|
VSAN
A virtual storage area network (virtual SAN, VSAN or vSAN) is a logical representation of a physical storage area network (SAN). A VSAN abstracts the storage-related operations from the physical storage layer, and provides shared storage access to the applications and virtual machines by combining the servers' local storage over a network into a single or multiple storage pools. The use of VSANs allows the isolation of traffic within specific portions of the network. If a problem occurs in one VSAN, that problem can be handled with a minimum of disruption to the rest of the network. VSANs can also be configured separately and independently. Technology Operation A VSAN operates as a dedicated piece of software responsible for storage access, and depending on the vendor, can run either as a virtual storage appliance (VSA), a storage controller that runs inside an isolated virtual machine (VM) or as an ordinary user-mode application, such as StarWind Virtual SAN, or DataCore SANsym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Storage Area Network
A storage area network (SAN) or storage network is a computer network which provides access to consolidated, block device, block-level data storage. SANs are primarily used to access Computer data storage, data storage devices, such as disk arrays and tape libraries from Server (computing), servers so that the devices appear to the operating system as direct-attached storage. A SAN typically is a dedicated network of storage devices not accessible through the local area network (LAN). Although a SAN provides only block-level access, file systems built on top of SANs do provide file-level access and are known as shared-disk file systems. Newer SAN configurations enable hybrid SAN and allow traditional block storage that appears as local storage but also object storage for web services through APIs. Storage architectures Storage area networks (SANs) are sometimes referred to as ''network behind the servers'' and historically developed out of a centralized data storage mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disk Mirroring
In Data storage device, data storage, disk mirroring is the Replication (computing), replication of logical disk volumes onto separate physical hard disks in Real-time computing, real time to ensure continuous availability. It is most commonly used in RAID 1. A mirrored volume is a complete logical representation of separate volume copies. In a IT disaster recovery, disaster recovery context, mirroring data over long distance is referred to as storage replication. Depending on the technologies used, replication can be performed synchronously, Asynchronous communication, asynchronously, semi-synchronously, or point-in-time. Replication is enabled via microcode on the disk array controller or via Server (computing), server software. It is typically a proprietary solution, not compatible between various data storage device vendors. Mirroring is typically only synchronous. Synchronous writing typically achieves a recovery point objective (RPO) of zero lost data. Asynchronous replica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
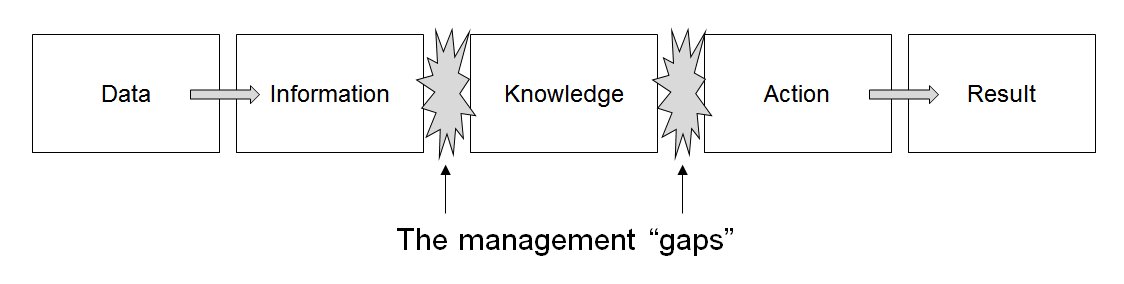
Data Management
Data management comprises all disciplines related to handling data as a valuable resource, it is the practice of managing an organization's data so it can be analyzed for decision making. Concept The concept of data management emerged alongside the evolution of computing technology. In the 1950s, as computers became more prevalent, organizations began to grapple with the challenge of organizing and storing data efficiently. Early methods relied on punch cards and manual sorting, which were labor-intensive and prone to errors. The introduction of database management systems in the 1970s marked a significant milestone, enabling structured storage and retrieval of data. By the 1980s, relational database models revolutionized data management, emphasizing the importance of data as an asset and fostering a data-centric mindset in business. This era also saw the rise of data governance practices, which prioritized the organization and regulation of data to ensure quality and complian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Networks
A computer network is a collection of communicating computers and other devices, such as printers and smart phones. In order to communicate, the computers and devices must be connected by wired media like copper cables, optical fibers, or by wireless communication. The devices may be connected in a variety of network topologies. In order to communicate over the network, computers use agreed-on rules, called communication protocols, over whatever medium is used. The computer network can include personal computers, servers, networking hardware, or other specialized or general-purpose hosts. They are identified by network addresses and may have hostnames. Hostnames serve as memorable labels for the nodes and are rarely changed after initial assignment. Network addresses serve for locating and identifying the nodes by communication protocols such as the Internet Protocol. Computer networks may be classified by many criteria, including the transmission medium used to carr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethernet
Ethernet ( ) is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 1983 as IEEE 802.3. Ethernet has since been refined to support higher bit rates, a greater number of nodes, and longer link distances, but retains much backward compatibility. Over time, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies such as Token Ring, FDDI and ARCNET. The original 10BASE5 Ethernet uses a thick coaxial cable as a shared medium. This was largely superseded by 10BASE2, which used a thinner and more flexible cable that was both less expensive and easier to use. More modern Ethernet variants use Ethernet over twisted pair, twisted pair and fiber optic links in conjunction with Network switch, switches. Over the course of its history, Ethernet data transfer rates have been increased from the original to the lates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VLAN
A virtual local area network (VLAN) is any broadcast domain that is partitioned and isolated in a computer network at the data link layer ( OSI layer 2).IEEE 802.1Q-2011, ''1.4 VLAN aims and benefits'' In this context, virtual refers to a physical object recreated and altered by additional logic, within the local area network. Basically, a VLAN behaves like a virtual switch or network link that can share the same physical structure with other VLANs while staying logically separate from them. VLANs work by applying tags to network frames and handling these tags in networking systems, in effect creating the appearance and functionality of network traffic that, while on a single physical network, behaves as if it were split between separate networks. In this way, VLANs can keep network applications separate despite being connected to the same physical network, and without requiring multiple sets of cabling and networking devices to be deployed. VLANs allow network administra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibre Channel Fabric
Switched fabric or switching fabric is a network topology in which network nodes interconnect via one or more network switches (particularly crossbar switches). Because a switched fabric network spreads network traffic across multiple physical links, it yields higher total throughput than broadcast networks, such as the early 10BASE5 version of Ethernet and most wireless networks such as Wi-Fi. The generation of high-speed serial data interconnects that appeared in 2001–2004 which provided point-to-point connectivity between processor and peripheral devices are sometimes referred to as fabrics; however, they lack features such as a message-passing protocol. For example, HyperTransport, the computer processor interconnect technology, continues to maintain a processor bus focus even after adopting a higher speed physical layer. Similarly, PCI Express is just a serial version of PCI; it adheres to PCI's host/peripheral load/store direct memory access (DMA)-based architecture on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Storage Area Network
A storage area network (SAN) or storage network is a computer network which provides access to consolidated, block device, block-level data storage. SANs are primarily used to access Computer data storage, data storage devices, such as disk arrays and tape libraries from Server (computing), servers so that the devices appear to the operating system as direct-attached storage. A SAN typically is a dedicated network of storage devices not accessible through the local area network (LAN). Although a SAN provides only block-level access, file systems built on top of SANs do provide file-level access and are known as shared-disk file systems. Newer SAN configurations enable hybrid SAN and allow traditional block storage that appears as local storage but also object storage for web services through APIs. Storage architectures Storage area networks (SANs) are sometimes referred to as ''network behind the servers'' and historically developed out of a centralized data storage mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software-defined Storage
Software-defined storage (SDS) is a marketing term for computer data storage software for policy-based provisioning and management of data storage independent of the underlying hardware. Software-defined storage typically includes a form of storage virtualization to separate the storage hardware from the software that manages it. The software enabling a software-defined storage environment may also provide policy management for features such as data deduplication, replication, thin provisioning, snapshots, copy-on-write clones, tiering and backup. Software-defined storage (SDS) hardware may or may not also have abstraction, pooling, or automation software of its own. When implemented as software only in conjunction with commodity servers with internal disks, it may suggest software such as a virtual or global file system or distributed block storage. If it is software layered over sophisticated large storage arrays, it suggests software such as storage virtualization or stor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Compression
In information theory, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Any particular compression is either lossy or lossless. Lossless compression reduces bits by identifying and eliminating statistical redundancy. No information is lost in lossless compression. Lossy compression reduces bits by removing unnecessary or less important information. Typically, a device that performs data compression is referred to as an encoder, and one that performs the reversal of the process (decompression) as a decoder. The process of reducing the size of a data file is often referred to as data compression. In the context of data transmission, it is called source coding: encoding is done at the source of the data before it is stored or transmitted. Source coding should not be confused with channel coding, for error detection and correction or line coding, the means for mapping data onto a sig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Deduplication
In computing, data deduplication is a technique for eliminating duplicate copies of repeating data. Successful implementation of the technique can improve storage utilization, which may in turn lower capital expenditure by reducing the overall amount of storage media required to meet storage capacity needs. It can also be applied to network data transfers to reduce the number of bytes that must be sent. The deduplication process requires comparison of data 'chunks' (also known as 'byte patterns') which are unique, contiguous blocks of data. These chunks are identified and stored during a process of analysis, and compared to other chunks within existing data. Whenever a match occurs, the redundant chunk is replaced with a small reference that points to the stored chunk. Given that the same byte pattern may occur dozens, hundreds, or even thousands of times (the match frequency is dependent on the chunk size), the amount of data that must be stored or transferred can be greatly reduce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |