|
Very-high-energy Gamma Ray
A very-high-energy gamma ray (VHEGR) is Gamma ray, gamma radiation with photon energy, photon energies of 100 GeV (gigaelectronvolt) to 100 TeV (teraelectronvolt), i.e., 1011 to 1014 electronvolts. This is approximately equal to wavelengths between 10−17 and 10−20 meters, or frequencies of 2 × 1025 to 2 × 1028 Hz. Such energy levels have been detected from emissions from astronomical sources such as some binary star systems containing a compact object. For example, radiation emitted from Cygnus X-3 has been measured at ranges from GeV to Exa-, exaelectronvolt-levels. Other astronomical sources include BL Lacertae, 3C 66A Markarian 421 and Markarian 501. Various other sources exist that are not associated with known bodies. For example, the High Energy Stereoscopic System, H.E.S.S. catalog contained 64 sources in November 2011. Detection Instruments to detect this radiation commonly measure the Cherenkov radiation produced by secondary particles generated from an energetic p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
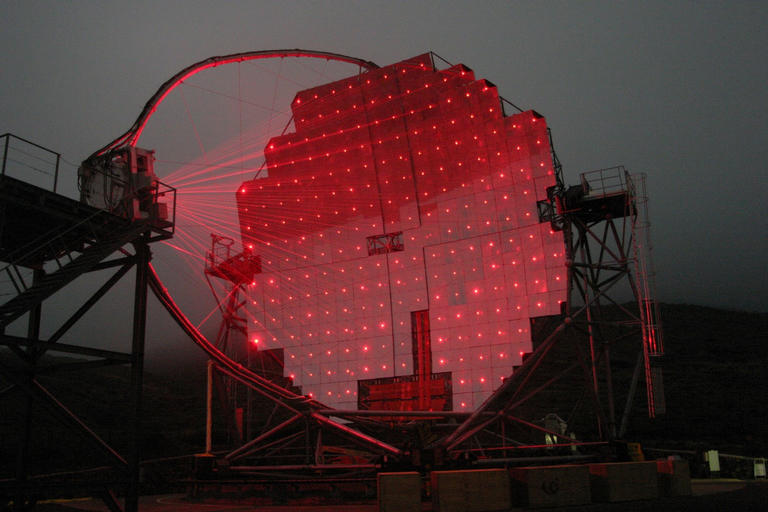
The MAGIC Telescope At Night
''The'' is a grammatical Article (grammar), article in English language, English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the Most common words in English, most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
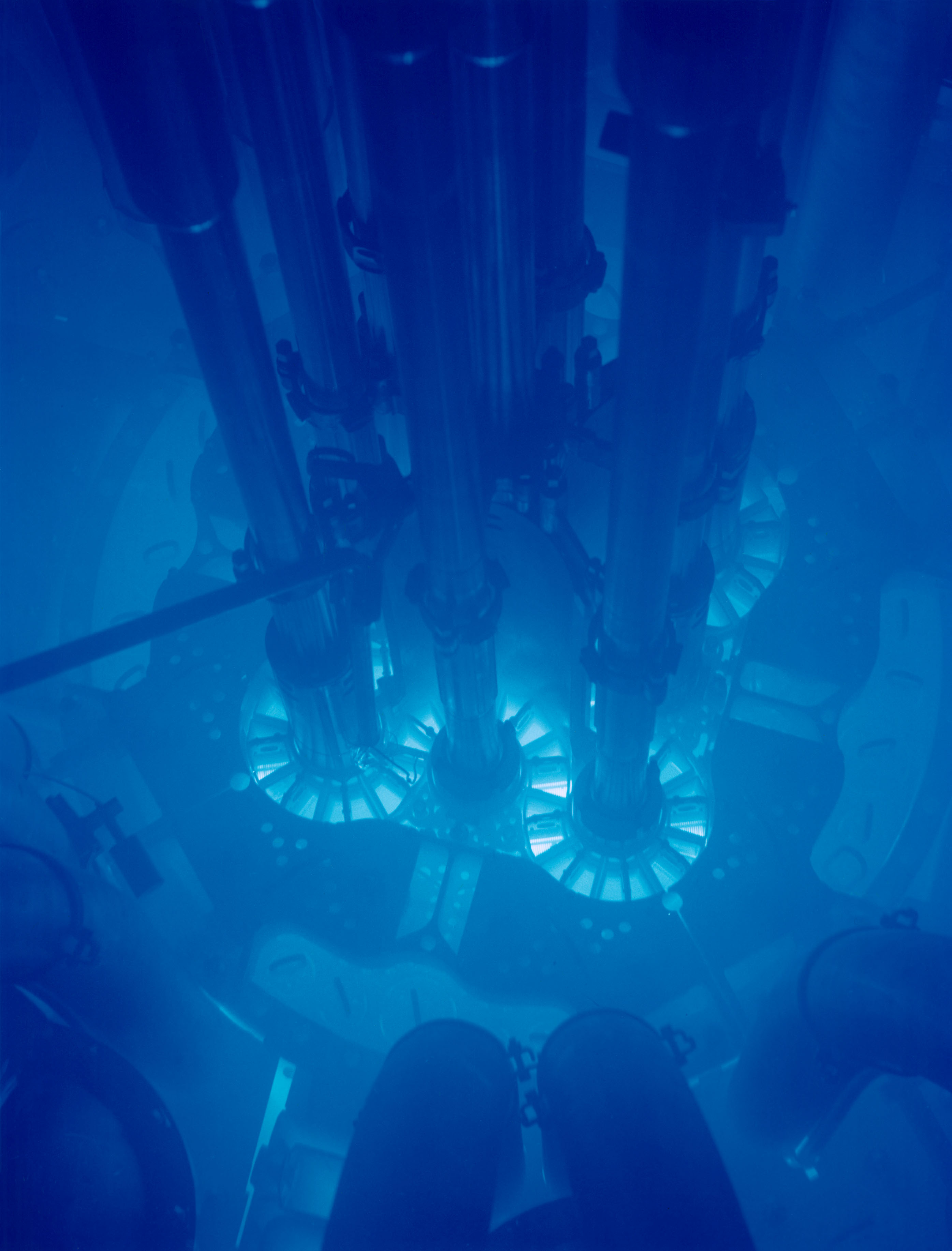
Cherenkov Radiation
Cherenkov radiation () is electromagnetic radiation emitted when a charged particle (such as an electron) passes through a dielectric medium (such as distilled water) at a speed greater than the phase velocity (speed of propagation of a wavefront in a medium) of light in that medium. A classic example of Cherenkov radiation is the characteristic blue glow of an underwater nuclear reactor. Its cause is similar to the cause of a sonic boom, the sharp sound heard when faster-than-sound movement occurs. The phenomenon is named after Soviet physicist Pavel Cherenkov. History The radiation is named after the Soviet scientist Pavel Cherenkov, the 1958 Nobel Prize winner, who was the first to detect it experimentally under the supervision of Sergey Vavilov at the Lebedev Institute in 1934. Therefore, it is also known as Vavilov–Cherenkov radiation. Cherenkov saw a faint bluish light around a radioactive preparation in water during experiments. His doctorate thesis was on lumin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Rays
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own galaxy, and from distant galaxies. Upon impact with Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere, cosmic rays produce air shower (physics), showers of secondary particles, some of which reach the Earth's surface, surface, although the bulk are Deflection (physics), deflected off into space by the Earth's magnetic field, magnetosphere or the heliosphere. Cosmic rays were discovered by Victor Francis Hess, Victor Hess in 1912 in balloon experiments, for which he was awarded the 1936 Nobel Prize in Physics. Direct measurement of cosmic rays, especially at lower energies, has been possible since the launch of the first satellites in the late 1950s. Particle detectors similar to those used in nuclear and high-energy physics are u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultra-high-energy Gamma Ray
Ultra-high-energy gamma rays are gamma rays with photon energies higher than 100 TeV (0.1 PeV). They have a frequency higher than 2.42 × 1028 Hz and a wavelength shorter than 1.24 × 10−20 m. The existence of these rays was confirmed in 2019. In a 18 May 2021 press release, China's Large High Altitude Air Shower Observatory (LHAASO) reported the detection of a dozen ultra-high-energy gamma rays with energies exceeding 1 peta-electron-volt (quadrillion electron-volts or PeV), including one at 1.4 PeV, the highest energy photon ever observed. The authors of the report have named the sources of these PeV gamma rays PeVatrons. In 2024, LHAASO announced the detection of a 2.5 PeV gamma ray originating from the Cygnus X region. Importance Ultra-high-energy gamma rays are of importance because they may reveal the source of cosmic rays. Discounting the relatively weak effect of gravity, they travel in a straight line from their source to an observer. This is unlike cosmic rays whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attojoule
The joule ( , or ; symbol: J) is the unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI). In terms of SI base units, one joule corresponds to one kilogram- metre squared per second squared One joule is equal to the amount of work done when a force of one newton displaces a body through a distance of one metre in the direction of that force. It is also the energy dissipated as heat when an electric current of one ampere passes through a resistance of one ohm for one second. It is named after the English physicist James Prescott Joule (1818–1889). Definition According to the International Bureau of Weights and Measures the joule is defined as "the work done when the point of application of 1 MKS unit of force ewtonmoves a distance of 1 metre in the direction of the force." In terms of SI base units and in terms of SI derived units with special names, the joule is defined as One joule is also equivalent to any of the following: * The work required to move ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landau–Pomeranchuk–Migdal Effect
In high-energy physics, the Landau–Pomeranchuk–Migdal effect, also known as the Landau–Pomeranchuk effect and the Pomeranchuk effect, or simply LPM effect, is a reduction of the bremsstrahlung and pair production cross sections at high energies or high matter densities. It is named in honor of Lev Landau, Isaak Pomeranchuk and Arkady Migdal. Overview A high energy particle undergoing multiple soft scatterings from a medium will experience interference effects between adjacent scattering sites. From uncertainty as the longitudinal momentum transfer gets small the particles wavelength will increase, if the wavelength becomes longer than the mean free path in the medium (the average distance between scattering sites) then the scatterings can no longer be treated as independent events, this is the LPM effect. The Bethe–Heitler spectrum for multiple scattering induced radiation assumes that the scatterings are independent, the quantum interference between successive scatteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muon
A muon ( ; from the Greek letter mu (μ) used to represent it) is an elementary particle similar to the electron, with an electric charge of −1 '' e'' and a spin of ''ħ'', but with a much greater mass. It is classified as a lepton. As with other leptons, the muon is not thought to be composed of any simpler particles. The muon is an unstable subatomic particle with a mean lifetime of , much longer than many other subatomic particles. As with the decay of the free neutron (with a lifetime around 15 minutes), muon decay is slow (by subatomic standards) because the decay is mediated only by the weak interaction (rather than the more powerful strong interaction or electromagnetic interaction), and because the mass difference between the muon and the set of its decay products is small, providing few kinetic degrees of freedom for decay. Muon decay almost always produces at least three particles, which must include an electron of the same charge as the muon and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensive Air Shower
Air showers are extensive cascades of subatomic particles and ionized nuclei, produced in the atmosphere when a ''primary'' cosmic ray enters the atmosphere. Particles of cosmic radiation can be protons, nuclei, electrons, photons, or (rarely) positrons. Upon entering the atmosphere, they interact with molecules and initiate a particle cascade that lasts for several generations, until the energy of the primary particle is fully converted. If the primary particle is a hadron, mostly light mesons like pions and kaons are produced in the first interactions, which then fuel a hadronic shower component that produces shower particles mostly through pion decay. Primary photons and electrons, on the other hand, produce mainly electromagnetic showers. Depending on the energy of the primary particle, the detectable size of the shower can reach several kilometers in diameter. The air shower phenomenon was unknowingly discovered by Bruno Rossi in 1933 in a laboratory experiment. In 1937 P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago Air Shower Array
The Chicago Air Shower Array (CASA) was a significant ultra high high-energy astrophysics experiment operating in the 1990s. It consisted of a very large array of scintillation detectors located at Dugway Proving Grounds in Utah, USA, approximately 80 kilometers southwest of Salt Lake City. The full CASA detector, consisting of 1089 detectors began operating in 1992 in conjunction with a second instrument, the Michigan Muon Array (MIA), under the name CASA-MIA. MIA was made of 2500 square meters of buried muon detectors. At the time of its operation, CASA-MIA was the most sensitive experiment built to date in the study of gamma ray and cosmic ray interactions at energies above 100 TeV (1014 electronvolts). Research topics on data from this experiment covered a wide variety of physics issues, including the search for gamma rays from Galactic sources (especially the Crab Nebula and the X-ray binaries Cygnus X-3 and Hercules X-1) and extragalactic sources (active Galactic nuclei and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VERITAS
In Roman mythology, Veritas (), meaning Truth, is the Goddess of Truth, a daughter of Saturn (mythology), Saturn (called Cronus by the Greeks, the Titan (mythology), Titan of Time, perhaps first by Plutarch) and the mother of Virtus (deity), Virtus. She is also sometimes considered the daughter of Jupiter (mythology), Jupiter (called Zeus by the Greeks), or a creation of Prometheus. The elusive goddess is said to have hidden in the bottom of a holy well. She is depicted both as a virgin dressed in white and as the "naked truth" (''nuda veritas'') holding a hand mirror. The eqivalent Greek goddess is Aletheia (Ancient Greek language, Ancient Greek: ). ''Veritas'' was the Roman virtue of Honesty, truthfulness, which was considered one of the main virtues any good Roman should possess. The German philosopher Martin Heidegger argues that the truth represented by ''aletheia'' (which essentially means "unconcealment") is different from that represented by ''veritas'', which is linked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Palma
La Palma (, ), also known as ''La isla bonita'' () and historically San Miguel de La Palma, is the most northwesterly island of the Canary Islands, a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in Macaronesia in the North Atlantic Ocean. La Palma has an area of making it the fifth largest of the eight main Canary Islands. The total population at the start of 2023 was 84,338, of whom 15,522 lived in the capital, Santa Cruz de La Palma and 20,375 in Los Llanos de Aridane. Its highest mountain is the Roque de los Muchachos, at , being second among the peaks of the Canaries after the Teide massif on Tenerife. In 1815, the German geologist Leopold von Buch visited the Canary Islands. It was as a result of his visit to Tenerife, where he visited the Las Cañadas caldera, and then later to La Palma, where he visited the Taburiente caldera, that the Spanish word for cauldron or large cooking pot – "caldera" – was introduced into the geological vocabulary. In the center of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAGIC (telescope)
MAGIC (Major Atmospheric Gamma Imaging Cherenkov Telescopes, later renamed to MAGIC Florian Goebel Telescopes) is a system of two Imaging Atmospheric Cherenkov telescopes situated at the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory on La Palma, one of the Canary Islands, at about 2200 m above sea level. MAGIC detects particle showers released by gamma rays, using the Cherenkov radiation, i.e., faint light radiated by the charged particles in the showers. With a diameter of 17 meters for the reflecting surface, it was the largest in the world before the construction of H.E.S.S. II. The first telescope was built in 2004 and operated for five years in standalone mode. A second MAGIC telescope (MAGIC-II), at a distance of 85 m from the first one, started taking data in July 2009. Together they integrate the MAGIC telescope stereoscopic system. MAGIC is sensitive to cosmic gamma rays with photon energies between 50 GeV (later lowered to 25 GeV) and 30 TeV due to its large m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |