|
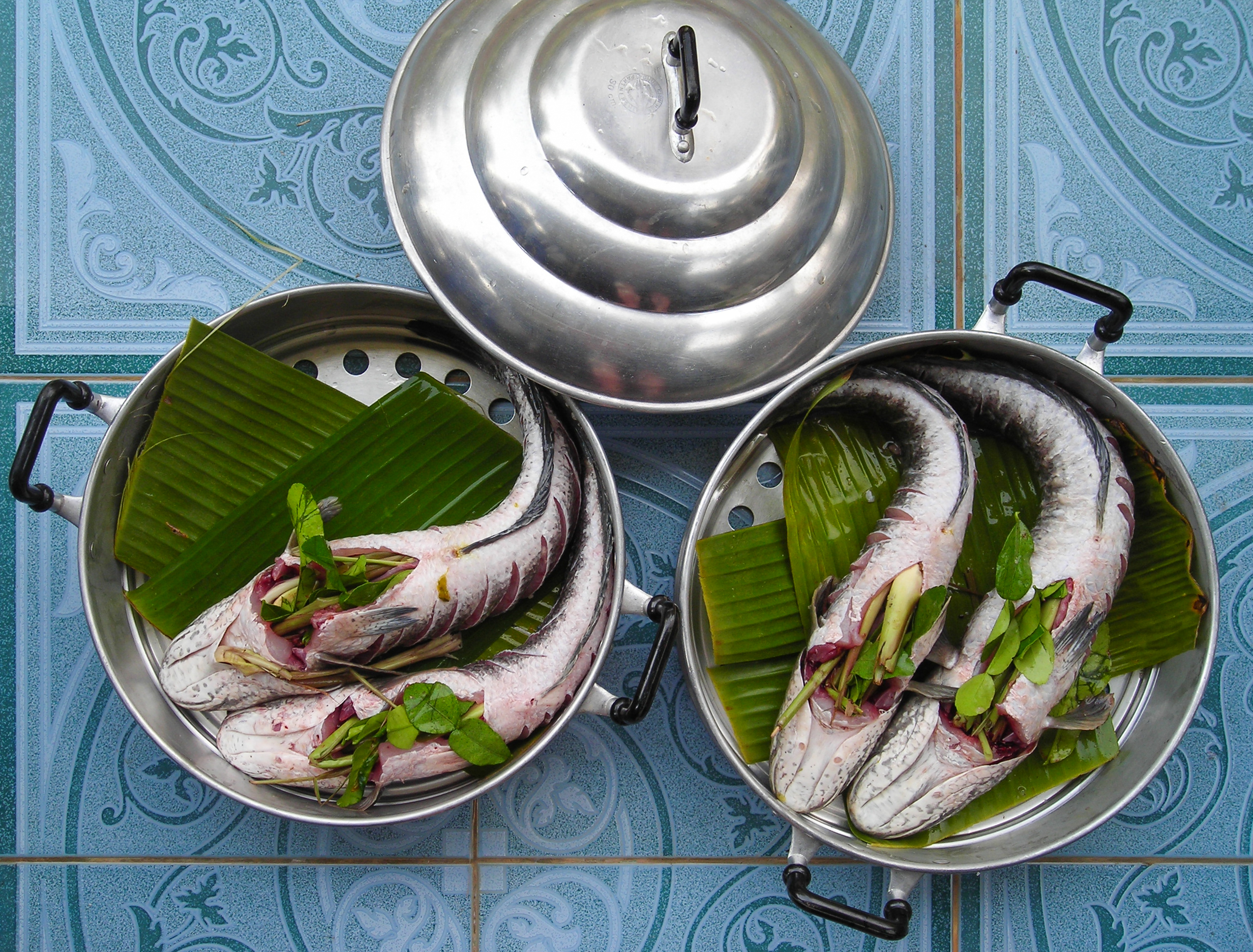
Ukha
Ukha ( ) is a clear Russian soup, made from various types of fish such as bream, wels catfish, northern pike, or even ruffe. It usually contains root vegetables, parsley root, leek, potato, bay leaf, dill, tarragon, and green parsley, and is spiced with black pepper, saffron, nutmeg, and fennel seed. Fish such as perch, tench, sheatfish, and burbot are sometimes used to add flavour to the soup. The roots of the soup originated in the culture of the Russian Cossack steppe riders and the soup is mostly associated in Russia with the Don region. While ukha is a fish dish that is made with broth, calling it a fish soup may not be absolutely correct. "Ukha" started to be used as a term for fish broth in Russian cuisine in the late 17th to early 18th centuries. In earlier times, this term referred to thick meat broths, and then later chicken. Beginning in the 15th century, fish was more and more often used to prepare ukha, thus creating a dish that had a distinctive ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Cuisine
Russian cuisine is a collection of the different dishes and cooking traditions of the Russians, Russian people as well as a list of culinary products popular in Russia, with most names being known since pre-Soviet times, coming from all kinds of social circles. History The history of Russian cuisine was divided in four groups: Old Russian cuisine (9th to 16th century), Old Moscow cuisine (17th century), the cuisine that existed during the ruling of Peter the Great, Peter and Catherine the Great (18th century), and finally Petersburg cuisine, which took place from the end of the 18th century to the 1860s. In the Old Russian period, the main food groups were bread, grains, and other foods that contained starch. Women baked pies with many different fillings, such as mushrooms or berries. During gatherings, a loaf of bread and salt was always present. Kasha, such as buckwheat and oats, were represented as wellbeing to the household. Many Russians used honey and berries and mad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish (food)
Many species of fish are caught by humans and consumed as food in virtually all regions around the world. Their meat has been an important dietary source of protein and other nutrients in the human diet. The English language does not have a special culinary name for food prepared from fish like with other animals (as with '' pig'' vs. ''pork''), or as in other languages (such as Spanish '' pez'' vs. '' pescado''). In culinary and fishery contexts, ''fish'' may include so-called shellfish such as molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms; but, more expansively, ''seafood'' covers both fish and other marine life used as food. Since 1961, the average annual increase in global apparent food fish consumption (3.2 percent) has outpaced population growth (1.6 percent) and exceeded the increase in consumption of meat from all terrestrial animals except poultry (4.9 percent), both combined (2.8 percent) and individually (bovine, ovine, porcine, et cetera). In ''per capita'' terms, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soup
Soup is a primarily liquid food, generally served warm or hot – though it is sometimes served chilled – made by cooking or otherwise combining meat or vegetables with Stock (food), stock, milk, or water. According to ''The Oxford Companion to Food'' (OCF), "soup" is "the most general of the terms which apply to liquid savoury dishes";Davidson, p. 735 others include broth, bisque (food), bisque, consommé, potage and many more. Although most soups are savoury, sweet soups are familiar in some parts of Europe. Soups have been made since prehistoric times, and have evolved over the centuries. Originally "sops" referred to pieces of bread covered with savoury liquid; gradually the term "soup" was transferred to the liquid itself. Soups are common to the cuisines of eastern and western countries and have been served at the grandest of banquets as well as in the humblest peasant homes. Name The term soup, or words like it, can be found in many languages. Similar terms in othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pirozhki
Pirozhki (, ; , ) are Russian baked or fried yeast-leavened boat-shaped buns with a variety of fillings. Pirozhki are a popular street food and comfort food. They are also popular in other countries. The word ''pirozhki'' is a diminutive of '' pirog'', the Russian name for pie. Terminology The stress in is on the last syllable: . ( rus, пирожо́к, r=pirožók, p=pʲɪrɐˈʐok, a=Ru-пирожок.ogg, singular) is the diminutive form of Russian '' pirog'', which means a full-sized pie. The word is derived from ''pir'', meaning "feast". Pirozhki are not to be confused with the Polish pierogi (a cognate term), which are called or ''pyrohy'' in Ukrainian and Doukhoborese, and ''vareniki'' in Russian. Variations A typical pirozhok is boat- or rarely crescent-shaped, made of yeast-leavened dough, with filling completely enclosed. Similar Russian pastries ( pirogs) of other shapes include coulibiac, kalitka, rasstegai, and vatrushka. Pirozhki are usually hand-siz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belarusian Cuisine
Belarusian cuisine refers to the culinary traditions native to Belarus and Belarusians, its people. It shares many similarities with the cuisines of other Central and Eastern European countries, particularly those of Polish cuisine, Poland, Russian cuisine, Russia, and Ukrainian cuisine, Ukraine. It is based predominantly on meat and various vegetables typical of the region. History Belarusian cuisine has predominantly Slavs, Slavic roots. Along with a Ruthenians, Ruthenian influence, it is also linked with Lithuanian cuisine, Lithuanian and Polish cuisine, Polish because of the long intermingling of these three peoples; first within the Grand Duchy of Lithuania (11th–16th centuries) and later within the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (16th–17th centuries). Still, some of the borrowed dishes spread throughout the society, such as lazanki (, a mixture of flour dumplings and stewed meat, related to Italian lasagna) and, above all, various dishes made of grated potatoes, typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broth
Broth, also known as bouillon (), is a savory liquid made of water in which meat, fish, or vegetables have been simmered for a short period of time. It can be eaten alone, but it is most commonly used to prepare other dishes, such as soups, gravies, and sauces. Commercially prepared liquid broths are available, typically chicken, beef, fish, and vegetable varieties. Dehydrated broth in the form of bouillon cubes was commercialized beginning in the early 20th century. Stock versus broth Many cooks and food writers use the terms ''broth'' and ''stock'' interchangeably. In 1974, James Beard (an American cook) wrote that stock, broth, and bouillon "are all the same thing". While many draw a distinction between stock and broth, the details of the distinction often differ. One possibility is that stocks are made primarily from animal bones, as opposed to meat, and therefore contain more gelatin, giving them a thicker texture. Another distinction that is sometimes made i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Don River (Russia)
The Don () is the fifth-longest river in Europe. Flowing from Central Russia to the Sea of Azov in Southern Russia, it is one of Russia's largest rivers and played an important role for traders from the Byzantine Empire. Its basin is between the Dnieper basin to the west, the lower Volga basin immediately to the east, and the Oka basin (tributary of the Volga) to the north. Native to much of the basin were Slavic nomads. The Don rises in the town of Novomoskovsk southeast of Tula (in turn south of Moscow), and flows 1,870 kilometres to the Sea of Azov. The river's upper half meanders subtly south; however, its lower half consists of a great eastern curve, including Voronezh, making its final stretch, an estuary, run west south-west. The main city on the river is Rostov-on-Don. Its main tributary is the Seversky Donets, centred on the mid-eastern end of Ukraine, thus the other country in the overall basin. To the east of a series of three great ship locks and as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cossack
The Cossacks are a predominantly East Slavic Eastern Christian people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe of eastern Ukraine and southern Russia. Cossacks played an important role in defending the southern borders of Ukraine and Russia, countering the Crimean-Nogai raids, alongside economically developing steppe regions north of the Black Sea and around the Azov Sea. Historically, they were a semi-nomadic and semi-militarized people, who, while under the nominal suzerainty of various Eastern European states at the time, were allowed a great degree of self-governance in exchange for military service. Although numerous linguistic and religious groups came together to form the Cossacks, most of them coalesced and became East Slavic–speaking Orthodox Christians. The rulers of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russian Empire endowed Cossacks with certain special privileges in return for the military duty to serve in the irregular troops: Zaporozhian Cossac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
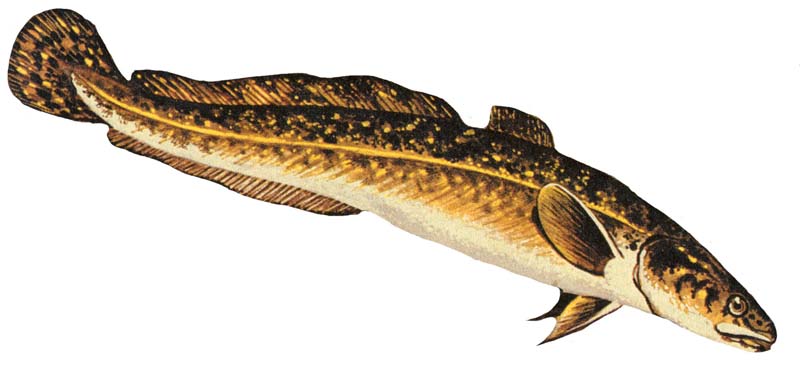
Burbot
The burbot (''Lota lota''), also known as bubbot, mariah, loche, cusk, freshwater cod, freshwater ling, freshwater cusk, the lawyer, coney-fish, lingcod, or eelpout, is a species of coldwater ray-finned fish native to the subarctic regions of the Northern hemisphere. It is the only member of the genus ''Lota'', and is the only freshwater species of the order Gadiformes. The species is closely related to marine fish such as the common ling and cusk, all of which belong to the family Lotidae (rocklings). Etymology The name burbot comes from the Latin word ''barba'', meaning beard, referring to its single chin whisker, or barbel. Its generic and specific names, ''Lota lota'', comes from the old French ''lotte'' fish, which is also named "barbot" in Old French. Description With an appearance like a cross between a catfish and an eel, the burbot has a serpent-like body, but is easily distinguished by a single barbel on the chin. The body is elongated and laterally compress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
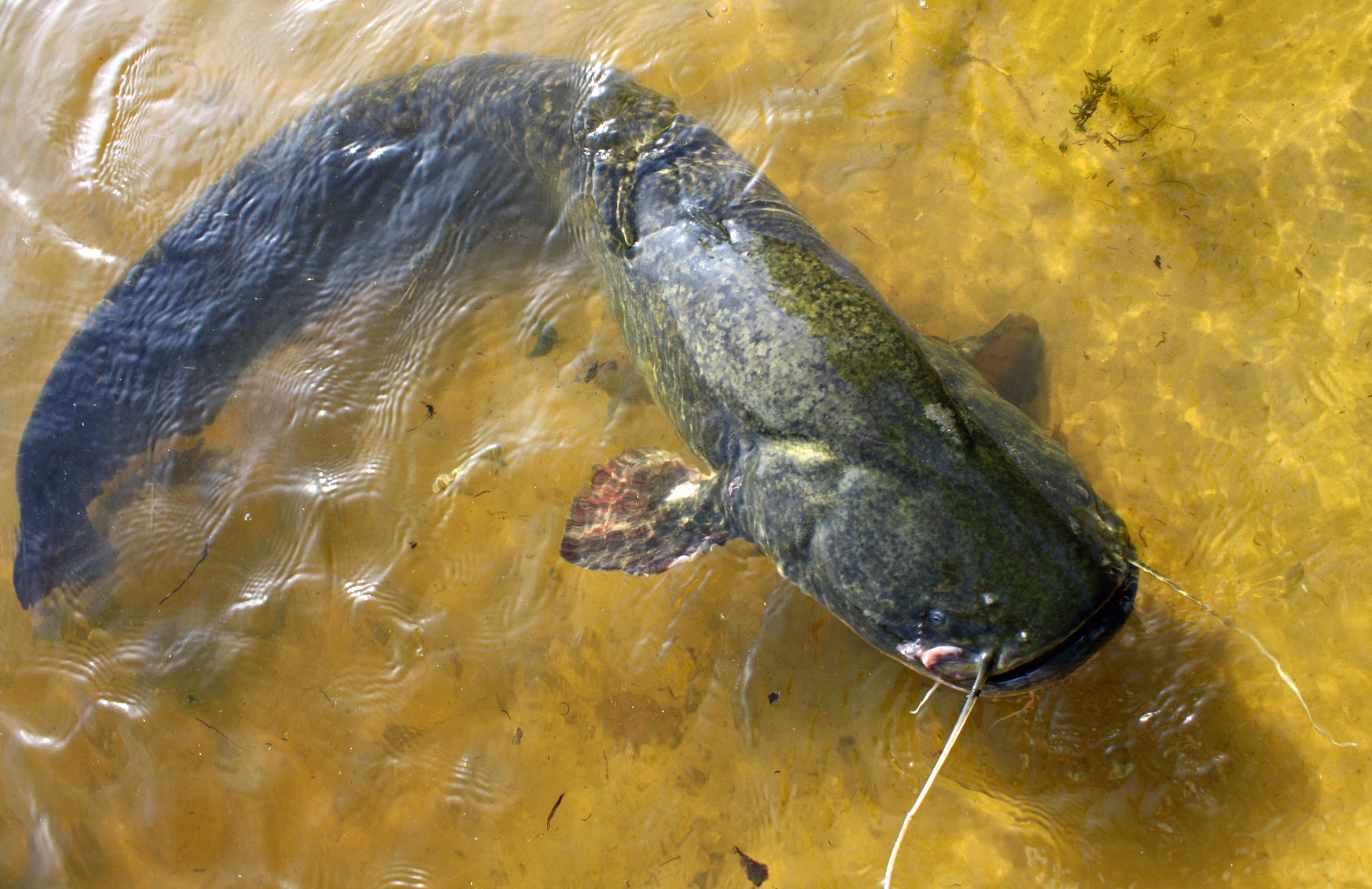
Wels Catfish
The wels catfish ( or ; ''Silurus glanis''), also called sheatfish or just wels, is a large species of catfish native to wide areas of central, southern, and eastern Europe, in the basins of the Baltic, Black and Caspian Seas. It has been introduced to Western Europe as a prized sport fish and is now found from the United Kingdom east to Kazakhstan and China and south to Greece and Turkey. Etymology The English common name comes from Wels, the common name of the species in German language. ''Wels'' is a variation of Old High German ''wal'', from Proto-Germanic ''*hwalaz'' – the same source as for ''whale'' – from Proto-Indo-European ''*(s)kʷálos'' ('sheatfish'). Evolution The earliest known fossil remains of the wels catfish are from the late Miocene (about 5.3 million years ago) of Ukraine. Potentially slightly older but less well-preserved remains from 6-7 million years ago are also known from the same region. During this time period, the dominant catfish in eastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tench
The tench or doctor fish (''Tinca tinca'') is a freshwater, fresh- and brackish water, brackish-water fish of the order Cypriniformes found throughout Eurasia from Western Europe including Great Britain, Britain and Ireland east into Asia as far as the Ob River, Ob and Yenisei Rivers. It is also found in Lake Baikal. It normally inhabits slow-moving freshwater habitats, particularly lakes and lowland rivers.B. Whitton (1982). ''Rivers, Lakes and Marshes'' p 163. Hodder & Staughton, London. Taxonomy The tench was first formally Species description, described in as ''Cyprinus tinca'' by Carl Linnaeus in 1758 in the 10th edition of Systema Naturae with its Type locality (biology), type locality given as "European lakes". In 1764 François Alexandre Pierre de Garsault proposed the new monospecific genus ''Tinca'', with ''Cyprinus tinca'' as the type species by absolute tautonymy. The 5th edition of ''Fishes of the World'' classified ''Tinca'' in the subfamily Tincinae, alongside th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |