|
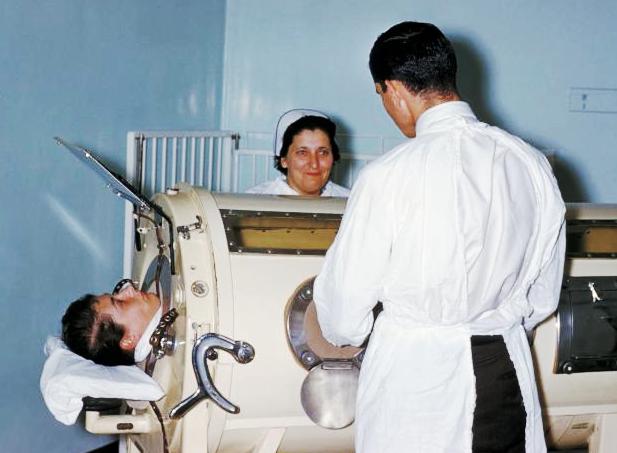
Ventilator
A ventilator is a type of breathing apparatus, a class of medical technology that provides mechanical ventilation by moving breathable air into and out of the lungs, to deliver breaths to a patient who is physically unable to breathe, or breathing insufficiently. Ventilators may be computerized microprocessor-controlled machines, but patients can also be ventilated with a simple, hand-operated bag valve mask. Ventilators are chiefly used in intensive-care medicine, home care, and emergency medicine (as standalone units) and in anesthesiology (as a component of an anesthesia machine). Ventilators are sometimes called "respirators", a term commonly used for them in the 1950s (particularly the "Bird respirator"). However, contemporary medical terminology uses the word "respirator" to refer to a face-mask that protects wearers against hazardous airborne substances. Function In its simplest form, a modern positive pressure ventilator, consists of a compressible air reservoir o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Ventilation
Mechanical ventilation or assisted ventilation is the Medicine, medical term for using a ventilator, ventilator machine to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air into and out of the lungs, with the main goal of helping the delivery of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide. Mechanical ventilation is used for many reasons, including to protect the airway due to mechanical or neurologic cause, to ensure adequate oxygenation, or to remove excess carbon dioxide from the lungs. Various healthcare providers are involved with the use of mechanical ventilation and people who require ventilators are typically monitored in an intensive care unit. Mechanical ventilation is termed invasive if it involves an instrument to create an airway that is placed inside the trachea. This is done through an endotracheal tube or nasotracheal tube. For non-invasive ventilation in people who are conscious, face or nasal masks are used. The two main types o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breathing Apparatus
A breathing apparatus or breathing set is equipment which allows a person to breathe in a hostile environment where breathing would otherwise be impossible, difficult, harmful, or hazardous, or assists a person to breathe. A respirator, medical ventilator, or resuscitator may also be considered to be breathing apparatus. Equipment that supplies or recycles breathing gas other than ambient air in a space used by several people is usually referred to as being part of a life-support system, and a life-support system for one person may include breathing apparatus, when the breathing gas is specifically supplied to the user rather than to the enclosure in which the user is the occupant. Breathing apparatus may be classified by type in several ways: * by breathing gas source: self-contained gas supply, remotely supplied gas, or purified ambient air, * by environment: underwater/hyperbaric, terrestrial/normobaric, or high altitude/hypobaric, * by breathing circuit type: open, semi-close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bag Valve Mask
A bag valve mask (BVM), sometimes known by the proprietary name Ambu bag or generically as a manual resuscitator or "self-inflating bag", is a hand-held device commonly used to provide Modes of mechanical ventilation, positive pressure ventilation to patients who are not breathing or not breathing adequately. The device is a required part of resuscitation kits for trained professionals in out-of-hospital settings (such as ambulance crews) and is also frequently used in hospitals as part of standard equipment found on a crash cart, in emergency rooms or other critical care settings. Underscoring the frequency and prominence of BVM use in the United States, the American Heart Association (AHA) Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiac Care recommend that "all healthcare providers should be familiar with the use of the bag-mask device." Manual resuscitators are also used within the hospital for temporary ventilation of patients dependent on mechanical ventilato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forrest Bird
Forrest Morton Bird (June 9, 1921 – August 2, 2015) was an American aviator, inventor, and biomedical engineer. He is best known for having created some of the first reliable mass-produced mechanical ventilators for acute and chronic cardiopulmonary care. Biography Bird was born in Stoughton, Massachusetts. Bird became a pilot at an early age with his father's encouragement. By age 14, he flew his first solo fight. By age 16 he was working to obtain multiple major pilot certifications. Bird enlisted with the United States Army Air Corps, and entered active duty in 1941 as a technical air training officer due to his advanced qualifications. This rank, combined with the onset of World War II, gave him the opportunity to pilot almost every aircraft in service, including early jet aircraft and helicopters. The newest models of aircraft were capable of exceeding altitudes at which humans can breathe, even with 100% oxygen supplementation, introducing the risk of hypoxia. Bird ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intensive-care Medicine
Intensive care medicine, usually called critical care medicine, is a medical specialty that deals with seriously or critically ill patients who have, are at risk of, or are recovering from conditions that may be life-threatening. It includes providing life support, invasive monitoring techniques, resuscitation, and end-of-life care. Doctors in this specialty are often called intensive care physicians, critical care physicians, or intensivists. Intensive care relies on multidisciplinary teams composed of many different health professionals. Such teams often include doctors, nurses, physical therapists, respiratory therapists, and pharmacists, among others. They usually work together in intensive care units (ICUs) within a hospital. Scope Patients are admitted to the intensive care unit if their medical needs are greater than what the general hospital ward can provide. Indications for the ICU include blood pressure support for cardiovascular instability (hypertension/hypot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive Pressure Ventilation
Positive airway pressure (PAP) is a mode of Modes of mechanical ventilation, respiratory ventilation used in the treatment of sleep apnea. PAP ventilation is also commonly used for those who are critically ill in hospital with respiratory failure, in newborn infants (neonates), and for the prevention and treatment of atelectasis in patients with difficulty taking deep breaths. In these patients, PAP ventilation can prevent the need for tracheal intubation, or allow earlier extubation. Sometimes patients with neuromuscular diseases use this variety of ventilation as well. CPAP is an acronym for "continuous positive airway pressure", which was developed by Dr. George Gregory and colleagues in the neonatal intensive care unit at the University of California, San Francisco. A variation of the PAP system was developed by Professor Colin Sullivan (physician), Colin Sullivan at Royal Prince Alfred Hospital in Sydney, Australia, in 1981. The main difference between BPAP and CPAP machines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracheotomy
Tracheotomy (, ), or tracheostomy, is a surgical airway management procedure which consists of making an incision on the front of the neck to open a direct airway to the trachea. The resulting stoma (hole) can serve independently as an airway or as a site for a tracheal tube (or tracheostomy tube) to be inserted; this tube allows a person to breathe without the use of the nose or mouth. Etymology and terminology The etymology of the word ''tracheotomy'' comes from two Greek words: the root ''tom-'' (from Greek τομή ''tomḗ'') meaning "to cut", and the word ''trachea'' (from Greek τραχεία ''tracheía''). The word ''tracheostomy'', including the root ''stom-'' (from Greek στόμα ''stóma'') meaning "mouth", refers to the making of a semi-permanent or permanent opening and to the opening itself. Some sources offer different definitions of the above terms. Part of the ambiguity is due to the uncertainty of the intended permanence of the stoma (hole) at the time i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-invasive Ventilation
Non-invasive ventilation (NIV) is the use of breathing support administered through a face mask, nasal mask, or a helmet. Air, usually with added oxygen, is given through the mask under positive pressure; generally the amount of pressure is alternated depending on whether someone is breathing in or out. It is termed "non-invasive" because it is delivered with a mask that is tightly fitted to the face or around the head, but without a need for tracheal intubation (a tube through the mouth into the windpipe). While there are similarities with regard to the interface, NIV is not the same as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), which applies a single level of positive airway pressure throughout the whole respiratory cycle; CPAP does not deliver ventilation but is occasionally used in conditions also treated with NIV. Non-invasive ventilation is used in acute respiratory failure caused by a number of medical conditions, most prominently chronic obstructive pulmonary disease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure
Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) is a form of positive airway pressure (PAP) ventilation in which a constant level of pressure greater than atmospheric pressure is continuously applied to the upper respiratory tract of a person. The application of positive pressure may be intended to prevent upper airway collapse, as occurs in obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), or to reduce the work of breathing in conditions such as acute decompensated heart failure. CPAP therapy is highly effective for managing obstructive sleep apnea. Compliance and acceptance of use of CPAP therapy can be a limiting factor, with 8% of people stopping use after the first night and 50% within the first year. Medical uses Moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea CPAP is the most effective treatment for moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea, in which the mild pressure from the CPAP prevents the airway from collapsing or becoming blocked. CPAP has been shown to be 100% effective at eliminating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anesthesia Machine
An anaesthetic machine (British English) or anesthesia machine (American English) is a medical device used to generate and mix a fresh gas flow of medical gases and inhalational anaesthetic agents for the purpose of inducing and maintaining anaesthesia. The machine is commonly used together with a mechanical ventilator, breathing system, suction equipment, and patient monitoring devices; strictly speaking, the term "anaesthetic machine" refers only to the component which generates the gas flow, but modern machines usually integrate all these devices into one combined freestanding unit, which is colloquially referred to as the "anaesthetic machine" for the sake of simplicity. In the developed world, the most frequent type in use is the continuous-flow anaesthetic machine or "Boyle's machine", which is designed to provide an accurate supply of medical gases mixed with an accurate concentration of anaesthetic vapour, and to deliver this continuously to the patient at a safe press ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |