|
Undecanal
Undecanal, also known as undecyl aldehyde, is an organic compound with the chemical formula C10H21CHO. It is an eleven-carbon aldehyde. A colourless, oily liquid, undecanal is a component of perfumes. Although it occurs naturally in citrus oils, it is produced commercially by hydroformylation In organic chemistry, hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an industrial process for the production of aldehydes () from alkenes (). This chemical reaction entails the net addition of a formyl group () and a hydrogen ... of decene. It has been registered under the EU REACH scheme at >1000 tonnes by Oxea, which confirms the status as irritant. Undecanal is used in the synthesis of Disparlure.https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Organic_Chemistry/Logic_of_Organic_Synthesis_(Rao)/05%3A_Strategies_in_Disparlure_Synthesis References Fatty aldehydes Alkanals {{organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Aldehydes
Fatty aldehydes are Aliphatic compound, aliphatic, long-chain aldehydes which may be mono- or Polyunsaturated aldehyde, polyunsaturated. The fatty aldehydes include compounds such as octanal, nonanal, decanal or dodecanal. The nomenclature is derived from the nomenclature of the alkanes, the ending ''-al'' is added to indicate the aldehyde group. Occurrence Fatty aldehydes are a natural component of many Natural product, natural ingredients such as the essential oils of various citrus fruits. Decanal, for example, is a component of orange peel. The Pheromone, pheromone cocktails of various insect pheromones contain fatty aldehydes. Fat aldehydes were also detected in the heart muscle of mammals. Preparation Fatty aldehydes can be prepared by dehydrogenation of fatty alcohols on copper-zinc Catalysis, catalysts. By the hydroformylation of alkenes, fatty aldehydes are produced on a large industrial scale. Use A large proportion of the fatty aldehydes prepared by hydroformylat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes (e.g. methane ) and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen (e.g. cyanide ion , hydrogen cyanide , chloroformic acid , carbon dioxide , and carbonate ion ). Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, and even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Formula
A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and ''plus'' (+) and ''minus'' (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name since it does not contain any words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae. The simplest types of chemical formulae are called '' empirical formulae'', which use letters and numbers indicating the numerical ''proportions'' of atoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 electrons. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes up about 0.025 percent of Earth's crust. Three Isotopes of carbon, isotopes occur naturally, carbon-12, C and carbon-13, C being stable, while carbon-14, C is a radionuclide, decaying with a half-life of 5,700 years. Carbon is one of the timeline of chemical element discoveries#Pre-modern and early modern discoveries, few elements known since antiquity. Carbon is the 15th abundance of elements in Earth's crust, most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the abundance of the chemical elements, fourth most abundant element in the universe by mass after hydrogen, helium, and oxygen. Carbon's abundance, its unique diversity of organic compounds, and its unusual abi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () (lat. ''al''cohol ''dehyd''rogenatum, dehydrogenated alcohol) is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group. Aldehydes are a common motif in many chemicals important in technology and biology. Structure and bonding Aldehyde molecules have a central carbon atom that is connected by a double bond to oxygen, a single bond to hydrogen and another single bond to a third substituent, which is carbon or, in the case of formaldehyde, hydrogen. The central carbon is often described as being sp2- hybridized. The aldehyde group is somewhat polar. The bond length is about 120–122 picometers. Physical properties and characterization Aldehydes have properties that are diverse and that depend on the remainder of the molecule. Smaller aldehydes such as formaldehyde and acetaldehyde are solubl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroformylation
In organic chemistry, hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an industrial process for the production of aldehydes () from alkenes (). This chemical reaction entails the net addition of a formyl group () and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention: production capacity reached 6.6 tons in 1995. It is important because aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resultant aldehydes are hydrogenated to Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols that are converted to detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in speciality chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and pharmaceuticals. The development of hydroformylation is one of the premier achievements of 20th-century Chemical industry, industrial chemistry. The process entails treatment of an alkene typically with high pressures (between 10 and 100 Atmosphere (unit), atmospheres) of carbon monoxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decene
Decene is an organic compound with the chemical formula . Decene contains a chain of ten carbon atoms with one double bond, making it an alkene. There are many isomers of decene depending on the position and geometry of the double bond. Dec-1-ene is the only isomer of industrial importance. As an alpha olefin, it is used as a comonomer in copolymers and is an intermediate in the production of epoxides, amines, oxo alcohols, synthetic lubricants, synthetic fatty acids and alkylated aromatics. The industrial processes used in the production of dec-1-ene are oligomerization of ethylene by the Ziegler process or by the cracking of petrochemical waxes. In ethenolysis, methyl oleate, the ''methyl ester'' of oleic acid, converts to 1-decene and methyl 9- decenoate: ::\overset + \longrightarrow \overset + \overset Dec-1-ene has been isolated from the leaves and rhizome of the plant '' Farfugium japonicum'' and has been detected as the initial product in the microbial degradation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated population of over 449million as of 2024. The EU is often described as a ''sui generis'' political entity combining characteristics of both a federation and a confederation. Containing 5.5% of the world population in 2023, EU member states generated a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of around €17.935 trillion in 2024, accounting for approximately one sixth of global economic output. Its cornerstone, the European Union Customs Union, Customs Union, paved the way to establishing European Single Market, an internal single market based on standardised European Union law, legal framework and legislation that applies in all member states in those matters, and only those matters, where the states ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
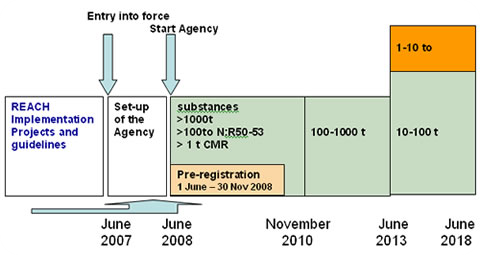
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation And Restriction Of Chemicals
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) is a European Union regulation dating from 18 December 2006, amended on 16 December 2008 by Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008. REACH addresses the production and use of chemical substances, and their potential impacts on both human health and the environment. Its 849 pages took seven years to pass, and it has been described as the most complex legislation in the Union's history and the most important in 20 years. It is the strictest law to date regulating chemical substances and will affect industries throughout the world. REACH entered into force on 1 June 2007, with a phased implementation over the next decade. The regulation also established the European Chemicals Agency, which manages the technical, scientific and administrative aspects of REACH. Overview When REACH is fully in force, it will require all companies manufacturing or importing chemical substances into the European Union in quantities of o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disparlure
Disparlure (chemical name ''cis''-7,8-epoxy-2-methyloctadecane) is a chemical compound with the formula C19H38O. It is a sex pheromone found in moths, such as the spongy moth (''Lymantria dispar''), and is used to attract a mate. Occurrences Disparlure is produced by female moths, such as the spongy and nun moths. It is a sex pheromone, a chemical that is released by the moths in order to attract a male mate. Disparlure has two enantiomers, referred to by (+) and (−). The (+)-enantiomer is typically used to attract the males by the females, while the (−)-enantiomer tends to have the opposite effect. The (−)-enantiomer inhibits attractions and turns the males away from females. Uses Disparlure, which is the synthetic form of the spongy moth sex pheromone, is used to detect its newly founded populations and estimate population density across the United States. The spongy moth is a very harmful pest for plants and affects forest, shade, and orchard trees across North America ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |