abdomen {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fundus Of The Urinary Bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. The typical adult human bladder will hold between 300 and (10 and ) before the urge to empty occurs, but can hold considerably more. The Latin phrase for "urinary bladder" is ''vesica urinaria'', and the term ''vesical'' or prefix ''vesico-'' appear in connection with associated structures such as vesical veins. The modern Latin word for "bladder" – ''cystis'' – appears in associated terms such as cystitis (inflammation of the bladder). Structure In humans, the bladder is a hollow muscular organ situated at the base of the pelvis. In gross anatomy, the bladder can be divided into a broad (base), a body, an apex, and a neck. The apex (also called the vertex) is directed forward toward the up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. The typical adult human bladder will hold between 300 and (10 and ) before the urge to empty occurs, but can hold considerably more. The Latin phrase for "urinary bladder" is ''vesica urinaria'', and the term ''vesical'' or prefix ''vesico-'' appear in connection with associated structures such as vesical veins. The modern Latin word for "bladder" – ''cystis'' – appears in associated terms such as cystitis (inflammation of the bladder). Structure In humans, the bladder is a hollow muscular organ situated at the base of the pelvis. In gross anatomy, the bladder can be divided into a broad (base), a body, an apex, and a neck. The apex (also called the vertex) is directed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seminal Vesicle
The seminal vesicles (also called vesicular glands or seminal glands) are a pair of convoluted tubular accessory glands that lie behind the urinary bladder of male mammals. They secrete fluid that largely composes the semen. The vesicles are 5–10 cm in size, 3–5 cm in diameter, and are located between the bladder and the rectum. They have multiple outpouchings, which contain secretory glands, which join together with the vasa deferentia at the ejaculatory ducts. They receive blood from the vesiculodeferential artery, and drain into the vesiculodeferential veins. The glands are lined with column-shaped and cuboidal cells. The vesicles are present in many groups of mammals, but not marsupials, monotremes or carnivores. Inflammation of the seminal vesicles is called seminal vesiculitis and most often is due to bacterial infection as a result of a sexually transmitted infection or following a surgical procedure. Seminal vesiculitis can cause pain in the lower abdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vas Deferens
The vas deferens (: vasa deferentia), ductus deferens (: ductūs deferentes), or sperm duct is part of the male reproductive system of many vertebrates. In mammals, spermatozoa are produced in the seminiferous tubules and flow into the epididymal duct. The end of the epididymis is connected to the vas deferens. The vas deferens ends with an opening into the ejaculatory duct at a point where the duct of the seminal vesicle also joins the ejaculatory duct. The vas deferens is a partially coiled tube which exits the abdominal cavity through the inguinal canal. Etymology ''Vas deferens'' is Latin, meaning "carrying-away vessel" while ''ductus deferens'', also Latin, means "carrying-away duct". Structure The human vas deferens measures 30–35 cm in length, and 2–3 mm in diameter. It is continuous proximally with the tail of the epididymis, and exhibits a tortuous, convoluted initial/proximal section (which measures 2–3 cm in length). Distally, it forms a dilated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatic Cord
The spermatic cord is the cord-like structure in males formed by the vas deferens (''ductus deferens'') and surrounding tissue that runs from the deep inguinal ring down to each testicle. Its serosal covering, the tunica vaginalis, is an extension of the peritoneum that passes through the transversalis fascia. Each testicle develops in the lower thoracic and upper lumbar region and migrates into the scrotum. During its descent it carries along with it the vas deferens, its vessels, nerves etc. There is one on each side. Structure The spermatic cord is ensheathed in three layers of tissue: * '' external spermatic fascia'', an extension of the innominate fascia that overlies the aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle. * '' cremasteric muscle and fascia'', formed from a continuation of the internal oblique muscle and its fascia. * '' internal spermatic fascia'', continuous with the transversalis fascia. The normal diameter of the spermatic cord is about 16 mm (range 11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatic Plexus
The spermatic plexus (or testicular plexus) is derived from the renal plexus, receiving branches from the aortic plexus. It accompanies the internal spermatic artery to the testis A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is Homology (biology), homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of Androgen, androgens, p .... Additional images File:Gray849.png, Lower half of right sympathetic cord. File:Gray1144.png, The scrotum. References External links Nerve plexus Nerves of the torso {{Neuroanatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |