|
User Pays
User pays, or beneficiary pays, is a pricing approach based on the idea that the most efficient allocation (and consumption) of resources occurs when consumers pay the full cost of the goods that they consume. In public finance it stands in opposition to another principle of " ability-to-pay," which states that those who have the means should share more of the burden of public services. The ability-to-pay principle is one of the reasons for the general acceptance of the progressive income tax system. The principle of user pays supports the idea of horizontal equity, which states that those in similar wealth and income positions should be treated equally by the tax system. The basic idea is that those who do not use a service should not be obligated to pay for it. As long as the beneficiary aligns exactly with the user, the user-pays principle works. Those who do not go to a movie are not obligated to pay for someone else to attend. In public goods, beneficiaries and users somet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pricing
Pricing is the Business process, process whereby a business sets and displays the price at which it will sell its products and services and may be part of the business's marketing plan. In setting prices, the business will take into account the price at which it could acquire the goods, the manufacturing cost, the marketplace, competition, market condition, brand, and quality of the product. Pricing is a fundamental aspect of product management and is one of the four Ps of the marketing mix, the other three aspects being product, promotion, and Distribution (business), place. Price is the only revenue generating element among the four Ps, the rest being cost center (business), cost centers. However, the other Ps of marketing will contribute to decreasing price elasticity and so enable price increases to drive greater revenue and profits. Pricing can be a manual or automatic process of applying prices to purchase and sales orders, based on factors such as a fixed amount, quantit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumption (economics)
Consumption refers to the use of resources to fulfill present needs and desires. It is seen in contrast to investing, which is spending for acquisition of ''future'' income. Consumption is a major concept in economics and is also studied in many other social sciences. Different schools of economists define consumption differently. According to mainstream economics, mainstream economists, only the final purchase of newly produced Good (economics), goods and Service (economics), services by individuals for immediate use constitutes consumption, while other types of expenditure — in particular, fixed investment, intermediate consumption, and government spending — are placed in separate categories (see consumer choice). Other economists define consumption much more broadly, as the aggregate of all economic activity that does not entail the design, production and marketing of goods and services (e.g., the selection, adoption, use, disposal and recycling of goods and services). E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Fuels
A fossil fuel is a flammable carbon compound- or hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the buried remains of prehistoric organisms (animals, plants or microplanktons), a process that occurs within geological formations. Reservoirs of such compound mixtures, such as coal, petroleum and natural gas, can be mining, extracted and combustion, burnt as fuel for human consumption to provide energy for direct use (such as for cooking, heating or lighting), to power heat engines (such as steam engine, steam or internal combustion engines) that can propulsion, propel vehicles, or to electricity generation, generate electricity via steam turbine generators. Some fossil fuels are further petroleum refining processes, refined into derivative (chemistry), derivatives such as kerosene, gasoline and diesel fuel, diesel, or converted into petrochemicals such as polyolefins (plastics), aromatic compound, aromatics and synthetic resins. The origin of fossil fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
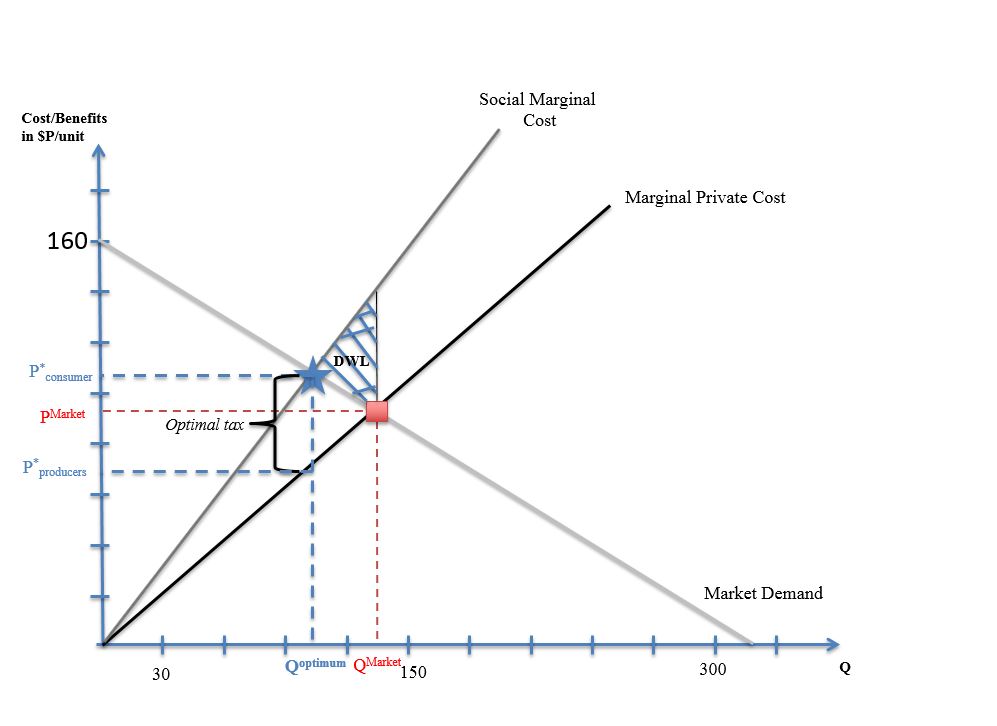
Social Cost
Social cost in neoclassical economics is the sum of the private costs resulting from a transaction and the costs imposed on the consumers as a consequence of being exposed to the transaction for which they are not compensated or charged. In other words, it is the sum of private and external costs. This might be applied to any number of economic problems: for example, social cost of carbon has been explored to better understand the costs of carbon emissions for proposed economic solutions such as a carbon tax. Private costs refer to direct costs to the producer for producing the good or service. Social cost includes these private costs and the additional costs (or external costs) associated with the production of the good which are not accounted for by the free market. In short, when the consequences of an action cannot be taken by the initiator, we will have external costs in the society. We will have private costs when initiator can take responsibility for agent's action.de V. G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global temperatures is Scientific consensus on climate change, driven by human activities, especially fossil fuel burning since the Industrial Revolution. Fossil fuel use, Deforestation and climate change, deforestation, and some Greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture, agricultural and Environmental impact of concrete, industrial practices release greenhouse gases. These gases greenhouse effect, absorb some of the heat that the Earth Thermal radiation, radiates after it warms from sunlight, warming the lower atmosphere. Carbon dioxide, the primary gas driving global warming, Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, has increased in concentratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environment (biophysical)
The natural environment or natural world encompasses all biotic and abiotic things occurring naturally, meaning in this case not artificial. The term is most often applied to Earth or some parts of Earth. This environment encompasses the interaction of all living species, climate, weather and natural resources that affect human survival and economic activity. The concept of the ''natural environment'' can be distinguished as components: * Complete ecological units that function as natural systems without massive civilized human intervention, including all vegetation, microorganisms, soil, rocks, plateaus, mountains, the atmosphere and natural phenomena that occur within their boundaries and their nature. * Universal natural resources and physical phenomena that lack clear-cut boundaries, such as air, water and climate, as well as energy, radiation, electric charge and magnetism, not originating from civilized human actions. In contrast to the natural environment is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. Unlike other gases, greenhouse gases absorb the radiations that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. The Earth is warmed by sunlight, causing its surface to radiate heat, which is then mostly absorbed by greenhouse gases. Without greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, the average temperature of Earth's surface would be about , rather than the present average of .Le Treut, H., R. Somerville, U. Cubasch, Y. Ding, C. Mauritzen, A. Mokssit, T. Peterson and M. Prather, 2007:Chapter 1: Historical Overview of Climate Change. In:Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. olomon, S., D. Qin, M. Manning, Z. Chen, M. Marquis, K.B. Averyt, M. Tignor and H.L. Miller (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New Yo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gasoline
Gasoline ( North American English) or petrol ( Commonwealth English) is a petrochemical product characterized as a transparent, yellowish, and flammable liquid normally used as a fuel for spark-ignited internal combustion engines. When formulated as a fuel for engines, gasoline is chemically composed of organic compounds derived from the fractional distillation of petroleum and later chemically enhanced with gasoline additives. It is a high-volume profitable product produced in crude oil refineries. The ability of a particular gasoline blend to resist premature ignition (which causes knocking and reduces efficiency in reciprocating engines) is measured by its octane rating. Tetraethyl lead was once widely used to increase the octane rating but is not used in modern automotive gasoline due to the health hazard. Aviation, off-road motor vehicles, and racing car engines still use leaded gasolines. Other substances are frequently added to gasoline to improve chemical st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Production (economics)
Production is the process of combining various inputs, both material (such as metal, wood, glass, or plastics) and immaterial (such as plans, or knowledge) in order to create output. Ideally this output (economics), output will be a goods and services, good or service which has value (economics), value and contributes to the utility (economics), utility of individuals. The area of economics that focuses on production is called production theory, and it is closely related to the consumption (or consumer) theory of economics. The production process and output directly result from productively utilising the original inputs (or factors of production). Known as primary producer goods or services, land, labour, and capital are deemed the three fundamental factors of production. These primary inputs are not significantly altered in the output process, nor do they become a whole component in the product. Under classical economics, materials and energy are categorised as secondary factors a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allocation (and Consumption) Of Resources
Allocation may refer to: Computing * Block allocation map * C++ allocators * Delayed allocation * File allocation table * IP address allocation * Memory allocation * No-write allocation (cache) * Register allocation Economics * Asset allocation * Economic system * Market allocation scheme * Resource allocation * Tax allocation district Telecommunication * Call-sign allocation plan * Frequency allocation * Type allocation code Other * Allocution (law), or allocutus, is a formal statement made to the court * Allocation (oil and gas) in hydrocarbon accounting to assign the proper portions of aggregated petroleum and gas flows back to contributing sources * Allocation voting in voting * Location-allocation, used in geographic information systems (GIS) * The allocation of scarce resources in operations research See also * Location (other) A location is a fixed geographical point. Location may also refer to: Arts and entertainment * ''Location'' (EP), by the Gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beneficiary
A beneficiary in the broadest sense is a natural person or other legal entity who receives money or other benefits from a benefactor. For example, the beneficiary of a life insurance policy is the person who receives the payment of the amount of insurance after the death of the insured. In trust law, beneficiaries are also known as '' cestui que use''. Most beneficiaries may be designed to designate where the assets will go when the owner(s) dies. However, if the primary beneficiary or beneficiaries are not alive or do not qualify under the restrictions, the assets will probably pass to the ''contingent beneficiaries''. Other restrictions such as being married or more creative ones can be used by a benefactor to attempt to control the behavior of the beneficiaries. Some situations such as retirement accounts do not allow any restrictions beyond the death of the primary beneficiaries, but trusts allow any restrictions that are not illegal or for an illegal purpose. The concept o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horizontal Equity
Economic equity is the construct, concept or idea of ''fairness'' in economics and ''justice'' in the distribution of wealth, resources, and taxation within a society. Equity is closely tied to taxation policies, welfare economics, and the discussions of public finance, influencing how resources are allocated among different segments of the population. Overview According to Peter Corning, there are three distinct categories of substantive fairness (equality, equity, and reciprocity) that must be combined and balanced in order to achieve a truly fair society. But while most of middle-income countries increased inequality in recent years, it is important to note that middle classes and—to a lesser extent—poorer-income groups seem to be getting an increasing share of income in recent years. To some, this advance is still vulnerable and needs to be quickly accelerated in the 21st century Definitions of equity Equity in economics refers to a condition of fairness where the econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |