|
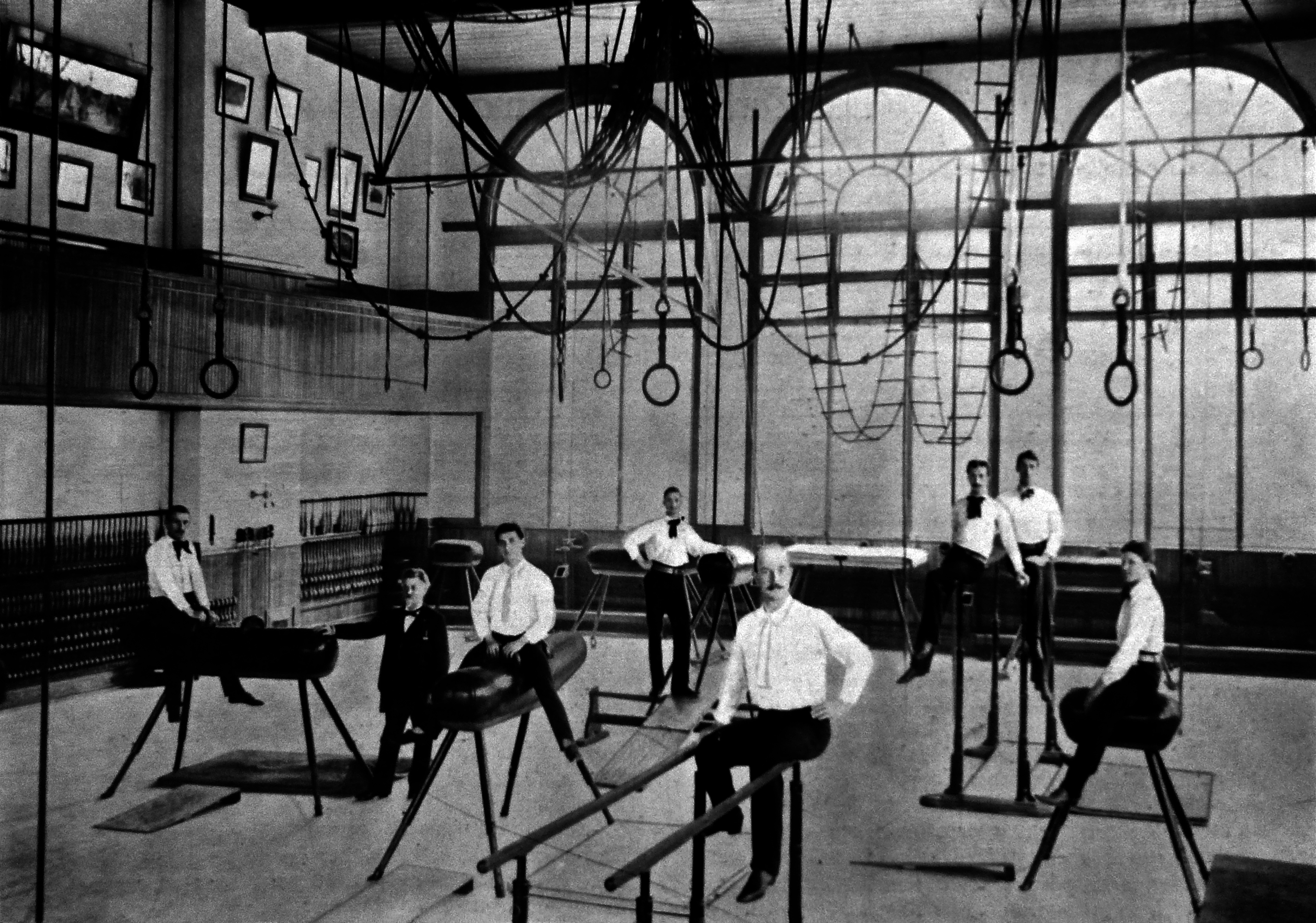
Turnverein
Turners (, ) are members of German-American gymnastic clubs called Turnvereine. They promoted German culture, physical culture, and liberal politics. Turners, especially Francis Lieber (1798–1872), were the leading sponsors of gymnastics as an American sport and the field of academic study. In Germany, a major gymnastic movement was started by ''Turnvater'' ("father of gymnastics") and nationalist Friedrich Ludwig Jahn in the early 19th century when Germany was occupied by Napoleon. The ''Turnvereine'' (; "gymnastic unions"; from German ''turnen'' meaning “to practice gymnastics,” and ''Verein'' meaning “club, union”) were not only athletic but also political, reflecting their origin in similar ethnocentric "national gymnastic" organizations in Europe (such as the Czech Sokol (sport organization), Sokol), who were participants in various national movements for independence. The Turner movement in Germany was generally Liberalism, liberal in nature, and many Turners t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Culture
Physical culture, also known as body culture, is a health and strength training movement that originated during the 19th century in Germany, the UK and the US. Origins The physical culture movement in the United States during the 19th century owed its origins to several cultural trends. In the United States, German immigrants after 1848 introduced a physical culture system based on gymnastics that became popular, especially in colleges. Many local Turner clubs introduced physical education (PE) in the form of 'German gymnastics' into American colleges and public schools. The perception of Turner as 'non-American' prevented the 'German system' from becoming the dominating form. They were especially important mainly in the cities with a large German-American population, but their influence slowly spread. By the late 19th century reformers worried that sedentary white-collar workers were suffering from various " diseases of affluence" that were partially attributed to their incr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
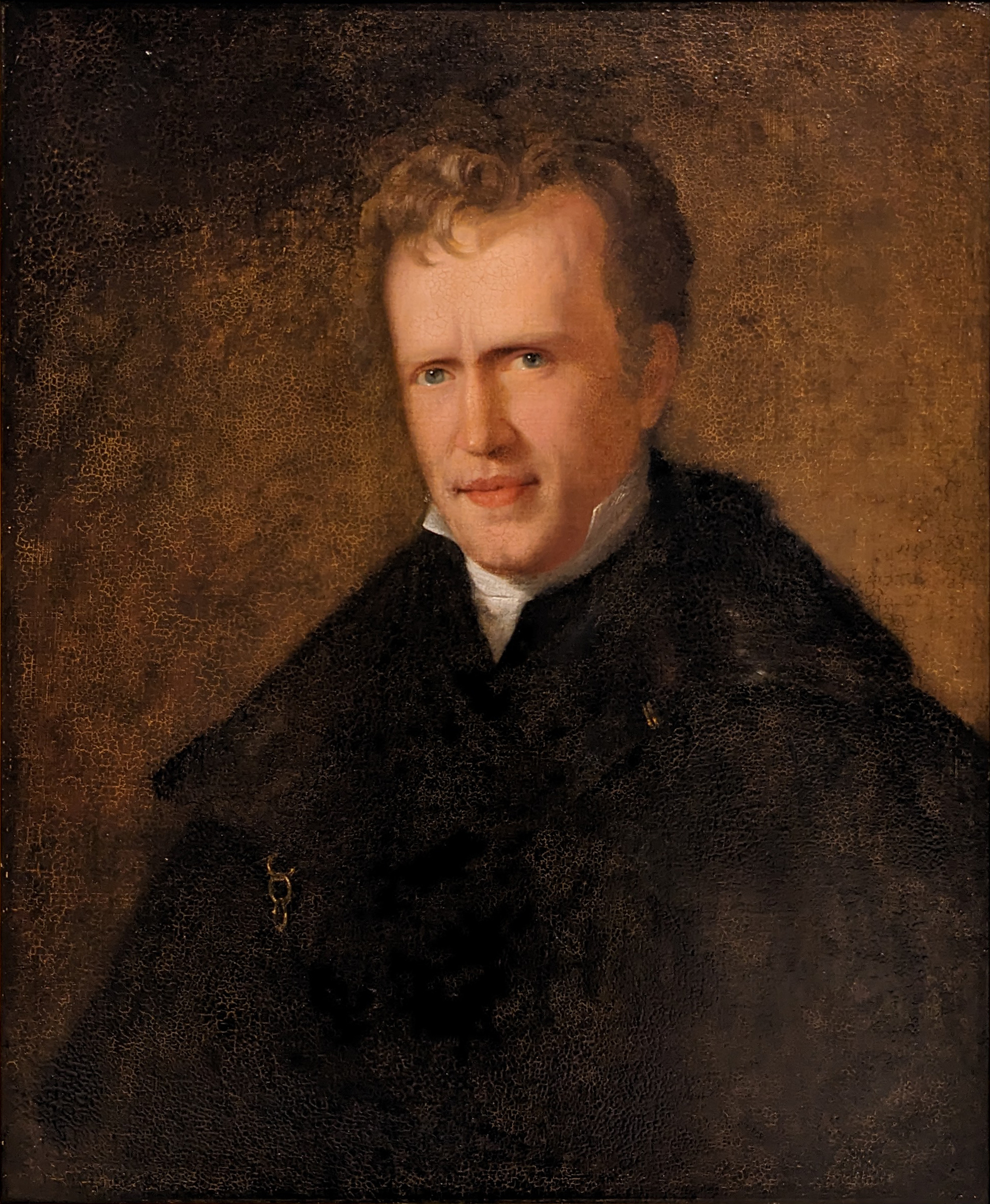
Friedrich Ludwig Jahn
(11August 177815October 1852) was a German gymnastics educator and nationalist whose writing is credited with the founding of the German gymnastics (Turner) movement, first realized at Volkspark Hasenheide in Berlin, the origin of modern sports clubs, as well as influencing the German Campaign of 1813, during which a coalition of German states effectively ended the occupation by Napoleon's First French Empire. His admirers know him as , roughly meaning "Father of Gymnastics ". Jahn invented the parallel bars, rings, high bar, the pommel horse and the vault horse. Life was born in the village of in Brandenburg, Prussia. He studied theology and philology from 1796 to 1802 at the universities in , , and . After the Battle of Jena–Auerstedt in 1806, he joined the Prussian army. In 1809, he went to Berlin where he became a teacher at the and at the Plamann School. Brooding upon what he saw as the humiliation of his native land by Napoleon, conceived the idea of restori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sokol (sport Organization)
The Sokol movement (, ) is an all-age gymnastics organization founded in Prague in the Czech lands of Austria-Hungary in 1862 by Miroslav Tyrš and Jindřich Fügner. It was based upon the principle of " a strong mind in a sound body". Sokol, through lectures, discussions, and group outings, provided what Tyrš viewed as physical, moral, and intellectual training for the nation. This training extended to men of all ages and classes, and eventually to women. The movement spread across all the regions populated by Slavic cultures, most of them part of either Austria-Hungary or the Russian Empire: present-day Slovakia, the Slovene Lands, Croatia, Serbia, Bulgaria, Poland ( Polish Sokół movement), Ukraine, and Belarus. In many of these nations, the organization also served as an early precursor to the Scouting movements. Though officially an institution "above politics", Sokol played an important part in the development of Czech nationalism and patriotism, which found expressi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German-American
German Americans (, ) are Americans who have full or partial German ancestry. According to the United States Census Bureau's figures from 2022, German Americans make up roughly 41 million people in the US, which is approximately 12% of the population. This represents a decrease from the 2012 census where 50.7 million Americans identified as German. The census is conducted in a way that allows this total number to be broken down in two categories. In the 2020 census, roughly two thirds of those who identify as German also identified as having another ancestry, while one third identified as German alone. German Americans account for about one third of the total population of people of German ancestry in the world. The first significant groups of German immigrants arrived in the British America, British colonies in the 1670s, and they settled primarily in the colonial states of Province of Pennsylvania, Pennsylvania, Province of New York, New York, and Colony of Virginia, Virginia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Yankee
''The Yankee'' (later retitled ''The Yankee and Boston Literary Gazette'') was one of the first cultural publications in the United States, founded and edited by John Neal (1793–1876), and published in Portland, Maine, as a weekly periodical and later converted to a longer, monthly format. Its two-year run concluded at the end of 1829. The magazine is considered unique for its independent journalism at the time. Neal used creative control of the magazine to improve his social status, help establish the American gymnastics movement, cover national politics, and critique American literature, art, theater, and social issues. Essays by Neal on American art and theater anticipated major changes and movements in those fields realized in the following decades. Conflicting opinions published in ''The Yankee'' on the cultural identity of Maine and New England presented readers with a complex portrait of the region. Many new, predominantly female, writers and editors started their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Follen
Charles (Karl) Theodor Christian Friedrich Follen (September 6, 1796 – January 13, 1840) was a Germans, German poet and patriot, who later moved to the United States and became the first professor of German language, German at Harvard University, a Unitarianism, Unitarian minister, and a radical Abolitionism in the United States, abolitionist. He was fired by Harvard for his abolitionist statements. Life in Europe Karl Theodor Christian Friedrich Follen was born at Romrod, in Landgraviate of Hesse-Darmstadt, Hesse-Darmstadt (present-day Germany), to Christoph Follenius (1759–1833) and Rosine Follenius (1766–1799). His father was a counselor-at-law and judge in Giessen, in Hesse-Darmstadt. His mother had retired to Romrod to avoid the French revolutionary troops that had occupied Giessen. He was the brother of August Ludwig Follen and Paul Follen, and the uncle of the biologist Carl Vogt. He was educated at the preparatory school at Giessen, where he distinguished himself ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Neal
John Neal (August 25, 1793 – June 20, 1876) was an American writer, critic, editor, lecturer, and activist. Considered both eccentric and influential, he delivered speeches and published essays, novels, poems, and short stories between the 1810s and 1870s in the United States and Great Britain, championing American literary nationalism and American literary regionalism, regionalism in their earliest stages. Neal advanced the development of Visual art of the United States, American art, fought for women's rights, advocated the end of Slavery in the United States, slavery and racial prejudice, and helped establish the Turners, American gymnastics movement. The first American author to use natural diction and a pioneer of colloquialism, Neal was the first to use the phrase ''son-of-a-bitch'' in a US work of fiction. He attained his greatest literary achievements between 1817 and 1835, during which time he was America's first daily newspaper columnist, the first American publishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Round Hill School
The Round Hill School for Boys was a short-lived experimental school in Northampton, Massachusetts. It was founded by George Bancroft and Joseph Cogswell in 1823. Though it failed as a viable venture — it closed in 1834 — it was an early effort to elevate secondary education in the United States for the sons of the New England elite. The incompatibility of the two founders was a fundamental cause of the eventual dissolution of the project. School founding On his return from the University of Göttingen, wishing to shed upon others some of the inspiration he had received, George Bancroft applied for leave to read lectures on history at Harvard University. His request was denied. After this disappointment, in an attempt to introduce some parts of the German system of education to the United States, and in conjunction with Joseph Cogswell, Bancroft founded the Round Hill School. He left the school after a few years, leaving Cogswell in sole possession. Early years During the fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
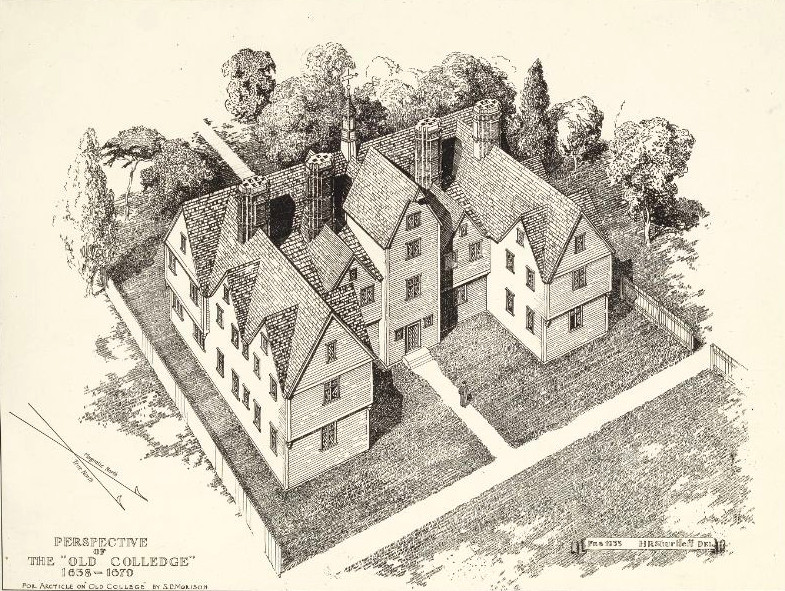
Harvard College
Harvard College is the undergraduate education, undergraduate college of Harvard University, a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Part of the Harvard Faculty of Arts and Sciences, Faculty of Arts and Sciences, Harvard College is Harvard University's traditional undergraduate program, offering BA (Bachelor of Arts) and BS (Bachelor of Science) degrees. It is highly selective, with fewer than four percent of applicants being offered admission as of 2022. Harvard College students participate in over 450 extracurricular organizations and nearly all live on campus. First-year students reside in or near Harvard Yard while upperclass students reside in other on-campus housing. History Harvard College was founded in 1636 by vote of the Massachusetts General Court, Great and General Court of the Massachusetts Bay Colony. Two years later, the college became home to North America's first known printing press, carri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milwaukee Bundesturnhalle
Milwaukee is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. Located on the western shore of Lake Michigan, it is the 31st-most populous city in the United States and the fifth-most populous city in the Midwest with a population of 577,222 at the 2020 census. It is the county seat of Milwaukee County. The Milwaukee metropolitan area is the 40th-most populous metropolitan area in the U.S. with 1.57 million residents. Founded in the early 19th century and incorporated in 1846, Milwaukee grew rapidly due to its location as a port city. Its history was heavily influenced by German immigrants and it continues to be a center for German-American culture, specifically known for its brewing industry. The city developed as an industrial powerhouse during the 19th and early 20th centuries. Milwaukee is an ethnically and culturally diverse city, however it continues to be one of the most racially segregated cities as a result of early-20th-century redlining. Milwaukee is ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iowa
Iowa ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the upper Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west; Wisconsin to the northeast, Illinois to the east and southeast, Missouri to the south, Nebraska to the west, South Dakota to the northwest, and Minnesota to the north. Iowa is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 26th largest in total area and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 31st most populous of the List of states and territories of the United States, 50 U.S. states, with a population of 3.19 million. The state's List of capitals in the United States, capital, List of cities in Iowa, most populous city, and largest List of metropolitan statistical areas, metropolitan area fully located within the state is Des Moines, Iowa, Des Moines. A portion of the larger Omaha–Council Bluffs metropolitan area, Omaha, Nebraska, metropolitan area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indiana
Indiana ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Michigan to the northwest, Michigan to the north and northeast, Ohio to the east, the Ohio River and Kentucky to the south and southeast, and the Wabash River and Illinois to the west. Nicknamed "the Hoosier State", Indiana is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 38th-largest by area and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 17th-most populous of the List of states and territories of the United States, 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the Union as the 19th state on December 11, 1816. Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous resistance to American settlement was broken with defeat of the Tecumseh's confederacy in 1813. The new settlers were primarily Americans of British people, British ancestry from the East Coast of the United States, eastern seaboard and the Upland South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |