|
Upgradeability
Upgrading is the process of replacing a product with a newer version of the same product. In computing and consumer electronics, an upgrade is generally a replacement of hardware, software or firmware with a newer or better version, in order to bring the system up to date or to improve its characteristics. Computing and consumer electronics Examples of common hardware upgrades include installing additional memory ( RAM), adding larger hard disks, replacing microprocessor cards or graphics cards, and installing new versions of software. Other upgrades are possible as well. Common software upgrades include changing the version of an operating system, an office suite, of an anti-virus program, or of various other tools. Common firmware upgrades include the updating of the iPod control menus, the Xbox 360 dashboard, or the non-volatile flash memory that contains the embedded operating system for a consumer electronics device. Users can often download software and firmware upgr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computer, computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both computer hardware, hardware and software. Computing has scientific, engineering, mathematical, technological, and social aspects. Major computing disciplines include computer engineering, computer science, cybersecurity, data science, information systems, information technology, and software engineering. The term ''computing'' is also synonymous with counting and calculation, calculating. In earlier times, it was used in reference to the action performed by Mechanical computer, mechanical computing machines, and before that, to Computer (occupation), human computers. History The history of computing is longer than the history of computing hardware and includes the history of methods intended for pen and paper (or for chalk and slate) with or without the aid of tables. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies are technology, technologies whose development, practical applications, or both are still largely unrealized. These technologies are generally innovation, new but also include old technologies finding new applications. Emerging technologies are often perceived as capable of changing the status quo. Emerging technologies are characterized by radical novelty (in application even if not in origins), relatively fast growth, coherence, prominent impact, and uncertainty and ambiguity. In other words, an emerging technology can be defined as "a radically novel and relatively fast growing technology characterised by a certain degree of coherence persisting over time and with the potential to exert a considerable impact on the socio-economic domain(s) which is observed in terms of the composition of actors, institutions and patterns of interactions among those, along with the associated knowledge production processes. Its most prominent impact, however, lies in the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System Restore
System Restore is a feature in Microsoft Windows that allows the user to revert their computer's state (including system files, installed applications, Windows Registry, and system settings) to that of a previous point in time, which can be used to recover from system malfunctions or other problems. First included in Windows Me, it has been included in all following desktop versions of Windows released since, excluding Windows Server. In Windows 10 and Windows 11, System Restore is turned off by default and must be enabled by users in order to function. This does not affect personal files such as documents, music, pictures, and videos. In prior Windows versions it was based on a file filter that watched changes for a certain set of file extensions, and then copied files before they were overwritten. An updated version of System Restore introduced by Windows Vista uses the Shadow Copy service as a backend (allowing block-level changes in files located in any directory on the volu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
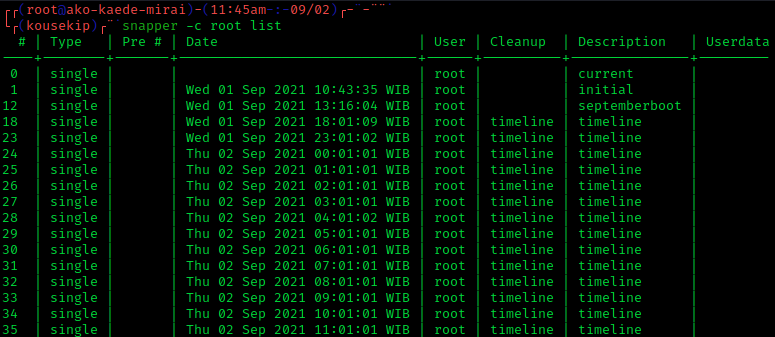
Snapshot (computer Storage)
In Computer, computer systems, a snapshot is the State (computer science), state of a system at a particular point in time. The term was coined as an analogy to that in Snapshot (photography), photography. Rationale A full backup of a large data set may take a long time to complete. On Computer multitasking, multi-tasking or multi-user systems, there may be writes to that data while it is being backed up. This prevents the backup from being Atomicity (database systems), atomic and introduces a version skew that may result in data corruption. For example, if a user moves a file into a directory that has already been backed up, then that file would be completely missing on the Computer data storage, backup media, since the backup operation had already taken place before the addition of the file. Version skew may also cause corruption with files which change their size or contents underfoot while being read. One Backup#Approaches to backing up live data, approach to safely backin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomicity (database Systems)
In database systems, atomicity (; from ) is one of the ACID (''Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability'') transaction properties. An atomic transaction is an ''indivisible'' and '' irreducible'' series of database operations such that either ''all'' occur, or ''none'' occur. A guarantee of atomicity prevents partial database updates from occurring, because they can cause greater problems than rejecting the whole series outright. As a consequence, the transaction cannot be observed to be in progress by another database client. At one moment in time, it has not yet happened, and at the next it has already occurred in whole (or nothing happened if the transaction was cancelled in progress). An example of transaction atomicity could be a digital monetary transfer from bank account A to account B. It consists of two operations, debiting the money from account A and crediting it to account B. Performing both of these operations inside of an atomic transaction ensures that the da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OSTree
libostree (previously OSTree) is a system for versioning updates of Linux-based operating systems. It can be considered "Git Git () is a distributed version control system that tracks versions of files. It is often used to control source code by programmers who are developing software collaboratively. Design goals of Git include speed, data integrity, and suppor ... for operating system binaries". It operates in userspace, and will work on top of any Linux file system. At its core is a Git-like content-addressed object store with branches (or "refs") to track meaningful file system trees within the store. Features OSTree is closely inspired by Git. It operates on commits which refer to filesystem trees. To refer to different commits while maintaining a user-readable name, OSTree provides "references" (analogous to branches in Git), such as exampleos/buildmain/x86_64-runtime. Files provided by commits are by default immutable, done by mounting the filesystem itself ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
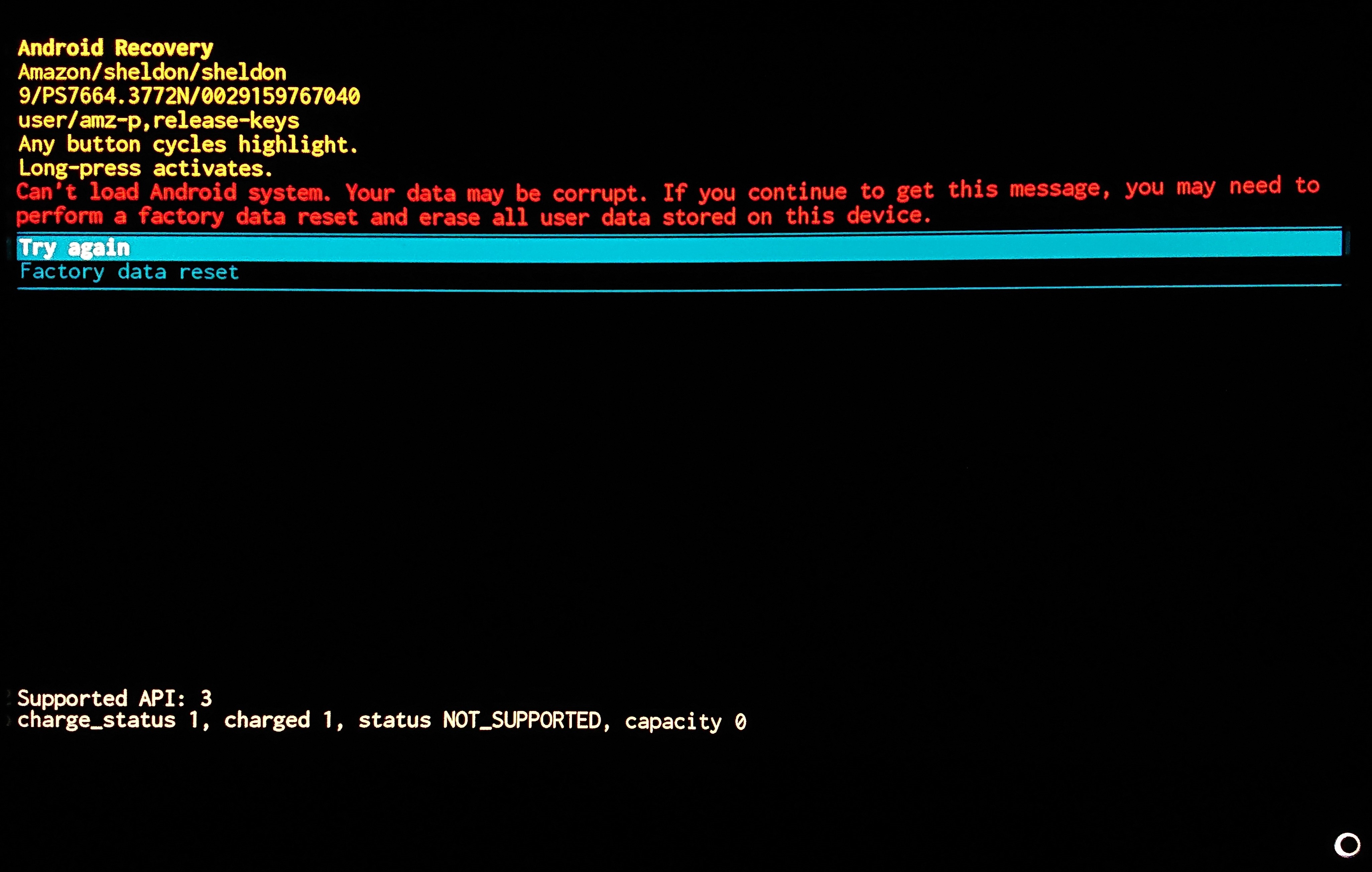
Brick (electronics)
A brick (or bricked device) is a mobile device, game console, router, computer or other electronic device that is no longer functional due to corrupted firmware, a hardware problem, or other damage. The term analogizes the device to a brick's modern technological usefulness. "Brick" is also used as a verb to describe a device entering such a state. Cause and prevention Bricking a device is most often a result of interrupting an attempt to update the device. Many devices have an update procedure which must not be interrupted before completion; if interrupted by a power failure, user intervention, or any other reason, the existing firmware may be partially overwritten and unusable. The risk of corruption can be minimized by taking all possible precautions against interruption. Bricking a device may also be done intentionally as punishment for severe transgressions involving its use, but this is exceptionally rare and typically only done as a last resort. Installing firmware ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OtherOS
OtherOS is a feature of early versions of Sony Computer Entertainment's PlayStation 3 video game console, allowing user installed software, such as Linux or FreeBSD. Software running in the OtherOS environment has access to 6 of the 7 Synergistic Processing Unit, Synergistic Processing Elements. Sony implemented a hypervisor that restricts access to the RSX Reality Synthesizer graphics chip. IBM provided an introduction to programming parallel applications on the PlayStation 3. The feature was controversially removed by Sony since PlayStation 3 system software, system firmware update 3.21, released on April 1, 2010. A class action lawsuit was filed against Sony on behalf of users, but was dismissed with prejudice in 2011 by a federal judge. The judge stated: "As a legal matter, ... plaintiffs have failed to allege facts or articulate a theory on which Sony may be held liable." However, this decision was overturned in a 2014 appellate court decision finding that plaintiffs had inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IPhone 7
The iPhone 7 and iPhone 7 Plus are smartphones that were developed and marketed by Apple Inc. They are the List of iPhone models, tenth generation of the iPhone. They were announced on September 7, 2016, at the Bill Graham Civic Auditorium in San Francisco by Apple CEO Tim Cook, and were released on September 16, 2016, succeeding the iPhone 6, iPhone 6 Plus, iPhone 6S and iPhone 6S Plus as the flagship devices in the iPhone series. Apple also released the iPhone 7 and iPhone 7 Plus in numerous countries worldwide throughout September and October 2016. They were succeeded as flagship devices by the iPhone 8 and iPhone 8 Plus on September 12, 2017, and were discontinued with the announcement of the iPhone 11 and iPhone 11 Pro on September 10, 2019. The iPhone 7's overall design is similar to the iPhone 6 and iPhone 6S. Changes introduced included new color options (Matte Black and Jet Black), water and dust resistance, a new capacitive, static home button, revised antenna bands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freeware
Freeware is software, often proprietary, that is distributed at no monetary cost to the end user. There is no agreed-upon set of rights, license, or EULA that defines ''freeware'' unambiguously; every publisher defines its own rules for the freeware it offers. For instance, modification, redistribution by third parties, and reverse engineering are permitted by some publishers but prohibited by others. Unlike with free and open-source software, which are also often distributed free of charge, the source code for freeware is typically not made available. Freeware may be intended to benefit its producer by, for example, encouraging sales of a more capable version, as in the freemium and shareware business models. History The term ''freeware'' was coined in 1982 by Andrew Fluegelman, who wanted to sell PC-Talk, the communications application he had created, outside of commercial distribution channels. Fluegelman distributed the program via the same process as ''shareware''. As s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |