|
Ulnare
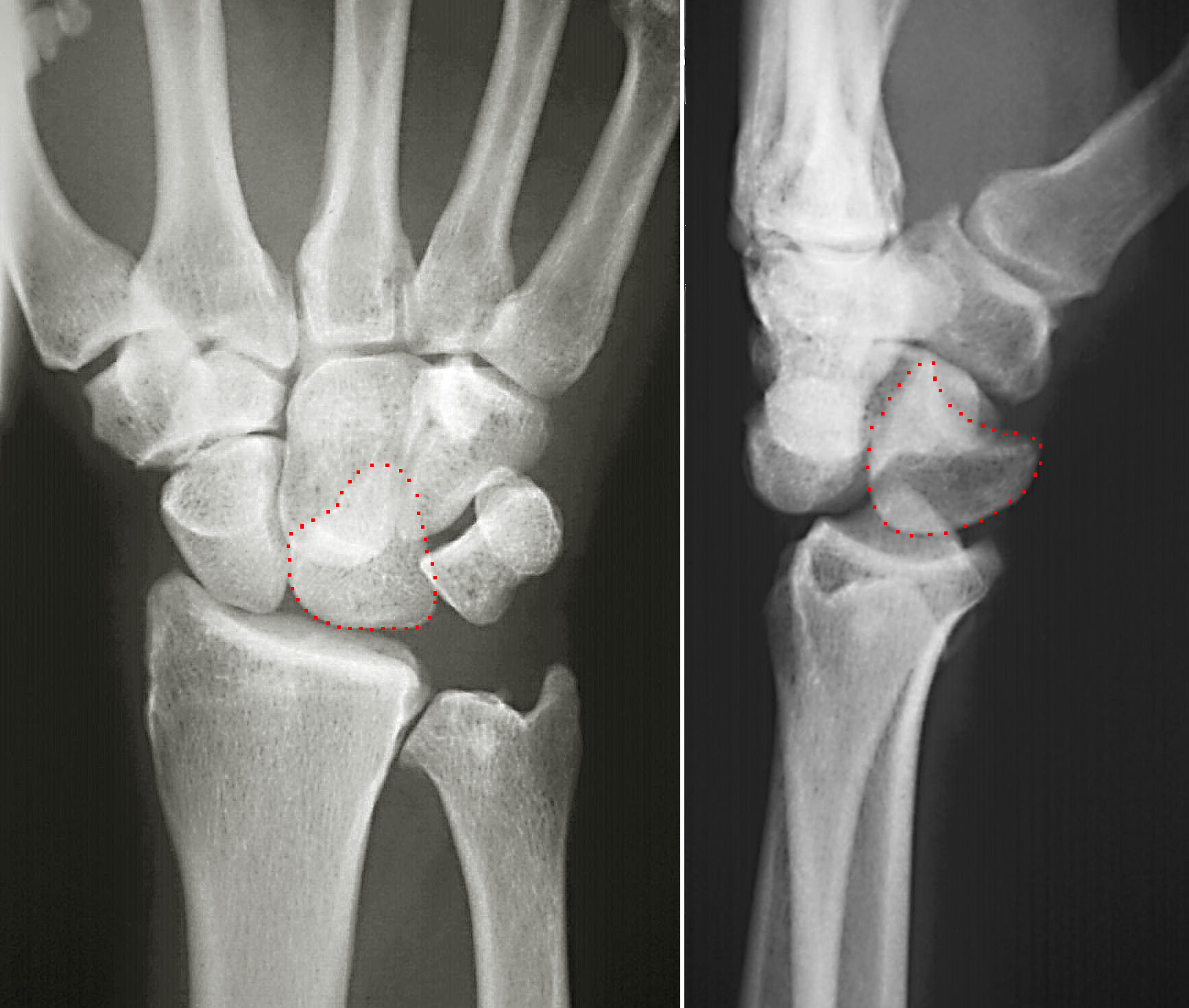
The triquetral bone (; also called triquetrum, pyramidal, three-faced, and formerly cuneiform bone) is located in the wrist on the medial side of the proximal row of the carpus between the lunate and pisiform bones. It is on the ulnar side of the hand, but does not directly articulate with the ulna. Instead, it is connected to and articulates with the ulna through the Triangular fibrocartilage discManaster, B. J., Julia Crim "Imaging Anatomy: Musculoskeletal E-Book" Elsevier Health Sciences, 2016, p. 326. and ligament, which forms part of the ulnocarpal joint capsule. It connects with the pisiform, hamate, and lunate bones. It is the 2nd most commonly fractured carpal bone. Structure The triquetral is one of the eight carpal bones of the hand. It is a three-faced bone found within the proximal row of carpal bones. Situated beneath the pisiform, it is one of the carpal bones that form the carpal arch, within which lies the carpal tunnel. The triquetral bone may be distinguished b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpal Bone
The carpal bones are the eight small bones that make up the wrist (carpus) that connects the hand to the forearm. The terms "carpus" and "carpal" are derived from the Latin carpus and the Greek καρπός (karpós), meaning "wrist". In human anatomy, the main role of the carpal bones is to articulate with the radial and ulnar heads to form a highly mobile condyloid joint (i.e. wrist joint),Kingston 2000, pp 126-127 to provide attachments for thenar and hypothenar muscles, and to form part of the rigid carpal tunnel which allows the median nerve and tendons of the anterior forearm muscles to be transmitted to the hand and fingers. In tetrapods, the carpus is the sole cluster of bones in the wrist between the radius and ulna and the metacarpus. The bones of the carpus do not belong to individual fingers (or toes in quadrupeds), whereas those of the metacarpus do. The corresponding part of the foot is the tarsus. The carpal bones allow the wrist to move and rotate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accessory Bone
An accessory bone or supernumerary bone is a bone that is not normally present in the body, but can be found as a anatomical variation, variant in a significant number of people. It poses a risk of being misdiagnosis, misdiagnosed as bone fractures on radiography. Wrist and hand Os ulnostyloideum The ''os ulnostyloideum'' is an ulnar styloid process that is not fused to the rest of the ulna bone.R. O'Rahilly. ''A survey of carpal and tarsal anomalies.'' J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1953; 35: 626–642 On X-rays, an ''os ulnostyloideum'' is sometimes mistaken for an avulsion fracture of the styloid process. However, the distinction between these is extremely difficult.T.E. Keats, M.W. Anderson. ''Atlas of normal roentgen variants that may simulate disease''. 7th edition, Mosby Inc. 2001 It is alleged that the os ulnostyloideum has a close relationship with or is synonymous with the os triquetrum secundarium. Os centrale The ''os carpi centrale'' (also briefly ''os centrale'') i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpal Bones
The carpal bones are the eight small bones that make up the wrist (carpus) that connects the hand to the forearm. The terms "carpus" and "carpal" are derived from the Latin wikt:carpus#Latin, carpus and the Greek language, Greek wikt:καρπός#Ancient Greek, καρπός (karpós), meaning "wrist". In human anatomy, the main role of the carpal bones is to joint, articulate with the radius (bone), radial and ulnar heads to form a highly mobile condyloid joint (i.e. wrist joint),Kingston 2000, pp 126-127 to provide attachments for thenar and hypothenar muscles, and to form part of the rigid carpal tunnel which allows the median nerve and tendons of the anterior compartment of the forearm, anterior forearm muscles to be transmitted to the hand and fingers. In tetrapods, the carpus is the sole cluster of bones in the wrist between the radius (bone), radius and ulna and the metacarpus. The bones of the carpus do not belong to individual fingers (or toes in quadrupeds), whereas those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpal Tunnel
In the human body, the carpal tunnel or carpal canal is a flattened body cavity on the flexor ( palmar/volar) side of the wrist, bounded by the carpal bones and flexor retinaculum. It forms the passageway that transmits the median nerve and the tendons of the extrinsic flexor muscles of the hand from the forearm to the hand. The median artery is an anatomical variant (increasingly found). When present it lies between the radial artery, and the ulnar artery and runs with the median nerve supplying the same structures innervated. When swelling or degeneration occurs in the tendons and sheaths of any of the nine flexor muscles ( flexor pollicis longus, four flexor digitorum profundus and four flexor digitorum superficialis) passing through the carpal tunnel, the canal can narrow and compress/entrap the median nerve, resulting in a compression neuropathy known as carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). If untreated, neuropraxia, parasthesia and muscle atrophy (especially of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carpal bones." (2) the wrist joint or radiocarpal joint, the joint between the radius and the carpus and; (3) the anatomical region surrounding the carpus including the distal parts of the bones of the forearm and the proximal parts of the metacarpus or five metacarpal bones and the series of joints between these bones, thus referred to as ''wrist joints''. "With the large number of bones composing the wrist (ulna, radius, eight carpas, and five metacarpals), it makes sense that there are many, many joints that make up the structure known as the wrist." This region also includes the carpal tunnel, the anatomical snuff box, bracelet lines, the flexor retinaculum, and the extensor retinaculum. As a consequence of these various definitions, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeletal System
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of most animals. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is a rigid outer shell that holds up an organism's shape; the endoskeleton, a rigid internal frame to which the organs and soft tissues attach; and the hydroskeleton, a flexible internal structure supported by the hydrostatic pressure of body fluids. Vertebrates are animals with an endoskeleton centered around an axial vertebral column, and their skeletons are typically composed of bones and cartilages. Invertebrates are other animals that lack a vertebral column, and their skeletons vary, including hard-shelled exoskeleton (arthropods and most molluscs), plated internal shells (e.g. cuttlebones in some cephalopods) or rods (e.g. ossicles in echinoderms), hydrostatically supported body cavities (most), and spicules (sponges). Cartilage is a rigid connective tissue that is found in the skeletal systems of vertebrates and invert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pisiform Bone
The pisiform bone ( or ), also spelled pisiforme (from the Latin ''pisiformis'', pea-shaped), is a small knobbly, sesamoid bone that is found in the wrist. It forms the ulnar border of the carpal tunnel. Structure The pisiform is a sesamoid bone, with no covering membrane of periosteum. It is the last carpal bone to ossify. The pisiform bone is a small bone found in the proximal row of the wrist ( carpus). It is situated where the ulna joins the wrist, within the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle. It only has one side that acts as a joint, articulating with the triquetral bone. It is on a plane anterior to the other carpal bones and is spheroidal in form. The pisiform bone has four surfaces: # The ''dorsal surface'' is smooth and oval, and articulates with the triquetral: this facet approaches the superior, but not the inferior border of the bone. # The ''palmar surface'' is rounded and rough, and gives attachment to the transverse carpal ligament, the flexor carpi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral (anatomy)
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether a vertebrate is a biped or a quadruped, due to the difference in the neuraxis, or if an invertebrate is a non-bilaterian. A non-bilaterian has no anterior or posterior surface for example but can still have a descriptor used such as proximal or distal in relation to a body part that is nearest to, or furthest from its middle. International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standards for subdisciplines of anatomy. For example, '' Terminolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsum (anatomy)
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether a vertebrate is a biped or a quadruped, due to the difference in the neuraxis, or if an invertebrate is a non-bilaterian. A non-bilaterian has no anterior or posterior surface for example but can still have a descriptor used such as proximal or distal in relation to a body part that is nearest to, or furthest from its middle. International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standards for subdisciplines of anatomy. For example, '' Termi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
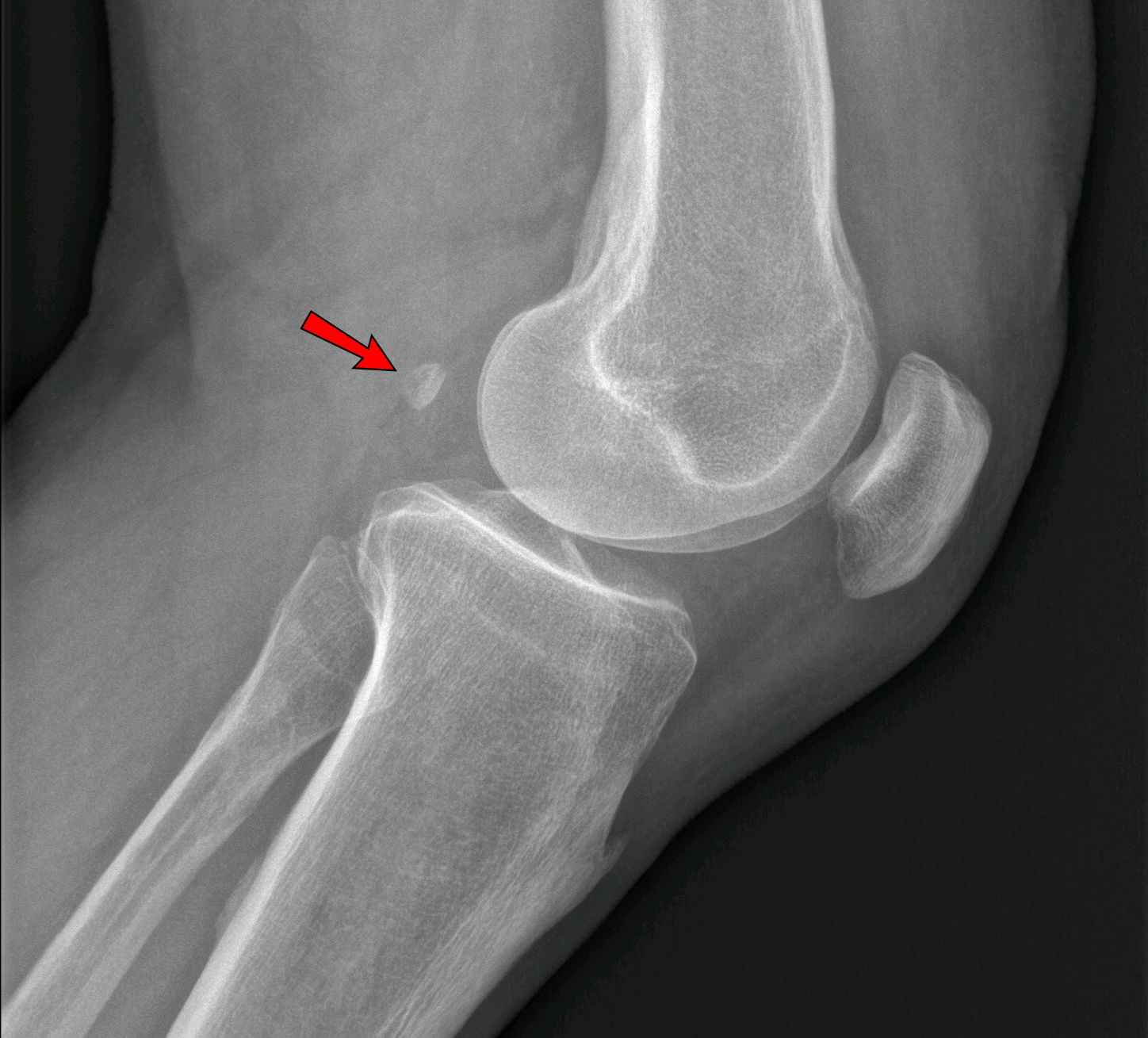
Avulsion Fracture
An avulsion fracture is a bone fracture which occurs when a fragment of bone tears away from the main mass of bone as a result of physical trauma. This can occur at the ligament by the application of forces external to the body (such as a fall or pull) or at the tendon by a muscular contraction that is stronger than the forces holding the bone together. Generally muscular avulsion is prevented by the neurological limitations placed on muscle contractions. Highly trained Athlete, athletes can overcome this neurological inhibition of strength and produce a much greater force output capable of breaking or avulsing a bone. Types Dental avulsion dental trauma, Traumatic complete displacement of a tooth from its socket in alveolar bone. It is a serious dental emergency in which Treatment of knocked-out (avulsed) teeth, prompt management (within 20–40 minutes of injury) affects the prognosis of the tooth. Tuberosity avulsion of the 5th metatarsal file:Proximal fractures of 5th me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunate Bone
The lunate bone (semilunar bone) is a carpal bone in the human hand. It is distinguished by its deep concavity and crescentic outline. It is situated in the center of the proximal row carpal bones, which lie between the ulna and radius and the hand. The lunate carpal bone is situated between the lateral scaphoid bone and medial triquetral bone. Structure The lunate is a crescent-shaped carpal bone found within the hand. The lunate is found within the proximal row of carpal bones. Proximally, it abuts the radius. Laterally, it articulates with the scaphoid bone, medially with the triquetral bone, and distally with the capitate bone. The lunate also articulates on its distal and medial surface with the hamate bone. The lunate is stabilised by a medial ligament to the scaphoid bone and a lateral ligament to the triquetral bone. Ligaments between the radius and carpal bone also stabilise the position of the lunate, as does its position in the lunate fossa of the radius. Bone Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hand
A hand is a prehensile, multi-fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the Koala#Characteristics, koala (which has two thumb#Opposition and apposition, opposable thumbs on each "hand" and fingerprints extremely similar to human fingerprints) are often described as having "hands" instead of paws on their front limbs. The raccoon is usually described as having "hands" though opposable thumbs are lacking. Some evolutionary anatomists use the term ''hand'' to refer to the appendage of digits on the forelimb more generally—for example, in the context of whether the three Digit (anatomy), digits of the bird hand involved the same Homology (biology), homologous loss of two digits as in the dinosaur hand. The human hand usually has five digits: Finger numbering#Four-finger system, four fingers plus one thumb; however, these are often referred to collectively as Finger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |