|
Vacuum Insulated Panel
A vacuum insulated panel (VIP) is a form of thermal insulation consisting of a gas-tight enclosure surrounding a rigid core, from which the air has been evacuated. It is used in building construction, refrigeration units, and insulated shipping containers to provide better insulation performance than conventional insulation materials. Construction VIPs consist of: * Membrane walls, used to prevent air from entering the panel. * A panel of a rigid, highly-porous material, such as fumed silica, aerogel, perlite, or glass fiber, to support the membrane walls against atmospheric pressure once the air is evacuated. * Chemicals (known as getters) to collect gases leaked through the membrane or offgassed from the membrane materials. These are added to VIPs with glass-fiber or foam cores, because cores with bigger pore size require a higher vacuum (less than about 1 mbar) during the planned service life. Thermal performance Heat transfer occurs by three modes: convection, conduction and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Insulation
Thermal insulation is the reduction of heat transfer (i.e., the transfer of thermal energy between objects of differing temperature) between objects in thermal contact or in range of radiative influence. Thermal insulation can be achieved with specially engineered methods or processes, as well as with suitable object shapes and materials. Heat flow is an inevitable consequence of contact between objects of different temperature. Thermal insulation provides a region of insulation in which thermal conduction is reduced, creating a thermal break or thermal barrier, or thermal radiation is reflected rather than absorbed by the lower-temperature body. The insulating capability of a material is measured as the inverse of thermal conductivity, thermal conductivity (k). Low thermal conductivity is equivalent to high insulating capability (R-value (insulation), resistance value). In thermal engineering, other important properties of insulating materials are product density, density (ρ) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Radiation
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation emitted by the thermal motion of particles in matter. All matter with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation. The emission of energy arises from a combination of electronic, molecular, and lattice oscillations in a material. Kinetic energy is converted to electromagnetism due to charge-acceleration or dipole oscillation. At room temperature, most of the emission is in the infrared (IR) spectrum, though above around 525 °C (977 °F) enough of it becomes visible for the matter to visibly glow. This visible glow is called incandescence. Thermal radiation is one of the fundamental mechanisms of heat transfer, along with conduction and convection. The primary method by which the Sun transfers heat to the Earth is thermal radiation. This energy is partially absorbed and scattered in the atmosphere, the latter process being the reason why the sky is visibly blue. Much of the Sun's radiation tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Insulation Materials
This is a list of insulation materials used around the world. Typical R-values are given for various materials and structures as approximations based on the average of available figures and are sorted by lowest value.'' R-value at 1 m'' gives R-values normalised to a thickness and sorts by median The median of a set of numbers is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a Sample (statistics), data sample, a statistical population, population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as the “ ... value of the range. References {{Reflist Building insulation materials ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerogel
Aerogels are a class of manufacturing, synthetic porous ultralight material derived from a gel, in which the liquid component for the gel has been replaced with a gas, without significant collapse of the gel structure. The result is a solid with extremely low density and extremely low thermal conductivity. Aerogels can be made from a variety of chemical compounds. Silica aerogels feel like fragile expanded polystyrene, styrofoam to the touch, while some polymer-based aerogels feel like rigid foams. Aerogels are produced by extracting the liquid component of a gel through supercritical drying or freeze-drying. This allows the liquid to be slowly dried off without causing the solid matrix in the gel to collapse from capillary action, as would happen with conventional evaporation. The first aerogels were produced from silica gels. Kistler's later work involved aerogels based on alumina, Chromium(III) oxide, chromia, and tin dioxide. Carbon aerogels were first developed in the late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R-value (insulation)
The ''R''-value is a measure of how well a two-dimensional barrier, such as a layer of insulation, a window or a complete wall or ceiling, resists the conductive flow of heat, in the context of construction. R-value is the temperature difference per unit of heat flux needed to sustain one unit of heat flux between the warmer surface and colder surface of a barrier under steady-state conditions. The measure is therefore equally relevant for lowering energy bills for heating in the winter, for cooling in the summer, and for general comfort. The ''R-value'' is the building industry term for thermal resistance "per unit area." It is sometimes denoted RSI-value if the SI units are used. An R-value can be given for a material (e.g., for polyethylene foam), or for an assembly of materials (e.g., a wall or a window). In the case of materials, it is often expressed in terms of R-value per metre. R-values are additive for layers of materials, and the higher the R-value the better th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineral Wool
Mineral wool is any fibrous material formed by spinning or drawing molten mineral or rock materials such as slag and ceramics. Applications of mineral wool include thermal insulation (as both structural insulation and pipe insulation), filtration, soundproofing, and hydroponic growth medium. Naming Mineral wool is also known as rock wool, mineral cotton, mineral fiber, man-made mineral fiber (MMMF), and man-made vitreous fiber (MMVF). Specific mineral wool products are stone wool and slag wool. Europe also includes glass wool which, together with ceramic fiber, are entirely artificial fibers that can be made into different shapes and are spiky to touch. History Slag wool was first made in 1840 in Wales by Edward Parry, "but no effort appears to have been made to confine the wool after production; consequently it floated about the works with the slightest breeze, and became so injurious to the men that the process had to be abandoned". A method of making mineral wool ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
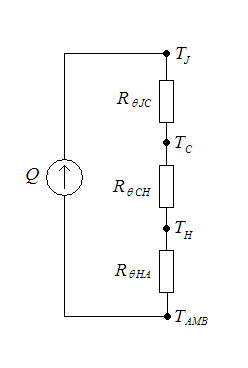
Thermal Resistance
In heat transfer, thermal engineering, and thermodynamics, thermal conductance and thermal resistance are fundamental concepts that describe the ability of materials or systems to conduct heat and the opposition they offer to the heat current. The ability to manipulate these properties allows engineers to control temperature gradient, prevent thermal shock, and maximize the efficiency of thermal systems. Furthermore, these principles find applications in a multitude of fields, including materials science, mechanical engineering, electronics, and energy management. Knowledge of these principles is crucial in various scientific, engineering, and everyday applications, from designing efficient temperature control, thermal insulation, and thermal management in industrial processes to optimizing the performance of electronic devices. Thermal conductance (''G'') measures the ability of a material or system to conduct heat. It provides insights into the ease with which heat can pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to heat conduction, conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k, \lambda, or \kappa and is measured in W·m−1·K−1. Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low thermal conductivity than in materials of high thermal conductivity. For instance, metals typically have high thermal conductivity and are very efficient at conducting heat, while the opposite is true for insulating materials such as mineral wool or Styrofoam. Metals have this high thermal conductivity due to free electrons facilitating heat transfer. Correspondingly, materials of high thermal conductivity are widely used in heat sink applications, and materials of low thermal conductivity are used as thermal insulation. The reciprocal of thermal conductivity is called thermal resistivity. The defining equation for thermal conductivity is \mathbf = - k \nabla T, where \mathbf is the heat flux, k is the thermal conductivity, and \nabla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mean Free Path
In physics, mean free path is the average distance over which a moving particle (such as an atom, a molecule, or a photon) travels before substantially changing its direction or energy (or, in a specific context, other properties), typically as a result of one or more successive collisions with other particles. Scattering theory Imagine a beam of particles being shot through a target, and consider an infinitesimally thin slab of the target (see the figure). The atoms (or particles) that might stop a beam particle are shown in red. The magnitude of the mean free path depends on the characteristics of the system. Assuming that all the target particles are at rest but only the beam particle is moving, that gives an expression for the mean free path: :\ell = (\sigma n)^, where is the mean free path, is the number of target particles per unit volume, and is the effective cross-sectional area for collision. The area of the slab is , and its volume is . The typical number of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conduction (heat)
Thermal conduction is the diffusion of thermal energy (heat) within one material or between materials in contact. The higher temperature object has molecules with more kinetic energy; collisions between molecules distributes this kinetic energy until an object has the same kinetic energy throughout. Thermal conductivity, frequently represented by , is a property that relates the rate of heat loss per unit area of a material to its rate of change of temperature. Essentially, it is a value that accounts for any property of the material that could change the way it conducts heat. Heat spontaneously flows along a temperature gradient (i.e. from a hotter body to a colder body). For example, heat is conducted from the hotplate of an electric stove to the bottom of a saucepan in contact with it. In the absence of an opposing external driving energy source, within a body or between bodies, temperature differences decay over time, and thermal equilibrium is approached, temperature becomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Building Construction
Construction are processes involved in delivering buildings, infrastructure, industrial facilities, and associated activities through to the end of their life. It typically starts with planning, financing, and design that continues until the asset is built and ready for use. Construction also covers repairs and maintenance work, any works to expand, extend and improve the asset, and its eventual demolition, dismantling or decommissioning. The construction industry contributes significantly to many countries' gross domestic products ( GDP). Global expenditure on construction activities was about $4 trillion in 2012. In 2022, expenditure on the construction industry exceeded $11 trillion a year, equivalent to about 13 percent of global GDP. This spending was forecasted to rise to around $14.8 trillion in 2030. The construction industry promotes economic development and brings many non-monetary benefits to many countries, but it is one of the most hazardous industries. For exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convection
Convection is single or Multiphase flow, multiphase fluid flow that occurs Spontaneous process, spontaneously through the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the convection is unspecified, convection due to the effects of thermal expansion and buoyancy can be assumed. Convection may also take place in soft solids or mixtures where particles can flow. Convective flow may be Transient state, transient (such as when a Multiphasic liquid, multiphase mixture of oil and water separates) or steady state (see convection cell). The convection may be due to Gravity, gravitational, Electromagnetism, electromagnetic or Fictitious force, fictitious body forces. Convection (heat transfer), Heat transfer by natural convection plays a role in the structure of Earth's atmosphere, its oceans, and its Earth's mantle, mantle. Discrete convective cells in the atmosphere can be identified by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |