|
Underwater Survey
An underwater survey is a survey performed in an underwater environment or conducted remotely on an underwater object or region. Surveys can have several meanings. The word originates in Medieval Latin with meanings of ''looking over'' and ''detailed study of a subject''. One meaning is the accurate measurement of a geographical region, usually to plot the positions of features as a scale map of the region. This meaning is often used in scientific contexts, and also in civil engineering and mineral extraction. Another meaning, often used in a civil, structural, or marine engineering context, is the inspection of a structure or vessel to compare the actual condition with the specified nominal condition, usually to report on the actual condition and compliance with, or deviations from, the nominal condition, for quality control, damage assessment, valuation, insurance, maintenance, and similar purposes. In other contexts it can mean inspection of a region to establish presence and di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
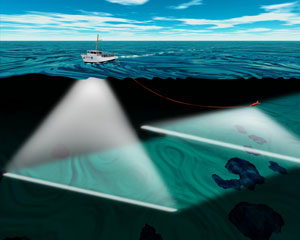
Sonar Operations By Survey Ship
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigation, navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect objects on or under the surface of the water, such as other vessels. "Sonar" can refer to one of two types of technology: ''passive'' sonar means listening for the sound made by vessels; ''active'' sonar means emitting pulses of sounds and listening for echoes. Sonar may be used as a means of acoustic location and of measurement of the echo characteristics of "targets" in the water. Acoustic location in air was used before the introduction of radar. Sonar may also be used for robot navigation, and sodar (an upward-looking in-air sonar) is used for atmospheric investigations. The term ''sonar'' is also used for the equipment used to generate and receive the sound. The acoustic frequencies used in sonar systems vary from very low (infrasonic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underwater Construction
Underwater construction is industrial construction in an underwater environment. It is a part of the marine construction industry. It can involve the use of a variety of building materials, mainly concrete and steel. There is often, but not necessarily, a significant component of commercial diving involved. Some underwater work can be done by divers, but they are limited by depth and site conditions. And it is hazardous work, with expensive risk reduction and mitigation, and a limited range of suitable equipment. Remotely operated underwater vehicles are an alternative for some classes of work, but are also limited and expensive. When reasonably practicable, the bulk of the work is done out of the water, with underwater work restricted to installation, modification and repair, and inspection. Scope and applications Underwater construction is common in the civil engineering, coastal engineering, energy, and petroleum extraction industries. Civil engineering *Construction bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Information System
A geographic information system (GIS) consists of integrated computer hardware and Geographic information system software, software that store, manage, Spatial analysis, analyze, edit, output, and Cartographic design, visualize Geographic data and information, geographic data. Much of this often happens within a spatial database; however, this is not essential to meet the definition of a GIS. In a broader sense, one may consider such a system also to include human users and support staff, procedures and workflows, the Geographic Information Science and Technology Body of Knowledge, body of knowledge of relevant concepts and methods, and institutional organizations. The uncounted plural, ''geographic information systems'', also abbreviated GIS, is the most common term for the industry and profession concerned with these systems. The academic discipline that studies these systems and their underlying geographic principles, may also be abbreviated as GIS, but the unambiguous GIScie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wide Area Augmentation System
The Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS) is an air navigation aid developed by the Federal Aviation Administration to augment the Global Positioning System (GPS), with the goal of improving its accuracy, integrity, and availability. Essentially, WAAS is intended to enable aircraft to rely on GPS for all phases of flight, including approaches with vertical guidance to any airport within its coverage area. It may be further enhanced with the local-area augmentation system (LAAS) also known by the preferred ICAO term ''ground-based augmentation system'' (GBAS) in critical areas. WAAS uses a network of ground-based reference stations, in North America and Hawaii, to measure small variations in the GPS satellites' signals in the western hemisphere. Measurements from the reference stations are routed to master stations, which queue the received deviation correction (DC) and send the correction messages to geostationary WAAS satellites in a timely manner (every 5 seconds or better) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Diving
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which study the physical world, and the social sciences, which study individuals and societies. While referred to as the formal sciences, the study of logic, mathematics, and theoretical computer science are typically regarded as separate because they rely on deductive reasoning instead of the scientific method as their main methodology. Meanwhile, applied sciences are disciplines that use scientific knowledge for practical purposes, such as engineering and medicine. The history of science spans the majority of the historical record, with the earliest identifiable predecessors to modern science dating to the Bronze Age in Egypt and Mesopotamia (). Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped the Greek natural phil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. The discipline involves Survey (archaeology), surveying, Archaeological excavation, excavation, and eventually Post excavation, analysis of data collected, to learn more about the past. In broad scope, archaeology relies on cross-disciplinary research. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baseline (surveying)
In surveying, a baseline is generally a line between two points on the Earth's surface and the direction and/or distance between them. In a triangulation network, at least one distance between two stations needs to be measured to calculate the size of the triangles by trigonometry. In relative Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) surveying, a baseline is the line between two GNSS receivers to determine the 3D coordinate difference. United States In the United States Public Land Survey System, a baseline is specifically the principal east-west line (i.e., a parallel) upon which all rectangular surveys in a defined area are based. The baseline meets its corresponding principal meridian (north-south line) at the point of origin, or '' initial point'', for the land survey. For example, the baseline for Nebraska and Kansas is shared as the border for both states, at the 40th parallel north. More specifically a baseline may be the line that divides a survey township ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remotely Operated Underwater Vehicle
A remotely operated underwater vehicle (ROUV) or remotely operated vehicle (ROV) is a free-swimming submersible craft used to perform underwater observation, inspection and physical tasks such as valve operations, hydraulic functions and other general tasks within the subsea oil and gas industry, military, scientific and other applications. ROVs can also carry tooling packages for undertaking specific tasks such as pull-in and connection of flexible flowlines and umbilicals, and component replacement. They are often used to do research and commercial work at great depths beyond the capacities of most submersibles and divers. Description This meaning is different from remote control vehicles operating on land or in the air because ROVs are designed specifically to function in underwater environments, where conditions such as high pressure, limited visibility, and the effects of buoyancy and water currents pose unique challenges. While land and aerial vehicles use wireless commu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photomosaic
A photographic mosaic or photomosaic is a picture (usually a photograph) that has been divided into tiled sections, usually equal sized, each of which is replaced with another photograph that matches the target photo.Cartwright (2007) p.102 quote: Photographic mosaic, also known as Photomosaic, a portmanteau of photo and mosaic, is a picture that is divided into small sections. When viewed as a whole, it appears to be one image, when in fact the image is made up of hundreds or even thousands of smaller images. When viewed at low magnifications, the individual pixels appear as the primary image, while close examination reveals that the image is in fact made up of many hundreds or thousands of smaller images. Most of the time they are a computer-created type of photomontage, montage. There are two kinds of mosaic, depending on how the matching is done. In the simpler kind, each part of the target image is averaged down to a single color. Each of the library images is also reduced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submersible
A submersible is an underwater vehicle which needs to be transported and supported by a larger ship, watercraft or dock, platform. This distinguishes submersibles from submarines, which are self-supporting and capable of prolonged independent operation at sea. There are many types of submersibles, including both human-occupied vehicles (HOVs) and uncrewed craft, variously known as remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) or unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs). Submersibles have many uses including oceanography, underwater archaeology, ocean exploration, tourism, underwater work, equipment maintenance and underwater search and recovery, recovery and underwater videography. History The first recorded self-propelled underwater vessel was a small oar-powered submarine conceived by William Bourne (mathematician), William Bourne (c. 1535 – 1582) and designed and built by Dutch inventor Cornelis Drebbel in 1620, with two more improved versions built in the following four years.Konstam (201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
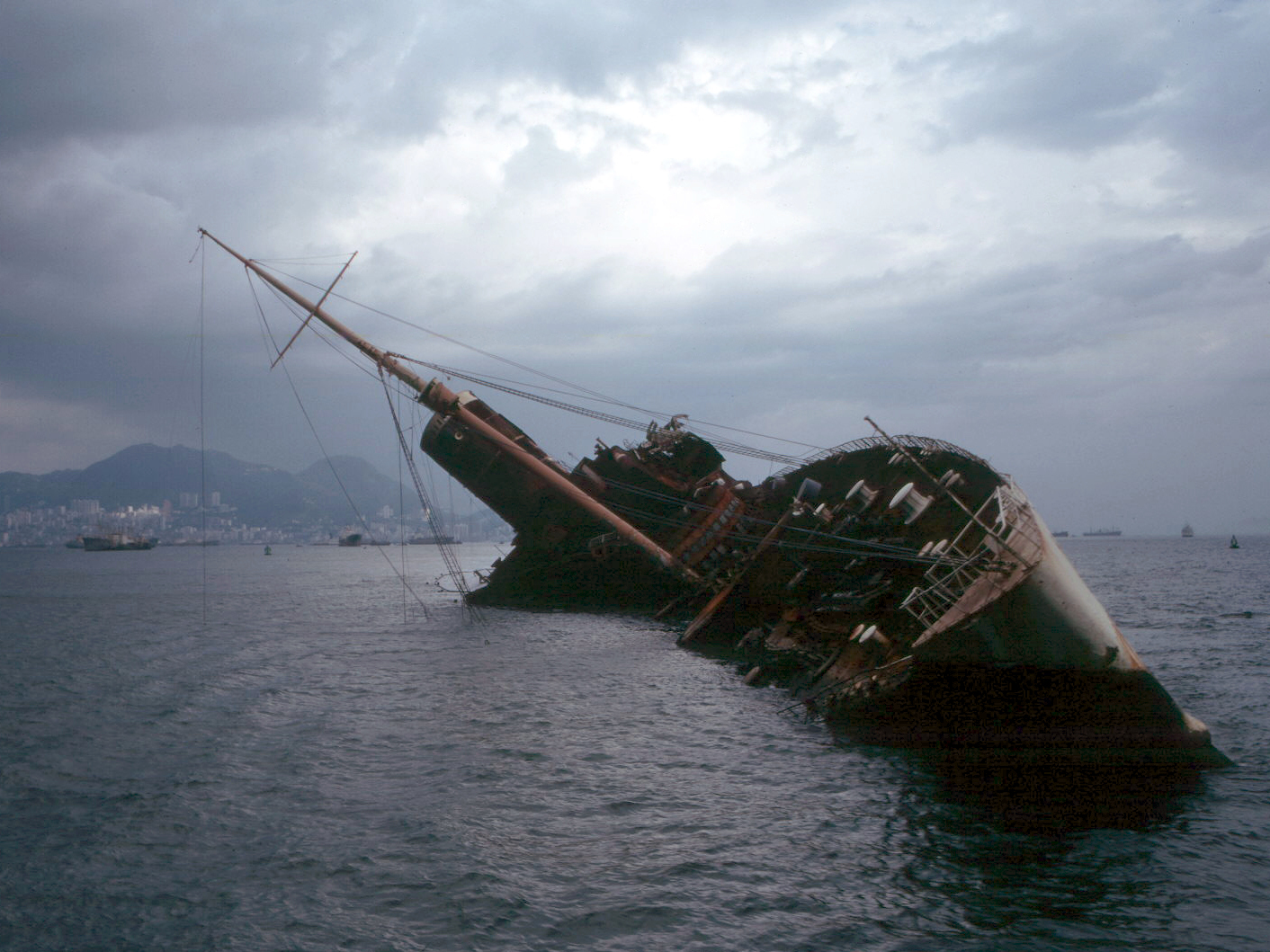
Marine Salvage
Marine salvage is the process of recovering a ship and its cargo after a shipwreck or other maritime casualty. Salvage may encompass towing, lifting a vessel, or effecting repairs to a ship. Salvors are normally paid for their efforts. However, protecting the coastal environment from oil spillages or other Contamination, contaminants from a modern ship can also be a motivator, as oil, cargo, and other pollutants can easily leak from a wreck and in these instances, governments or authorities may organise the salvage. Before the invention of radio, salvage services would be given to a stricken vessel by any passing ship. Today, most salvage is carried out by specialist salvage firms with dedicated crews and equipment. Law of salvage, The legal significance of salvage is that a successful salvorsalvor: A person or company involved in salvage activities. is entitled to a reward, which is a proportion of the total value of the ship and its cargo. The bounty is determined subsequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Impact
Ecology () is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere levels. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history. Ecology is a branch of biology, and is the study of abundance, biomass, and distribution of organisms in the context of the environment. It encompasses life processes, interactions, and adaptations; movement of materials and energy through living communities; successional development of ecosystems; cooperation, competition, and predation within and between species; and patterns of biodiversity and its effect on ecosystem processes. Ecology has practical applications in fields such as conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource management, and human ecology. The word ''ecology'' () was coined in 1866 by the German scientist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |