|
Value-added Tax
A value-added tax (VAT or goods and services tax (GST), general consumption tax (GCT)) is a consumption tax that is levied on the value added at each stage of a product's production and distribution. VAT is similar to, and is often compared with, a sales tax. VAT is an indirect tax, because the consumer who ultimately bears the burden of the tax is not the entity that pays it. Specific goods and services are typically exempted in various jurisdictions. Products exported to other countries are typically exempted from the tax, typically via a rebate to the exporter. VAT is usually implemented as a destination-based tax, where the tax rate is based on the location of the customer. VAT raises about a fifth of total tax revenues worldwide and among the members of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). As of January 2025, 175 of the Member states of the United Nations, 193 countries with UN membership employ a VAT, including all OECD members except the Tax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countries With VAT
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. When referring to a specific polity, the term "country" may refer to a sovereign state, state with limited recognition, constituent country, or dependent territory. Most sovereign states, but not all countries, are members of the United Nations. There is no universal agreement on the number of "countries" in the world, since several states have disputed sovereignty status or limited recognition, and a number of non-sovereign entities are commonly considered countries. The definition and usage of the word "country" are flexible and have changed over time. ''The Economist'' wrote in 2010 that "any attempt to find a clear definition of a country soon runs into a thicket of exceptions and anomalies." Areas much smaller than a political entity may be referred to as a "country", such as the West Country in England, "big sky country" (used in various contexts of the American West), "coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertical Integration
In microeconomics, management and international political economy, vertical integration, also referred to as vertical consolidation, is an arrangement in which the supply chain of a company is integrated and owned by that company. Usually each member of the supply chain produces a different Product (business), product or (market-specific) service, and the products combine to satisfy a common need. It contrasts with horizontal integration, wherein a company produces several items that are related to one another. Vertical integration has also described management styles that bring large portions of the supply chain not only under a common ownership but also into one corporation (as in the 1920s when the Ford River Rouge complex began making much of its own steel rather than buying it from suppliers). Vertical integration can be desirable because it secures supplies needed by the firm to produce its product and the market needed to sell the product, but it can become undesirable wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute For Fiscal Studies
The Institute for Fiscal Studies (IFS) is an independent economic research institute based in London, United Kingdom, which specialises in UK taxation and public policy. It produces both academic and policy-related findings. The institute's stated aim is "to provide top quality economic analysis independent of government, political party or any other vested interest. Our goal is to promote effective economic and social policies by understanding better their impact on individuals, families, businesses and the government's finances." Its offices are in the Bloomsbury area of Central London close to the British Museum and University College London. History The institute was founded in response to the passing of the Finance Act 1965, by four financial professionals: a banker and later Conservative Party politician ( Will Hopper), an investment trust manager (Bob Buist), a stockbroker ( Nils Taube), and a tax consultant ( John Chown). In 1964, the then Chancellor of the Excheq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; , OCDE) is an international organization, intergovernmental organization with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and international trade, world trade. It is a forum (legal), forum whose member countries describe themselves as committed to democracy and the market economy, providing a platform to compare policy experiences, seek answers to common problems, identify good practices, and coordinate domestic and international policies of its members. The majority of OECD members are generally regarded as developed country, developed countries, with High-income economy, high-income economies, and a very high Human Development Index. their collective population is 1.38 billion people with an average life expectancy of 80 years and a median age of 40, against a global average of 30. , OECD Member countries collectively comprised 62.2% of list of countries by GDP (nominal), global nom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proportional Tax
A proportional tax is a tax imposed so that the tax rate is fixed, with no change as the taxable base amount increases or decreases. The amount of the tax is in proportion to the amount subject to taxation. "Proportional" describes a distribution effect on income or expenditure, referring to the way the rate remains consistent (does not progress from "low to high" or "high to low" as income or consumption changes), where the marginal tax rate is equal to the average tax rate.Hyman, David M. (1990) ''Public Finance: A Contemporary Application of Theory to Policy'', 3rd, Dryden Press: Chicago, ILJames, Simon (1998) ''A Dictionary of Taxation'', Edgar Elgar Publishing Limited: Northampton, MA It can be applied to individual taxes or to a tax system as a whole; a year, multi-year, or lifetime. Proportional taxes maintain equal tax incidence regardless of the ability-to-pay and do not shift the incidence disproportionately to those with a higher or lower economic well-being. Althou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
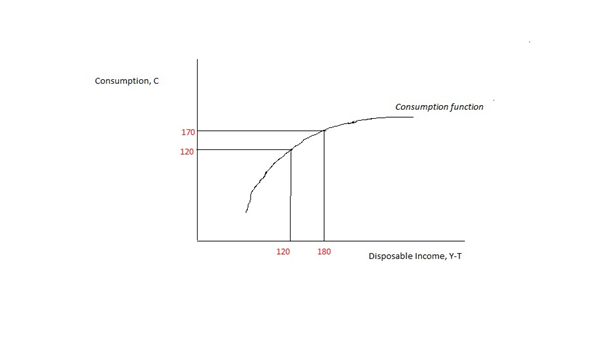
Marginal Propensity To Consume
In economics, the marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is a metric that quantifies induced consumption, the concept that the increase in personal consumer spending ( consumption) occurs with an increase in disposable income (income after taxes and transfers). The proportion of disposable income which individuals spend on consumption is known as propensity to consume. MPC is the proportion of additional income that an individual consumes. For example, if a household earns one extra dollar of disposable income, and the marginal propensity to consume is 0.65, then of that dollar, the household will spend 65 cents and save 35 cents. Obviously, the household cannot spend ''more'' than the extra dollar (without borrowing or using savings). If the extra money accessed by the individual gives more economic confidence, then the MPC of the individual may well exceed 1, as they may borrow or utilise savings. According to John Maynard Keynes, marginal propensity to consume is less than one. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regressive Tax
A regressive tax is a tax imposed in such a manner that the tax rate decreases as the amount subject to taxation increases. "Regressive" describes a distribution effect on income or expenditure, referring to the way the rate progresses from high to low, so that the average tax rate exceeds the marginal tax rate.Hyman, David M. (1990) ''Public Finance: A Contemporary Application of Theory to Policy'', 3rd, Dryden Press: Chicago, ILJames, Simon (1998) ''A Dictionary of Taxation'', Edgar Elgar Publishing Limited: Northampton, MA The regressivity of a particular tax can also factor the propensity of the taxpayers to engage in the taxed activity relative to their resources (the demographics of the tax base). In other words, if the activity being taxed is more likely to be carried out by the poor and less likely to be carried out by the rich, the tax may be considered regressive. To measure the effect, the income elasticity of the good being taxed as well as the income effect on cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campaña Nomasiva
Campana or Campaña (Spanish for "campaign" or occasionally "countryside") is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Al Campana (1926–2009), American National Football League running back * Alex Campana (born 1988), English footballer * Cosetta Campana (born 1961), Italian former sprinter * Dino Campana (1885–1932), Italian poet * Drake Campana (born 1986), stage name of American musician and actor Drake Bell * Fabio Campana (1819–1882), Italian composer, opera director, conductor and singing teacher * Fernando Campana (born 1961), half of the Campana brothers, Brazilian designers * Francesca Campana ( – 1665), Roman singer, spinet player and composer * Francesco Campana ( – 1546), Italian statesman * Francesco Federico or François Frédéric Campana (1771–1807), Italian general in Napoleon's army * Giacinto Campana (born ), Italian painter of the Baroque period * Giampietro Campana (1808–1880), Italian art collector and embezzler * Giorgia Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
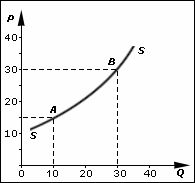
Supply Curve
In economics, supply is the amount of a resource that firms, producers, labourers, providers of financial assets, or other economic agents are willing and able to provide to the marketplace or to an individual. Supply can be in produced goods, labour time, raw materials, or any other scarce or valuable object. Supply is often plotted graphically as a supply curve, with the price per unit on the vertical axis and quantity supplied as a function of price on the horizontal axis. This reversal of the usual position of the dependent variable and the independent variable is an unfortunate but standard convention. The supply curve can be either for an individual seller or for the market as a whole, adding up the quantity supplied by all sellers. The quantity supplied is for a particular time period (e.g., the tons of steel a firm would supply in a year), but the units and time are often omitted in theoretical presentations. In the goods market, supply is the amount of a product per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Model
An economic model is a theoretical construct representing economic processes by a set of variables and a set of logical and/or quantitative relationships between them. The economic model is a simplified, often mathematical, framework designed to illustrate complex processes. Frequently, economic models posit structural parameters. A model may have various exogenous variables, and those variables may change to create various responses by economic variables. Methodological uses of models include investigation, theorizing, and fitting theories to the world. Overview In general terms, economic models have two functions: first as a simplification of and abstraction from observed data, and second as a means of selection of data based on a paradigm of econometric study. ''Simplification'' is particularly important for economics given the enormous complexity of economic processes. This complexity can be attributed to the diversity of factors that determine economic activity; t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supply And Demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a Market (economics), market. It postulates that, Ceteris_paribus#Applications, holding all else equal, the unit price for a particular Good (economics), good or other traded item in a perfect competition, perfectly competitive market, will vary until it settles at the market clearing, market-clearing price, where the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied such that an economic equilibrium is achieved for price and quantity transacted. The concept of supply and demand forms the theoretical basis of modern economics. In situations where a firm has market power, its decision on how much output to bring to market influences the market price, in violation of perfect competition. There, a more complicated model should be used; for example, an oligopoly or product differentiation, differentiated-product model. Likewise, where a buyer has market power, models such as monopsony will be more a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |