|
Two-way Analysis Of Variance
In statistics, the two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) is an extension of the one-way ANOVA that examines the influence of two different categorical independent variables on one continuous dependent variable. The two-way ANOVA not only aims at assessing the main effect of each independent variable but also if there is any interaction between them. History In 1925, Ronald Fisher mentions the two-way ANOVA in his celebrated book, ''Statistical Methods for Research Workers'' (chapters 7 and 8). In 1934, Frank Yates published procedures for the unbalanced case. Since then, an extensive literature has been produced. The topic was reviewed in 1993 by Yasunori Fujikoshi. In 2005, Andrew Gelman proposed a different approach of ANOVA, viewed as a multilevel model. Data set Let us imagine a data set for which a dependent variable may be influenced by two factors which are potential sources of variation. The first factor has I levels and the second has J levels . Each combination (i,j) d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistics
Statistics (from German: '' Statistik'', "description of a state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments.Dodge, Y. (2006) ''The Oxford Dictionary of Statistical Terms'', Oxford University Press. When census data cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey samples. Representative sampling assures that inferences and conclusions can reasonably extend from the sample to the population as a whole. An ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Design
The design of experiments (DOE, DOX, or experimental design) is the design of any task that aims to describe and explain the variation of information under conditions that are hypothesized to reflect the variation. The term is generally associated with experiments in which the design introduces conditions that directly affect the variation, but may also refer to the design of quasi-experiments, in which natural conditions that influence the variation are selected for observation. In its simplest form, an experiment aims at predicting the outcome by introducing a change of the preconditions, which is represented by one or more independent variables, also referred to as "input variables" or "predictor variables." The change in one or more independent variables is generally hypothesized to result in a change in one or more dependent variables, also referred to as "output variables" or "response variables." The experimental design may also identify control variables that must ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press in the world. It is also the King's Printer. Cambridge University Press is a department of the University of Cambridge and is both an academic and educational publisher. It became part of Cambridge University Press & Assessment, following a merger with Cambridge Assessment in 2021. With a global sales presence, publishing hubs, and offices in more than 40 Country, countries, it publishes over 50,000 titles by authors from over 100 countries. Its publishing includes more than 380 academic journals, monographs, reference works, school and university textbooks, and English language teaching and learning publications. It also publishes Bibles, runs a bookshop in Cambridge, sells through Amazon, and has a conference venues business in Cambridge at the Pitt Building and the Sir Geoffrey Cass Spo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Linear Model
The general linear model or general multivariate regression model is a compact way of simultaneously writing several multiple linear regression models. In that sense it is not a separate statistical linear model. The various multiple linear regression models may be compactly written as : \mathbf = \mathbf\mathbf + \mathbf, where Y is a matrix with series of multivariate measurements (each column being a set of measurements on one of the dependent variables), X is a matrix of observations on independent variables that might be a design matrix (each column being a set of observations on one of the independent variables), B is a matrix containing parameters that are usually to be estimated and U is a matrix containing errors (noise). The errors are usually assumed to be uncorrelated across measurements, and follow a multivariate normal distribution. If the errors do not follow a multivariate normal distribution, generalized linear models may be used to relax assumptions about Y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jennifer Hill
Jennifer Lynn Hill (born 1969) is an American statistician specializing in causal inference with applications to social statistics. She is a professor of applied statistics at New York University in the Steinhardt School of Culture, Education, and Human Development. Education and career Hill majored in economics at Swarthmore College, graduating in 1991. She earned a master's degree in statistics at Rutgers University in 1995, and completed a Ph.D. in statistics at Harvard University in 2000. Her dissertation, ''Applications of Innovative Statistical Methodology for the Social Sciences'', was jointly supervised by political scientist Gary King and statistician Donald Rubin. She became an assistant professor in the Columbia University School of International and Public Affairs The School of International and Public Affairs at Columbia University (SIPA) is the international affairs and public policy school of Columbia University, a private Ivy League university located in M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Errors And Residuals In Statistics
In statistics and optimization, errors and residuals are two closely related and easily confused measures of the deviation of an observed value of an element of a statistical sample from its " true value" (not necessarily observable). The error of an observation is the deviation of the observed value from the true value of a quantity of interest (for example, a population mean). The residual is the difference between the observed value and the '' estimated'' value of the quantity of interest (for example, a sample mean). The distinction is most important in regression analysis, where the concepts are sometimes called the regression errors and regression residuals and where they lead to the concept of studentized residuals. In econometrics, "errors" are also called disturbances. Introduction Suppose there is a series of observations from a univariate distribution and we want to estimate the mean of that distribution (the so-called location model). In this case, the errors ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Noise
In statistics, the fraction of variance unexplained (FVU) in the context of a regression task is the fraction of variance of the regressand (dependent variable) ''Y'' which cannot be explained, i.e., which is not correctly predicted, by the explanatory variables ''X''. Formal definition Suppose we are given a regression function f yielding for each y_i an estimate \widehat_i = f(x_i) where x_i is the vector of the ''i''th observations on all the explanatory variables. We define the fraction of variance unexplained (FVU) as: :\begin \text & = = = \left( = 1- , \text\right) \\ pt & = 1 - R^2 \end where ''R''2 is the coefficient of determination and ''VAR''err and ''VAR''tot are the variance of the residuals and the sample variance of the dependent variable. ''SS''''err'' (the sum of squared predictions errors, equivalently the residual sum of squares), ''SS''''tot'' (the total sum of squares), and ''SS''''reg'' (the sum of squares of the regression, equivalently the explai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
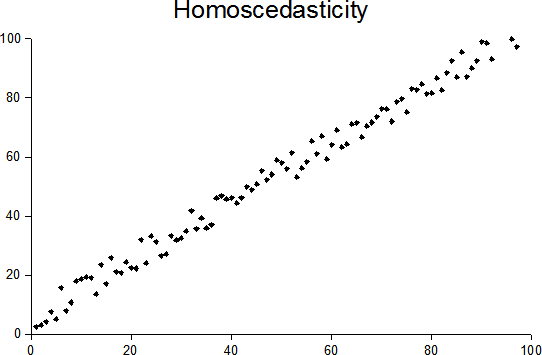
Homoscedasticity
In statistics, a sequence (or a vector) of random variables is homoscedastic () if all its random variables have the same finite variance. This is also known as homogeneity of variance. The complementary notion is called heteroscedasticity. The spellings ''homoskedasticity'' and ''heteroskedasticity'' are also frequently used. Assuming a variable is homoscedastic when in reality it is heteroscedastic () results in unbiased but inefficient point estimates and in biased estimates of standard errors, and may result in overestimating the goodness of fit as measured by the Pearson coefficient. The existence of heteroscedasticity is a major concern in regression analysis and the analysis of variance, as it invalidates statistical tests of significance that assume that the modelling errors all have the same variance. While the ordinary least squares estimator is still unbiased in the presence of heteroscedasticity, it is inefficient and generalized least squares should be used i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Distribution
In statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is : f(x) = \frac e^ The parameter \mu is the mean or expectation of the distribution (and also its median and mode), while the parameter \sigma is its standard deviation. The variance of the distribution is \sigma^2. A random variable with a Gaussian distribution is said to be normally distributed, and is called a normal deviate. Normal distributions are important in statistics and are often used in the natural and social sciences to represent real-valued random variables whose distributions are not known. Their importance is partly due to the central limit theorem. It states that, under some conditions, the average of many samples (observations) of a random variable with finite mean and variance is itself a random variable—whose distribution converges to a normal dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Independence (probability Theory)
Independence is a fundamental notion in probability theory, as in statistics and the theory of stochastic processes. Two events are independent, statistically independent, or stochastically independent if, informally speaking, the occurrence of one does not affect the probability of occurrence of the other or, equivalently, does not affect the odds. Similarly, two random variables are independent if the realization of one does not affect the probability distribution of the other. When dealing with collections of more than two events, two notions of independence need to be distinguished. The events are called pairwise independent if any two events in the collection are independent of each other, while mutual independence (or collective independence) of events means, informally speaking, that each event is independent of any combination of other events in the collection. A similar notion exists for collections of random variables. Mutual independence implies pairwise independe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Variable
A random variable (also called random quantity, aleatory variable, or stochastic variable) is a mathematical formalization of a quantity or object which depends on random events. It is a mapping or a function from possible outcomes (e.g., the possible upper sides of a flipped coin such as heads H and tails T) in a sample space (e.g., the set \) to a measurable space, often the real numbers (e.g., \ in which 1 corresponding to H and -1 corresponding to T). Informally, randomness typically represents some fundamental element of chance, such as in the roll of a dice; it may also represent uncertainty, such as measurement error. However, the interpretation of probability is philosophically complicated, and even in specific cases is not always straightforward. The purely mathematical analysis of random variables is independent of such interpretational difficulties, and can be based upon a rigorous axiomatic setup. In the formal mathematical language of measure theory, a rando ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |