|
Vascular Snare
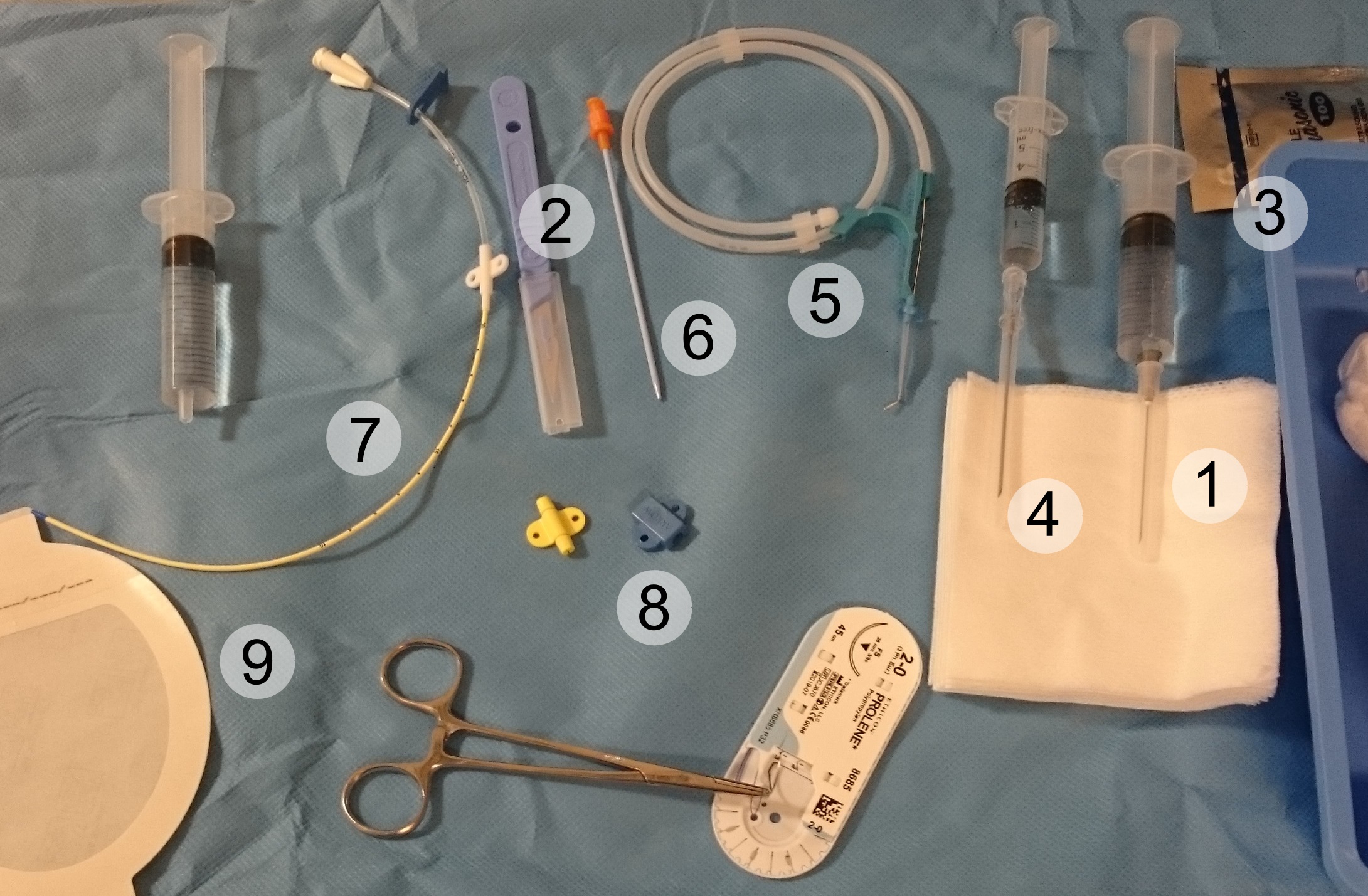
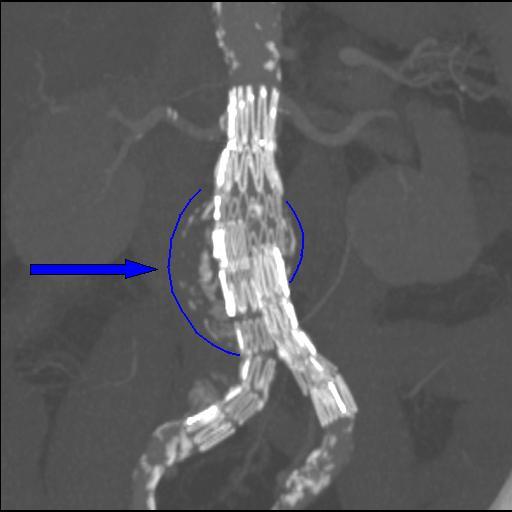
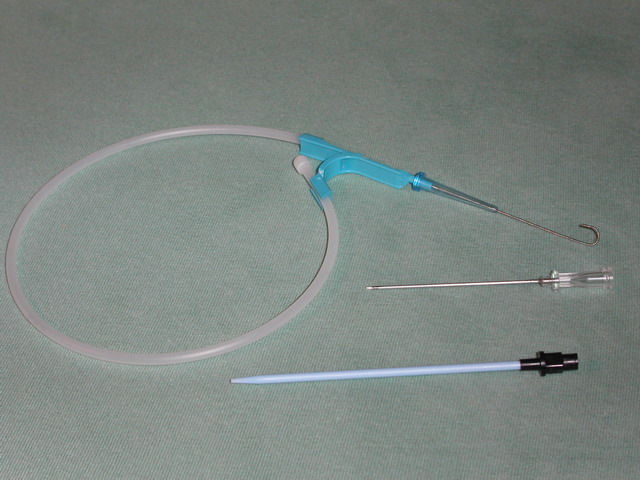
A vascular snare is an endovascular device that is used to remove foreign bodies from inside arteries and veins. The snare consists of several radiopaque loops of wire inside a catheter, which when extended flower out, and which collapse when withdrawn into the catheter. Uses Vascular snares are used to retrieve inferior vena cava filters, lost guide wires, or broken central venous catheters. Vascular snaring is a component technique in endovascular aneurysm repair in some devices. Technique A snare catheter is inserted using the Seldinger technique under fluoroscopic Fluoroscopy (), informally referred to as "fluoro", is an imaging technique that uses X-rays to obtain real-time moving images of the interior of an object. In its primary application of medical imaging, a fluoroscope () allows a surgeon to see t ... guidance. The snare wire is advanced under direct visualization and flowered open. The object being retrieved is captured within the loops of snare, and retriev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endovascular Surgery
Vascular surgery is a surgical subspecialty in which vascular diseases involving the arteries, veins, or lymphatic vessels, are managed by medical therapy, minimally-invasive catheter procedures and surgical reconstruction. The specialty evolved from general and cardiovascular surgery where it refined the management of just the vessels, no longer treating the heart or other organs. Modern vascular surgery includes open surgery techniques, endovascular (minimally invasive) techniques and medical management of vascular diseases - unlike the parent specialities. The vascular surgeon is trained in the diagnosis and management of diseases affecting all parts of the vascular system excluding the coronaries and intracranial vasculature. Vascular surgeons also are called to assist other physicians to carry out surgery near vessels, or to salvage vascular injuries that include hemorrhage control, dissection, occlusion or simply for safe exposure of vascular structures. History Early lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreign Body
A foreign body (FB) is any object originating outside the body of an organism. In machinery, it can mean any unwanted intruding object. Most references to foreign bodies involve propulsion through natural orifices into hollow organs. Foreign bodies can be inert or irritating. If they irritate they will cause inflammation and scarring. They can bring infection into the body or acquire infectious agents and protect them from the body's immune defenses. They can obstruct passageways either by their size or by the scarring they cause. Some can be toxic or generate toxic chemicals from reactions with chemicals produced by the body, as is the case with many examples of ingested metal objects. With sufficient force (as in firing of bullets), a foreign body can become lodged into nearly any tissue. Gastrointestinal tract One of the most common locations for a foreign body is the alimentary tract. It is possible for foreign bodies to enter the tract from the mouth or rectum. Both c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artery
An artery () is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in the pulmonary circulation that carry blood to the lungs for oxygenation, and the umbilical arteries in the fetal circulation that carry deoxygenated blood to the placenta. It consists of a multi-layered artery wall wrapped into a tube-shaped channel. Arteries contrast with veins, which carry deoxygenated blood back towards the heart; or in the pulmonary and fetal circulations carry oxygenated blood to the lungs and fetus respectively. Structure The anatomy of arteries can be separated into gross anatomy, at the macroscopic scale, macroscopic level, and histology, microanatomy, which must be studied with a microscope. The arterial system of the human body is divided into systemic circulation, systemic arteries, carrying blood from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vein
Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and fetal circulations which carry oxygenated blood to the heart. In the systemic circulation, arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, and veins return deoxygenated blood to the heart, in the deep veins. There are three sizes of veins: large, medium, and small. Smaller veins are called venules, and the smallest the post-capillary venules are microscopic that make up the veins of the microcirculation. Veins are often closer to the skin than arteries. Veins have less smooth muscle and connective tissue and wider internal diameters than arteries. Because of their thinner walls and wider lumens they are able to expand and hold more blood. This greater capacity gives them the term of ''capacitance vessels''. At any time, nearly 70% o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiopaque
Radiodensity (or radiopacity) is opacity to the radio wave and X-ray portion of the electromagnetic spectrum: that is, the relative inability of those kinds of electromagnetic radiation to pass through a particular material. Radiolucency or hypodensity indicates greater passage (greater transradiancy) to X-ray photonsNovelline, Robert. ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. 1997. . and is the analogue of transparency and translucency with visible light. Materials that inhibit the passage of electromagnetic radiation are called radiodense or radiopaque, while those that allow radiation to pass more freely are referred to as radiolucent. Radiopaque volumes of material have white appearance on radiographs, compared with the relatively darker appearance of radiolucent volumes. For example, on typical radiographs, bones look white or light gray (radiopaque), whereas muscle and skin look black or dark gray, being mostly invisible (radiolucent). Tho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catheter
In medicine, a catheter ( ) is a thin tubing (material), tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgical procedure. Catheters are manufactured for specific applications, such as cardiovascular, urological, gastrointestinal, neurovascular and ophthalmic procedures. The process of inserting a catheter is called ''catheterization''. In most uses, a catheter is a thin, flexible tube (''soft'' catheter) though catheters are available in varying levels of stiffness depending on the application. A catheter left inside the body, either temporarily or permanently, may be referred to as an "indwelling catheter" (for example, a peripherally inserted central catheter). A permanently inserted catheter may be referred to as a "permcath" (originally a trademark). Catheters can be inserted into a body cavity, duct, or vessel, brain, skin or adipose tissue. Functional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Vena Cava Filter
An inferior vena cava filter is a medical device made of metal that is implanted by vascular surgeons or interventional radiologists into the inferior vena cava to prevent a life-threatening pulmonary embolism (PE) or venous thromboembolism (VTE). The filter is designed to trap a blood clot and prevent its travel to the lung where it would form a pulmonary embolism. Their effectiveness and safety profile is well established, and they may be used when anticoagulant treatment is not sufficient. Results from the PREPIC study and other studies which have shown many long-term complications of IVC filters led to the introduction of retrievable IVC filters. The first retrievable IVC filters were approved by FDA in 2003 and 2004. In 2012, the American College of Chest Physicians recommended IVC filters for those with contraindications to anticoagulation who either have acute PE or acute proximal deep vein thrombosis (above the knee). History The first IVC filter was created by Kaz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guide Wire (medicine) , a tensioned cable providing structural support, sometimes incorrectly called "guide wire"
{{dab ...
A guide wire may refer to: *A step in the Seldinger technique *Guide Wire, a character in the anime series ''Rave Master'' *Guidewire Software See also *Guy-wire A guy-wire, guy-line, guy-rope, down guy, or stay, also called simply a guy, is a tensioned cable designed to add stability to a freestanding structure. They are used commonly for ship masts, radio masts, wind turbines, utility poles, and ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Venous Catheter
A central venous catheter (CVC), also known as a central line (c-line), central venous line, or central venous access catheter, is a catheter placed into a large vein. It is a form of venous access. Placement of larger catheters in more centrally located veins is often needed in critically ill patients, or in those requiring prolonged intravenous therapies, for more reliable vascular access. These catheters are commonly placed in veins in the neck (internal jugular vein), chest (subclavian vein or axillary vein), groin (femoral vein), or through veins in the arms (also known as a PICC line, or peripherally inserted central catheters). Central lines are used to administer medication or fluids that are unable to be taken by mouth or would harm a smaller peripheral vein, obtain blood tests (specifically the "central venous oxygen saturation"), administer fluid or blood products for large volume resuscitation, and measure central venous pressure. The catheters used are commonl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endovascular Aneurysm Repair
Endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) is a type of minimally-invasive endovascular surgery used to treat pathology of the aorta, most commonly an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA). When used to treat thoracic aortic disease, the procedure is then specifically termed TEVAR for "thoracic endovascular aortic/aneurysm repair." EVAR involves the placement of an expandable stent graft within the aorta to treat aortic disease without operating directly on the aorta. In 2003, EVAR surpassed open aortic surgery as the most common technique for repair of AAA, and in 2010, EVAR accounted for 78% of all intact AAA repair in the United States. Medical uses Standard EVAR is appropriate for aneurysms that begin below the renal arteries, where there exists an adequate length of normal aorta (the ''"proximal aortic neck"'') for reliable attachment of the endograft without leakage of blood around the device ("'' endoleak''"). If the proximal aortic neck is also involved with the aneurysm, the pati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seldinger Technique
The Seldinger technique, also known as Seldinger wire technique, is a medical procedure to obtain safe access to blood vessels and other hollow organ (anatomy), organs. It is eponym, named after Sven Ivar Seldinger (1921–1998), a Sweden, Swedish radiology, radiologist who introduced the procedure in 1953. Uses The Seldinger technique is used for angiography, insertion of chest drains and central venous catheters, insertion of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy, PEG tubes using the push technique, insertion of the leads for an artificial pacemaker or implantable cardioverter-defibrillator, and numerous other interventional medical procedures. Complications The initial puncture is with a sharp instrument, and this may lead to hemorrhage or perforation of the organ in question. Infection is a possible complication, and hence asepsis is practiced during most Seldinger procedures. Loss of the guidewire into the cavity or blood vessel is a significant and generally preventable com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy (), informally referred to as "fluoro", is an imaging technique that uses X-rays to obtain real-time moving images of the interior of an object. In its primary application of medical imaging, a fluoroscope () allows a surgeon to see the internal anatomy, structure and physiology, function of a patient, so that the pumping action of the heart or the motion of swallowing, for example, can be watched. This is useful for both medical diagnosis, diagnosis and therapy and occurs in general radiology, interventional radiology, and image-guided surgery. In its simplest form, a fluoroscope consists of an X-ray generator, X-ray source and a fluorescence, fluorescent screen, between which a patient is placed. However, since the 1950s most fluoroscopes have included X-ray image intensifiers and cameras as well, to improve the image's visibility and make it available on a remote display screen. For many decades, fluoroscopy tended to produce live pictures that were not recorded, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |