|
Ultrafast
In optics, an ultrashort pulse, also known as an ultrafast event, is an electromagnetic pulse whose time duration is of the order of a picosecond (10−12 second) or less. Such pulses have a broadband optical spectrum, and can be created by mode-locked oscillators. Amplification of ultrashort pulses almost always requires the technique of chirped pulse amplification, in order to avoid damage to the gain medium of the amplifier. They are characterized by a high peak intensity (or more correctly, irradiance) that usually leads to nonlinear interactions in various materials, including air. These processes are studied in the field of nonlinear optics. In the specialized literature, "ultrashort" refers to the femtosecond (fs) and picosecond (ps) range, although such pulses no longer hold the record for the shortest pulses artificially generated. Indeed, x-ray pulses with durations on the attosecond time scale have been reported. The 1999 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anne L'Huillier
Anne Geneviève L'Huillier (; born 16 August 1958) is a French physicist. She is a professor of atomic physics at Lund University in Sweden. She leads an attosecond physics group which studies the movements of electrons in real time, which is used to understand chemical reactions on the atomic level. Her experimental and theoretical research are credited with laying the foundation for the field of attochemistry. In 2003 she and her group beat the world record for the shortest laser pulse, of 170 attoseconds. L'Huillier became a member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences in 2004. She has received various physics awards including the Wolf Prize in Physics in 2022 and the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2023. Life Education Anne L'Huillier was born in Paris in 1958. She was awarded a double master's degree in theoretical physics and mathematics, but switched for her doctorate degree to experimental physics at Pierre and Marie Curie University. Her dissertation was on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrashort Pulse
In optics, an ultrashort pulse, also known as an ultrafast event, is an electromagnetic pulse whose time duration is of the order of a picosecond (10−12 second) or less. Such pulses have a broadband optical spectrum, and can be created by mode-locked oscillators. Amplification of ultrashort pulses almost always requires the technique of chirped pulse amplification, in order to avoid damage to the gain medium of the amplifier. They are characterized by a high peak intensity (or more correctly, irradiance) that usually leads to nonlinear interactions in various materials, including air. These processes are studied in the field of nonlinear optics. In the specialized literature, "ultrashort" refers to the femtosecond (fs) and picosecond (ps) range, although such pulses no longer hold the record for the shortest pulses artificially generated. Indeed, x-ray pulses with durations on the attosecond time scale have been reported. The 1999 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferenc Krausz
Ferenc Krausz (born 17 May 1962) is a Hungaro-Austrian physicist working in Attosecond physics, attosecond science. He is a director at the Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics and a professor of experimental physics at the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich in Germany. His research team has generated and measured the first attosecond pulse (physics), light pulse and used it for capturing electrons' motion inside atoms, marking the birth of attophysics. In 2023, jointly with Pierre Agostini and Anne L'Huillier, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics. Academic career From 1981 until 1985 Krausz studied theoretical physics at Eötvös Loránd University and electrical engineering at the Technical University of Budapest in Hungary. From 1987 to 1991 he graduated with a Doctor of Philosophy, PhD at the Technical University of Vienna, in Austria, and from 1991 to 1993 he also did his habilitation there. 1996–1998 he became associate professor, from 1999 until 2004 profess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mode-locking
Mode locking is a technique in optics by which a laser can be made to produce pulses of light of extremely short duration, on the order of picoseconds (10−12 s) or femtoseconds (10−15 s). A laser operated in this way is sometimes referred to as a femtosecond laser, for example, in modern refractive surgery. The basis of the technique is to induce a fixed phase relationship between the longitudinal modes of the laser's resonant cavity. Constructive interference between these modes can cause the laser light to be produced as a train of pulses. The laser is then said to be "phase-locked" or "mode-locked". Laser cavity modes Although laser light is perhaps the purest form of light, it is not of a single, pure frequency or wavelength. All lasers produce light over some natural bandwidth or range of frequencies. A laser's bandwidth of operation is determined primarily by the gain medium from which the laser is constructed, and the range of frequencies over which a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femtochemistry
Femtochemistry is the area of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions on extremely short timescales (approximately 10−15 seconds or one femtosecond, hence the name) in order to study the very act of atoms within molecules (reactants) rearranging themselves to form new molecules (products). In a 1988 issue of the journal ''Science'', Ahmed Hassan Zewail published an article using this term for the first time, stating "Real-time femtochemistry, that is, chemistry on the femtosecond timescale...". Later in 1999, Zewail received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his pioneering work in this field showing that it is possible to see how atoms in a molecule move during a chemical reaction with flashes of laser light. Application of femtochemistry in biological studies has also helped to elucidate the conformational dynamics of stem-loop RNA structures. Many publications have discussed the possibility of controlling chemical reactions by this method, but this remains co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemistry, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. When chemical reactions occur, the atoms are rearranged and the reaction is accompanied by an Gibbs free energy, energy change as new products are generated. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the Atomic nucleus, nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive Chemical element, elements where both electronic and nuclear changes can occur. The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reagent, reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more Product (c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractive Index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is the ratio of the apparent speed of light in the air or vacuum to the speed in the medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refraction, refracted, when entering a material. This is described by Snell's law of refraction, , where and are the angle of incidence (optics), angle of incidence and angle of refraction, respectively, of a ray crossing the interface between two media with refractive indices and . The refractive indices also determine the amount of light that is reflectivity, reflected when reaching the interface, as well as the critical angle for total internal reflection, their intensity (Fresnel equations) and Brewster's angle. The refractive index, n, can be seen as the factor by which the speed and the wavelength of the radiation are reduced with respect to their vacuum values: the speed of light in a medium is , and similarly the wavelength in that me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
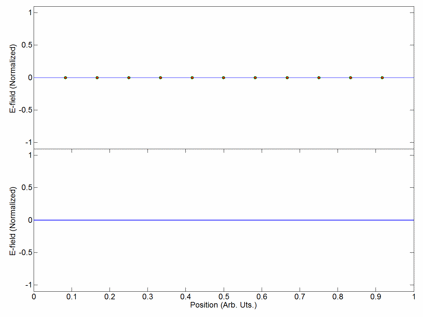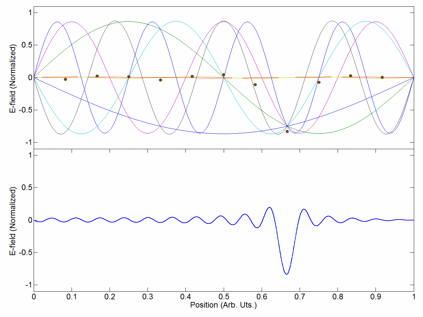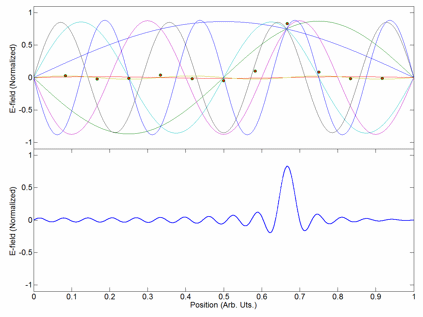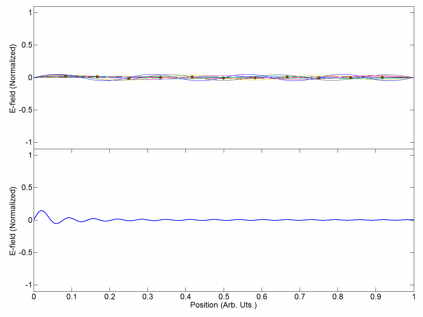
Wave Packet
In physics, a wave packet (also known as a wave train or wave group) is a short burst of localized wave action that travels as a unit, outlined by an Envelope (waves), envelope. A wave packet can be analyzed into, or can be synthesized from, a potentially-infinite set of component sinusoidal waves of different wavenumbers, with phases and amplitudes such that they interfere constructively only over a small region of space, and destructively elsewhere. Any signal of a limited width in time or space requires many frequency components around a center frequency within a Bandwidth (signal processing), bandwidth inversely proportional to that width; even a gaussian function is considered a wave packet because its Fourier transform is a "packet" of waves of frequencies clustered around a central frequency. Each component wave function, and hence the wave packet, are solutions of a wave equation. Depending on the wave equation, the wave packet's profile may remain constant (no #Non-dispe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wave
In physics, mathematics, engineering, and related fields, a wave is a propagating dynamic disturbance (change from List of types of equilibrium, equilibrium) of one or more quantities. ''Periodic waves'' oscillate repeatedly about an equilibrium (resting) value at some frequency. When the entire waveform moves in one direction, it is said to be a travelling wave; by contrast, a pair of superposition principle, superimposed periodic waves traveling in opposite directions makes a ''standing wave''. In a standing wave, the amplitude of vibration has nulls at some positions where the wave amplitude appears smaller or even zero. There are two types of waves that are most commonly studied in classical physics: mechanical waves and electromagnetic waves. In a mechanical wave, Stress (mechanics), stress and Strain (mechanics), strain fields oscillate about a mechanical equilibrium. A mechanical wave is a local deformation (physics), deformation (strain) in some physical medium that propa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of optical instruments, instruments that use or Photodetector, detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible light, visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation, and other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties. Most optical phenomena can be accounted for by using the Classical electromagnetism, classical electromagnetic description of light, however complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of Ray (optics), rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolute Value
In mathematics, the absolute value or modulus of a real number x, is the non-negative value without regard to its sign. Namely, , x, =x if x is a positive number, and , x, =-x if x is negative (in which case negating x makes -x positive), and For example, the absolute value of 3 and the absolute value of −3 is The absolute value of a number may be thought of as its distance from zero. Generalisations of the absolute value for real numbers occur in a wide variety of mathematical settings. For example, an absolute value is also defined for the complex numbers, the quaternions, ordered rings, fields and vector spaces. The absolute value is closely related to the notions of magnitude, distance, and norm in various mathematical and physical contexts. Terminology and notation In 1806, Jean-Robert Argand introduced the term ''module'', meaning ''unit of measure'' in French, specifically for the ''complex'' absolute value,Oxford English Dictionary, Draft Revision, Ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Envelope (waves)
In physics and engineering, the envelope of an oscillating signal is a smooth curve outlining its extremes. The envelope thus generalizes the concept of a constant amplitude into an instantaneous amplitude. The figure illustrates a modulated sine wave varying between an ''upper envelope'' and a ''lower envelope''. The envelope function may be a function of time, space, angle, or indeed of any variable. In beating waves A common situation resulting in an envelope function in both space ''x'' and time ''t'' is the superposition of two waves of almost the same wavelength and frequency: : \begin F(x, \ t) & = \sin \left[ 2 \pi \left( \frac - ( f + \Delta f )t \right) \right] + \sin \left[ 2 \pi \left( \frac - ( f - \Delta f )t \right) \right] \\[6pt] & \approx 2\cos \left[ 2 \pi \left( \frac - \Delta f \ t \right) \right] \ \sin \left[ 2 \pi \left( \frac - f \ t \right) \right] \end which uses the trigonometric formula for the Trigonometric identity#Product-to-sum an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |