|
Usable Fuel
In aviation, usable fuel is the Aviation fuel, fuel on board an aircraft that can actually be used by its engines. The opposite of usable fuel is unusable fuel.Websters dictionary oUnusable fuel visited 19 March, 2012 The unusable fuel figure is calculated for an aircraft fuel tank in "the most adverse fuel feed condition occurring under each intended operation and flight maneuver involving that tank".Cornell Law online library https://www.law.cornell.edu/cfr/text/14/23.959, accessed 24 November 2017 The figure usable fuel is used when calculating or defining other key figures of an aircraft such as MTOW, zero-fuel weight etc. Usable fuel is the total amount of fuel in an aircraft minus the fuel that cannot be fed into the engine(s): fuel under the pump-intake, fuel behind ribs of a tank, fuel in lines between the tanks and the engines etc. As this figure is calculated/defined for a plane in level flight it is possible that the engines of an aircraft run dry (out of fuel) even when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
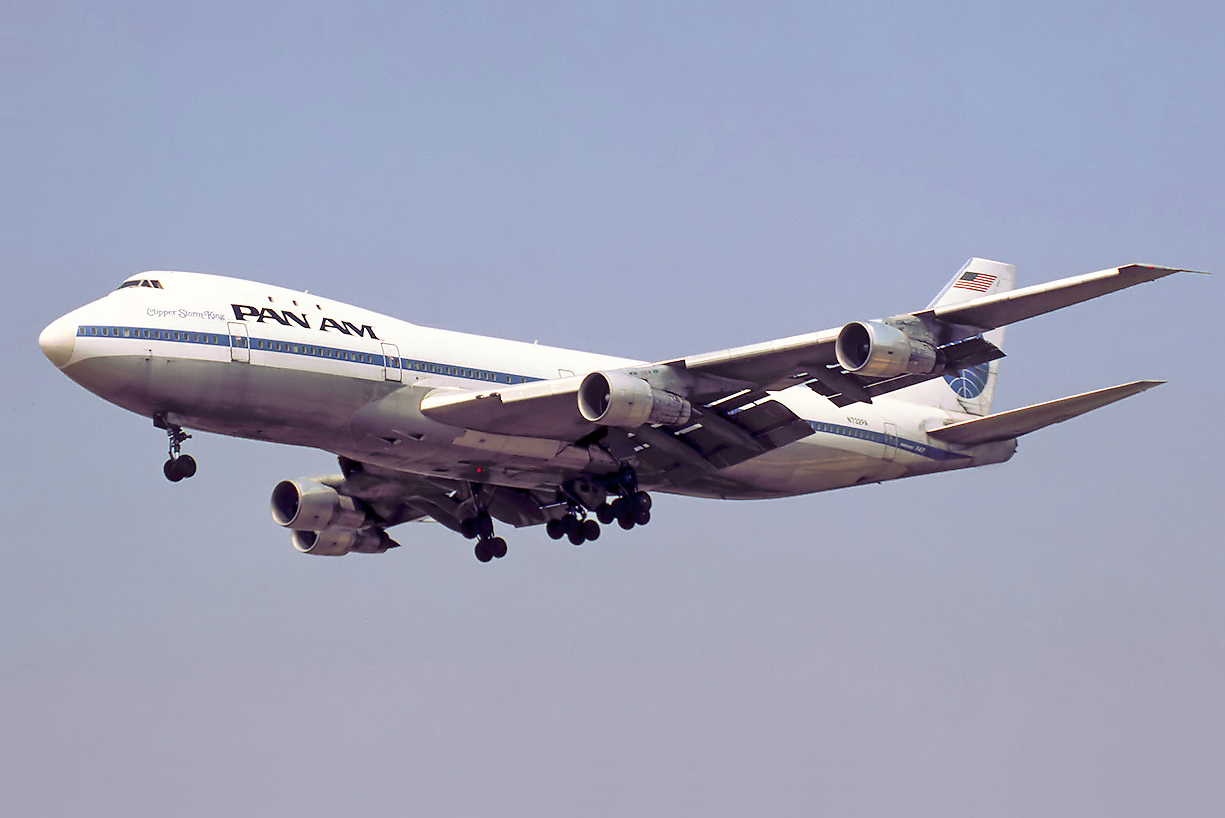
Aviation
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. ''Aircraft'' include fixed-wing and rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as lighter-than-air aircraft such as hot air balloons and airships. Aviation began in the 18th century with the development of the hot air balloon, an apparatus capable of atmospheric displacement through buoyancy. Clément Ader built the "Ader Éole" in France and made an uncontrolled, powered hop in 1890. This was the first powered aircraft, although it did not achieve controlled flight. Some of the most significant advancements in aviation technology came with the controlled gliding flying of Otto Lilienthal in 1896. A major leap followed with the construction of the '' Wright Flyer'', the first powered airplane by the Wright brothers in the early 1900s. Since that time, aviation has been technologically revolutionized by the introduction of the jet engine which enabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aviation Fuel
Aviation fuels are either petroleum-based or blends of petroleum and synthetic fuels, used to power aircraft. They have more stringent requirements than fuels used for ground applications, such as heating and road transport, and they contain additives to enhance or preserve properties important to fuel performance and handling. They are kerosene-based fuels (such as JP-8 and Jet A-1) used in gas-turbine-powered aircraft. Piston-engined aircraft use leaded gasoline, while those with diesel engines may use jet fuel (kerosene). By 2012, all U.S. Air Force aircraft had been certified to use a 50-50 blend of kerosene and synthetic fuel derived from coal or natural gas, in an effort to stabilize fuel costs. Types of aviation fuel Conventional aviation fuels Jet fuel Jet fuel is a clear to straw-colored fuel, based on either an unleaded kerosene (Jet A-1), or a naphtha–kerosene blend (Jet B). Similar to diesel fuel, it can be used in either Diesel engine, compression ignition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MTOW
The maximum takeoff weight (MTOW) or maximum gross takeoff weight (MGTOW) or maximum takeoff mass (MTOM) of an aircraft, also known as the maximum structural takeoff weight or maximum structural takeoff mass, is the maximum weight at which the pilot is allowed to attempt to take off, due to structural or other limits. The analogous term for rockets is gross lift-off mass, or GLOW. MTOW is usually specified in units of kilograms or pounds. MTOW is the heaviest weight at which the aircraft has been shown to meet all the airworthiness requirements applicable to it. It refers to the maximum permissible aircraft weight at the start of the takeoff run. MTOW of an aircraft is fixed and does not vary with altitude, air temperature, or the length of the runway to be used for takeoff or landing. Maximum permissible takeoff weight or "regulated takeoff weight", varies according to flap setting, altitude, air temperature, length of runway and other factors. It is different from one takeoff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zero-fuel Weight
The zero-fuel weight (ZFW) of an aircraft is the total weight of the airplane and all its contents, minus the total weight of the usable fuel on board. Unusable fuel is included in ZFW. Remember the takeoff weight components contributions: : OEW + PL + FOB = TOW Where OEW is the Operating Empty Weight (that is a characteristic of the plane), PL is the Payload actually embarked, and FOB the Fuel actually embarked and TOW the actual take-off weight. ZFW is also defined as OEW + PL. The previous formula becomes: : ZFW + FOB = TOW. For many types of airplane, the airworthiness limitations include a maximum zero-fuel weight. This limitation is specified to ensure bending moments on the wing roots are not excessive during flight. When the aircraft is loaded before flight, the zero-fuel weight must not exceed the maximum zero-fuel weight. Maximum zero fuel weight The maximum zero fuel weight (MZFW) is the maximum weight allowed before usable fuel and other specified usable agents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
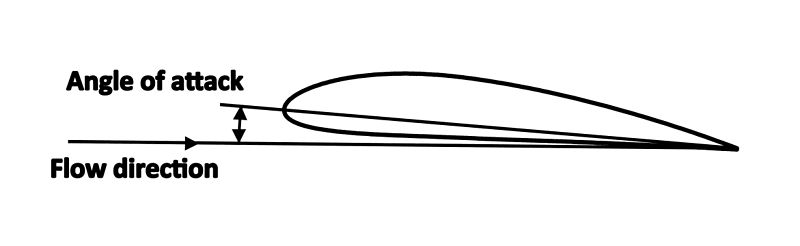
Angle Of Attack
In fluid dynamics, angle of attack (AOA, α, or \alpha) is the angle between a Airfoil#Airfoil terminology, reference line on a body (often the chord (aircraft), chord line of an airfoil) and the vector (geometry), vector representing the relative motion between the body and the fluid through which it is moving. Angle of attack is the angle between the body's reference line and the oncoming flow. This article focuses on the most common application, the angle of attack of a wing or airfoil moving through air. In aerodynamics, angle of attack specifies the angle between the chord line of the wing of a fixed-wing aircraft and the vector representing the relative motion between the aircraft and the atmosphere. Since a wing can have twist, a chord line of the whole wing may not be definable, so an alternate reference line is simply defined. Often, the chord line of the Wing root, root of the wing is chosen as the reference line. Another choice is to use a horizontal line on the fuse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cruise (flight)
Cruise is the phase of aircraft flight from when the aircraft levels off after a climb until it begins to descend for landing. Cruising usually comprises the majority of a flight, and may include small changes in heading (direction of flight), airspeed, and altitude. Airliner cruise Commercial or passenger aircraft are usually designed for optimum performance around their cruise speed ( VC) and cruise altitude. Factors affecting optimum cruise speed and altitude include payload, center of gravity, air temperature, and humidity. Cruise altitude is usually where the higher ground speed is balanced against the decrease in engine thrust and efficiency at higher altitudes. Common narrowbodies like the Airbus A320 and Boeing 737NG cruise at , while modern widebodies like the Airbus A350 and Boeing 787 cruise at . The typical cruising altitude for commercial airliners is . The speed which covers the greatest distance for a given amount of fuel is known as the maximum range spee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index Of Aviation Articles
Aviation is the design, development, production, operation, and use of aircraft, especially heavier-than-air aircraft. Articles related to aviation include: A Aviation accidents and incidents – Above Mean Sea Level (AMSL) – ADF – Accessory drive – Advance airfield – Advanced air mobility – Advanced technology engine – Adverse yaw – Aerial ramming – Aerial reconnaissance – Aerobatics – Aerodrome – Aerodrome mapping database (AMDB) – Aerodynamics – Aerofoil – Aerodrome beacon – Aeronautical Information Manual (AIM) – Aeronautical chart – Aeronautical Message Handling System – Aeronautical phraseology – Aeronautics – Aeronaval – Aerospace – Aerospace engineering – Afterburner – Agile Combat Employment (ACE) – Aileron – Air charter – Air defense identification zone (ADIZ) – Air freight terminal – Air traffic flow management – Air-augmented rocket – Airband – Airbase (AFB) – Airborne colli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |