|
Upper Class
Upper class in modern societies is the social class composed of people who hold the highest social status. Usually, these are the wealthiest members of class society, and wield the greatest political power. According to this view, the upper class is generally distinguished by immense wealth which is passed on from generation to generation. Prior to the 20th century, the emphasis was on ''aristocracy'', which emphasized generations of inherited noble status, not just recent wealth. Because the upper classes of a society may no longer rule the society in which they are living, they are often referred to as the old upper classes, and they are often culturally distinct from the newly rich middle classes that tend to dominate public life in modern social democracies. According to the latter view held by the traditional upper classes, no amount of individual wealth or fame would make a person from an undistinguished background into a member of the upper class as one must be born in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Class
A social class or social stratum is a grouping of people into a set of Dominance hierarchy, hierarchical social categories, the most common being the working class and the Bourgeoisie, capitalist class. Membership of a social class can for example be dependent on education, wealth, occupation, income, and belonging to a particular subculture or social network. Class is a subject of analysis for sociologists, political scientists, anthropologists and Social history, social historians. The term has a wide range of sometimes conflicting meanings, and there is no broad consensus on a definition of class. Some people argue that due to social mobility, class boundaries do not exist. In common parlance, the term social class is usually synonymous with Socioeconomic status, socioeconomic class, defined as "people having the same social, economic, cultural, political or educational status", e.g. the working class, "an emerging professional class" etc. However, academics distinguish socia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baile Del Santiago Antiguo
Baile ("dance" in Spanish) may refer to: * Baile (Spanish play), a Spanish dramatic form * Baile funk, a type of dance music from Rio de Janeiro * Baile, the Irish Gaelic word for a town, usually anglicized as "bally" or "balla" * Baile, the Scottish Gaelic word for a crofting township; see Township (Scotland) * Băile (other), several places in Romania {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European islands by area, largest European island, and the List of islands by area, ninth-largest island in the world. It is dominated by a maritime climate with narrow temperature differences between seasons. The island of Ireland, with an area 40 per cent that of Great Britain, is to the west – these islands, along with over List of islands of the British Isles, 1,000 smaller surrounding islands and named substantial rocks, comprise the British Isles archipelago. Connected to mainland Europe until 9,000 years ago by a land bridge now known as Doggerland, Great Britain has been inhabited by modern humans for around 30,000 years. In 2011, it had a population of about , making it the world's List of islands by population, third-most-populous islan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harrods 1909
Harrods is a Grade II listed luxury department store on Brompton Road in Knightsbridge, London, England. It was designed by C. W. Stephens for Charles Digby Harrod, and opened in 1905; it replaced the first store on the grounds founded by his father Charles Henry Harrod in 1849, which burned down in 1881. The store spans of selling space, making it the largest department store in Europe and one of the largest in the world. Harrods is one of the most famous department stores worldwide, attracting 15 million visitors annually . The original holding company, Harrod's Stores Limited, was formed and began trading on the London Stock Exchange in 1889. It was acquired by and merged into the House of Fraser in 1959, which itself was acquired by the Fayed brothers and became a privately held company in 1985. When the House of Fraser was relisted on the stock exchange, the Harrods business was split off to remain privately held in 1994. The present-day legal entity, the Harrods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castellans Of The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
Castellans of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth were the lowest rank of territorial official who could sit in the Senate of Poland. Their numbers varied over time and with the shifting borders of the Commonwealth. In the Kingdom of Poland and later in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Castellans () usually deferred to the higher ranking Voivodes (Polish: ''Wojewoda''), excepting three Distinguished Castellans of the cities of Trakai, Vilnius, and of Kraków - who ranked higher than the Voivodes. Competences With the exception of the Castellan of Kraków, whose seat was representative of the Commonwealth's capital until 1596, Castellans were usually considered subordinate to Voivodes. Two castellans in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania - those of Vilnius and Trakai - were also considered privileged, and had a status equal to a voivode. Castellans were in charge of a subdivision of a Voivodship called a Castellany (Polish: ''Kasztelania'') until the late 15th century when domains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voivodes Of The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
{{For, other uses of "voivod", "voyevoda", etc., Voivode of Transylvania, Voivode (Vlach leader), Voivode, Voivode (other) Voivodes of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth were one of the highest ranking officials who could sit in the Senate of Poland. They were the officials in charge of the voivodeships (provinces/palatinates) of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The office first appears as ''Palatine'' (''Palatinus'') who held the foremost position after the King. As Poland broke up into separate principalities, each Prince had his court and his own Palatine. When the Kingdom was (in part) consolidated, the Palatines became heads of those former Principalities, which then became Palatinates. As such, the Palatines were members of the King's Council (''comites palatini''). The title merged with the Polish Voivode or ''Wojewoda'' ( Slavic Woi-woda/вои-вода (Cyrillic), with two functions, in army or war, and as a “guide” or director, a lexical and institutiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostroróg Family
180px, Coat of the family was Nałęcz. 170px, Mikołaj Ostroróg (1593–1651) The House of Ostroróg was the name of an old Polish noble family taking their name from Ostroróg, a town in Szamotuły County, Greater Poland Voivodeship, Poland. They used the Nałęcz coat of arms. Members of the family held important civic posts in the Wielkpolska region in the Kingdom of Poland, particularly that of voivode. At the end of the 19th-century, family members settled in France, England and for a time, in Turkey. Coat of arms image:POL COA Ostroróg Hrabia.svg, Coat of Arms of Counts Ostroróg image:POL COA Ostroróg II.svg, Coat of Arms of Counts Ostroróg (II variant) Notable members * Sędziwój Ostroróg (1375–1441), voivode of Poznań Voivodeship * Dobrogost Ostroróg (1400-1478/79), castellan of Gniezno * Stanisław Ostroróg (1400–1477), voivode of Kalisz Voivodeship * Jan Ostroróg (1436–1501), voivode of Poznań Voivodeship, political thinker * Wacław O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Humanities Research Association
The Modern Humanities Research Association (MHRA) is a United Kingdom–based international organisation that aims to encourage and promote advanced study and research of humanities. It is most notable for producing the '' MHRA Style Guide''. History The MHRA was founded in 1918 in Christ's College, Cambridge. After an early change of name to MHRA in 1918, the unincorporated charity became an incorporated company with the same name on 2 October 1997. Its declared aim is to encourage and promote advanced study and research in the field of the modern humanities, which include the modern and medieval European languages, literatures and cultures. The current chair of the MHRA is Professor Derek Connon of Swansea University. Publications As well as the ''MHRA Style Guide'', the MHRA publishes six scholarly journals: * '' Annual Bibliography of English Language and Literature'' * '' The Modern Language Review'' * '' Austrian Studies'' * '' Portuguese Studies'' * '' The Slavonic and E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It shares Anglo-Scottish border, a land border with Scotland to the north and England–Wales border, another land border with Wales to the west, and is otherwise surrounded by the North Sea to the east, the English Channel to the south, the Celtic Sea to the south-west, and the Irish Sea to the west. Continental Europe lies to the south-east, and Ireland to the west. At the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census, the population was 56,490,048. London is both List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, the largest city and the Capital city, capital. The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic. It takes its name from the Angles (tribe), Angles, a Germanic peoples, Germanic tribe who settled du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridgeshire
Cambridgeshire (abbreviated Cambs.) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in the East of England and East Anglia. It is bordered by Lincolnshire to the north, Norfolk to the north-east, Suffolk to the east, Essex and Hertfordshire to the south, Northamptonshire to the west, and Bedfordshire to the south-west. The largest settlement is the city of Peterborough, and the city of Cambridge is the county town. The county has an area of and had an estimated population of 906,814 in 2022. Peterborough, in the north-west, and Cambridge, in the south, are by far the largest settlements. The remainder of the county is rural, and contains the city of Ely, Cambridgeshire, Ely in the east, Wisbech in the north-east, and St Neots and Huntingdon in the west. For Local government in England, local government purposes Cambridgeshire comprises a non-metropolitan county, with five Districts of England, districts, and the Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
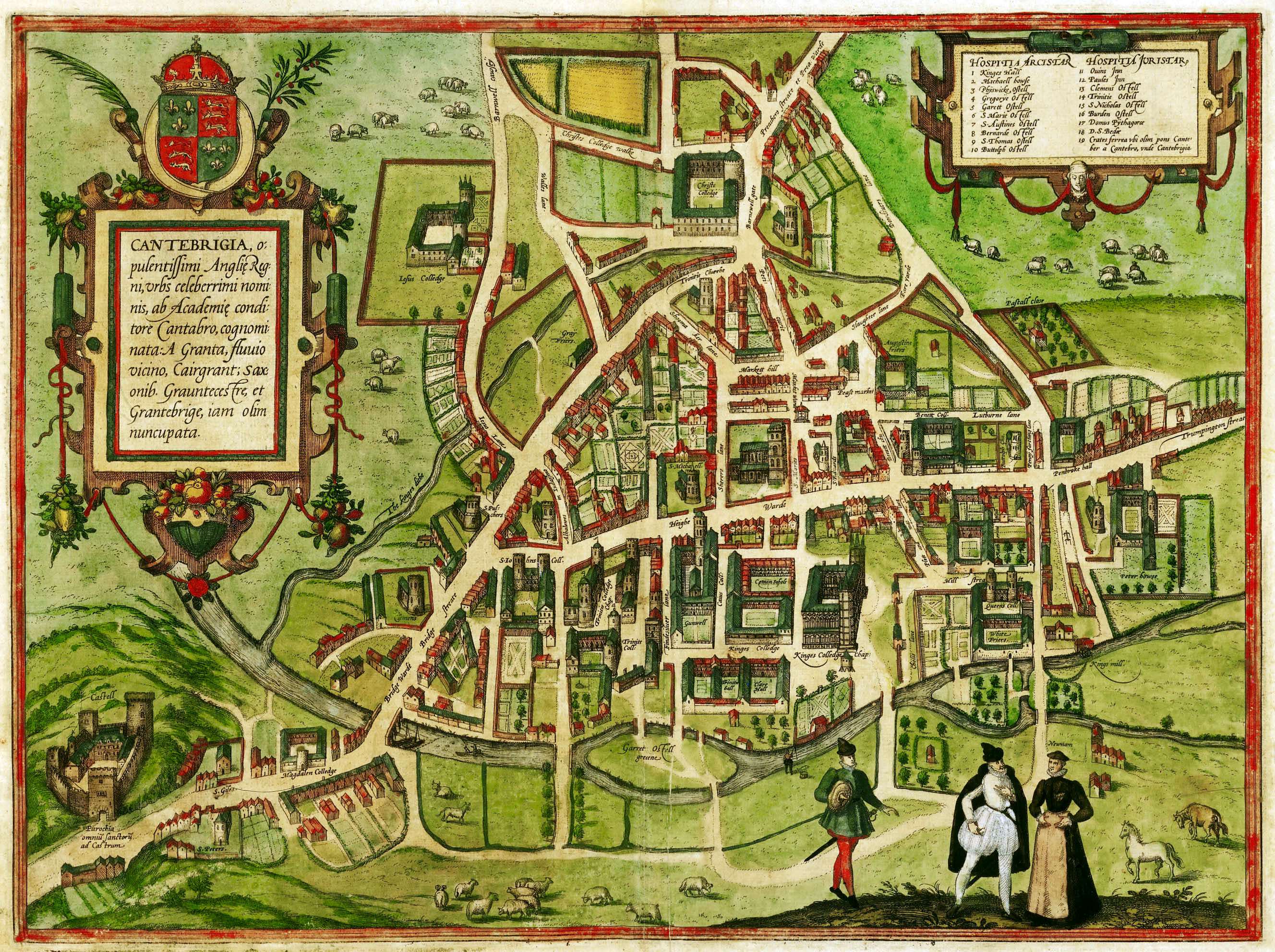
Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a List of cities in the United Kingdom, city and non-metropolitan district in the county of Cambridgeshire, England. It is the county town of Cambridgeshire and is located on the River Cam, north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of the City of Cambridge was 145,700; the population of the wider built-up area (which extends outside the city council area) was 181,137. (2021 census) There is archaeological evidence of settlement in the area as early as the Bronze Age, and Cambridge became an important trading centre during the Roman Britain, Roman and Viking eras. The first Town charter#Municipal charters, town charters were granted in the 12th century, although modern city status was not officially conferred until 1951. The city is well known as the home of the University of Cambridge, which was founded in 1209 and consistently ranks among the best universities in the world. The buildings of the university include King's College Chap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Slavonic And East European Review
''The Slavonic and East European Review'', the journal of the UCL School of Slavonic and East European Studies (University College London), is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal covering Slavonic and East European Studies. It was established in 1922 by Bernard Pares, Robert Seton-Watson, and Harold Williams and published by the Modern Humanities Research Association. External links *Journalon JSTOR JSTOR ( ; short for ''Journal Storage'') is a digital library of academic journals, books, and primary sources founded in 1994. Originally containing digitized back issues of academic journals, it now encompasses books and other primary source ... Vol 10(June 1931) Vol 11(July 1932) Vol 12(July 1933) Vol 13(1934) Vol 14(1935) 15(1936) Vol 16(1937) Vol 17(1938) Vol 25(November 1946) Vol 28(November 1949) Slavic studies journals Academic journals established in 1922 Quarterly journals English-language journals {{slavic-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |