|
Turnout (ballet)
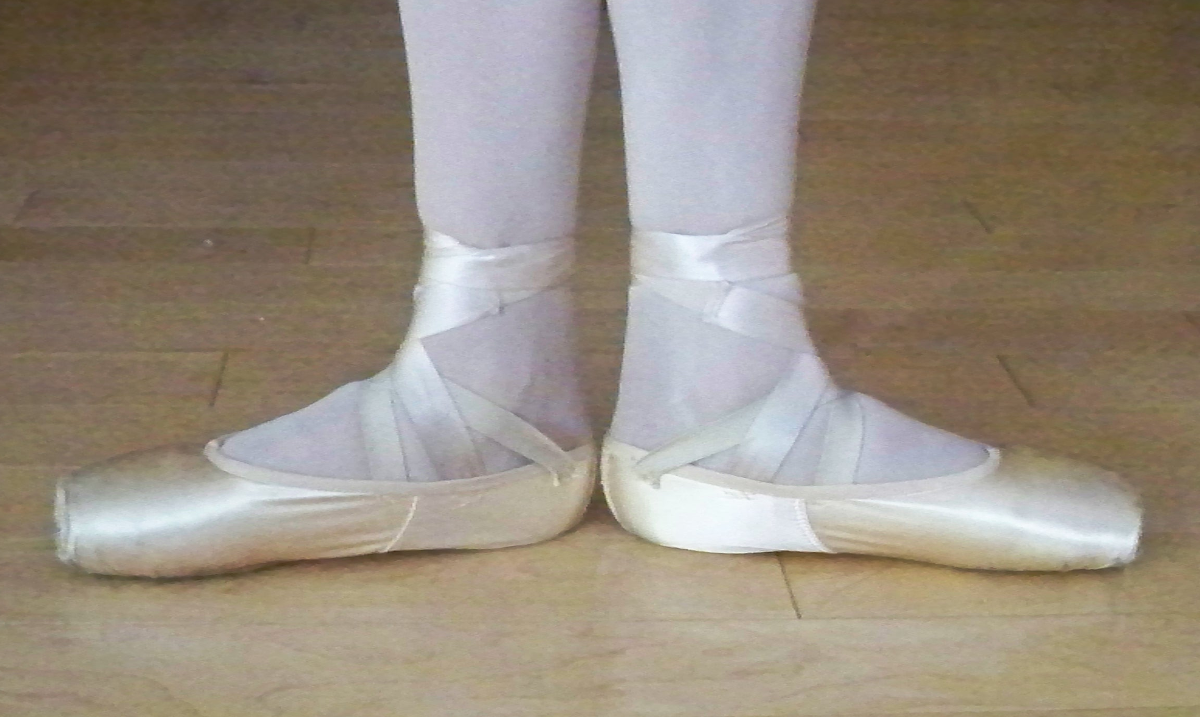
In ballet, turnout (also turn-out) is rotation of the leg at the hips which causes the feet (and knees) to turn outward, away from the front of the body. This rotation allows for greater extension of the leg, especially when raising it to the side and rear. Turnout is an essential part of classical ballet technique Technique or techniques may refer to: Music * The Techniques, a Jamaican rocksteady vocal group of the 1960s * Technique (band), a British female synth pop band in the 1990s * ''Technique'' (album), by New Order, 1989 * ''Techniques'' (album), by .... Turnout is measured in terms of the angle between the center lines of the feet when heels are touching, as in first position. Complete turnout (a 180° angle) is rarely attainable without conditioning.Kirstein, Stuart (1952), p. 26. Various exercises are used to improve turnout by increasing hip flexibility (to improve movement range), strengthening buttocks muscles (to enable a dancer to maintain turnout), or both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Position Turned Out
First most commonly refers to: * First, the ordinal form of the number 1 First or 1st may also refer to: Acronyms * Faint Images of the Radio Sky at Twenty-Centimeters, an astronomical survey carried out by the Very Large Array * Far Infrared and Sub-millimetre Telescope, of the Herschel Space Observatory * For Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology, an international youth organization * Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams, a global forum Arts and entertainment Albums * ''1st'' (album), by Streets, 1983 * ''1ST'' (SixTones album), 2021 * ''First'' (David Gates album), 1973 * ''First'', by Denise Ho, 2001 * ''First'' (O'Bryan album), 2007 * ''First'' (Raymond Lam album), 2011 Extended plays * ''1st'', by The Rasmus, 1995 * ''First'' (Baroness EP), 2004 * ''First'' (Ferlyn G EP), 2015 Songs * "First" (Lindsay Lohan song), 2005 * "First" (Cold War Kids song), 2014 * "First", by Lauren Daigle from the album '' How Can It Be'', 2015 * "First", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballet
Ballet () is a type of performance dance that originated during the Italian Renaissance in the fifteenth century and later developed into a concert dance form in France and Russia. It has since become a widespread and highly technical form of dance with Glossary of ballet, its own vocabulary. Ballet has been influential globally and has defined the foundational ballet technique, techniques which are used in many other dance genres and cultures. Various schools around the world have incorporated their own cultures. As a result, ballet has evolved in distinct ways. A ''ballet'' as a unified work of art, work comprises the choreography (dance), choreography and music for a ballet production. Ballets are choreographed and performed by trained ballet dancers. Traditional classical ballets are usually performed with classical music accompaniment and use elaborate costumes and staging, whereas modern ballets are often performed in simple costumes and without elaborate sets or scenery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
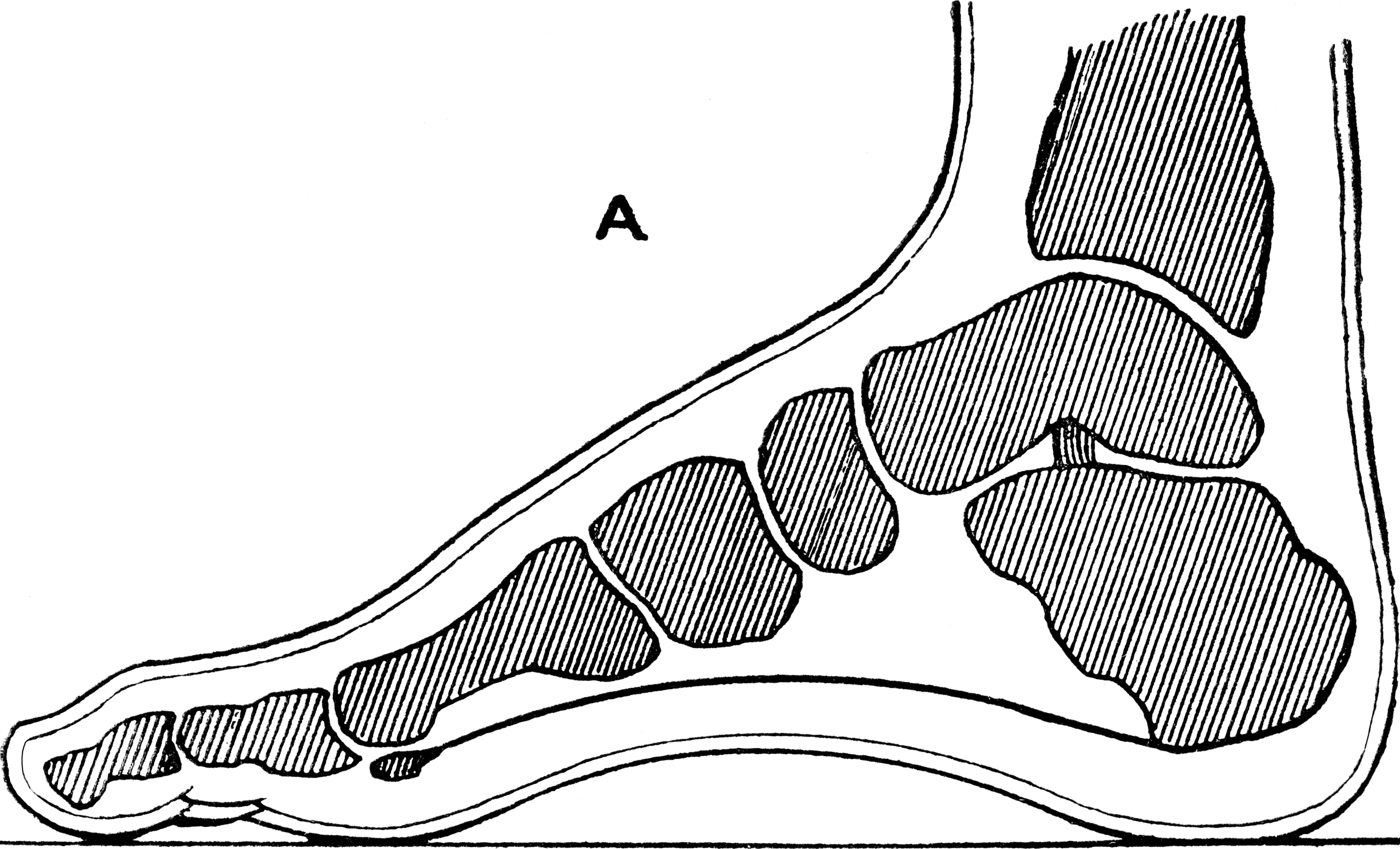
Feet
The foot (: feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is an organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws and/or nails. Etymology The word "foot", in the sense of meaning the "terminal part of the leg of a vertebrate animal" comes from Old English ''fot'', from Proto-Germanic *''fot'' (source also of Old Frisian ''fot'', Old Saxon ''fot'', Old Norse ''fotr'', Danish ''fod'', Swedish ''fot'', Dutch ''voet'', Old High German ''fuoz'', German ''Fuß'', Gothic ''fotus'', all meaning "foot"), from PIE root *''ped-'' "foot". The plural form ''feet'' is an instance of i-mutation. Structure The human foot is a strong and complex mechanical structure containing 26 bones, 33 joints (20 of which are actively articulated), and more than a hundred muscles, tendons, and ligaments.Podiatry Channel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Ballet
Classical ballet is any of the traditional, formal styles of ballet that exclusively employ classical ballet technique. It is known for its aesthetics and rigorous technique (such as en pointe, pointe work, turnout (ballet), turnout of the legs, and high extensions), its flowing, precise movements, and its ethereal qualities. There are stylistic variations related to an area or origin, which are denoted by classifications such as Russian ballet, French ballet, British ballet and Italian ballet. For example, Russian ballet features high extensions and dynamic turns, whereas Italian ballet tends to be more grounded, with a focus on fast, intricate footwork. Many of the stylistic variations are associated with specific training methods that have been named after their originators. Despite these variations, the performance and vocabulary of classical ballet are largely consistent throughout the world. History Ballet originated in the Italian Renaissance courts and was brought to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballet Technique
Ballet technique is the foundational principles of body movement and form used in ballet. It is an important aspect of ballet performance because ballet (especially classical ballet) puts great emphasis on the method and execution of movement., pp. 6-7 & 21. The techniques found in classical ballet are a framework for many other styles of dance, including jazz and contemporary ballet. Aspects of ballet technique include alignment, which refers to keeping the head, shoulders, and hips vertically aligned. Turnout refers to completing movements with legs rotated outward; this promotes clean footwork, graceful '' port de bras'' (movement of the arms), and correct body positions, lines and angles. Other aspects of ballet technique include posture, toe pointing, keeping shoulders down, and pulling up, which combines proper posture and lifting of the muscles to increase turnout and enhance alignment and thus improve the quality of turns. Ballet technique is also used to exhibit '' ballon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heel
The heel is the prominence at the posterior end of the foot. It is based on the projection of one bone, the calcaneus or heel bone, behind the articulation of the bones of the lower leg. Structure To distribute the compressive forces exerted on the heel during gait, and especially the stance phase when the heel contacts the ground, the sole of the foot is covered by a layer of subcutaneous connective tissue up to 2 cm thick (under the heel). This tissue has a system of pressure chambers that both acts as a shock absorber and stabilises the sole. Each of these chambers contains fibrofatty tissue covered by a layer of tough connective tissue made of collagen fibers. These septa ("walls") are firmly attached both to the plantar aponeurosis above and the sole's skin below. The sole of the foot is one of the most highly vascularized regions of the body surface, and the dense system of blood vessels further stabilize the septa. The Achilles tendon is the muscle tendon of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positions Of The Feet In Ballet
The positions of the feet in ballet is a fundamental part of classical ballet ballet technique, technique that defines standard placements of feet on the floor. There are five basic positions in modern-day classical ballet, known as the first through fifth positions. In 1725, dancing master Pierre Rameau credited the codification of these five positions to choreographer Pierre Beauchamp. Two additional positions, known as the sixth and seventh positions, were codified by Serge Lifar in the 1930s while serving as Ballet Master at the Paris Opéra Ballet, though their use is limited to Lifar's choreographies. The sixth and seventh positions were not Lifar's inventions, but revivals of positions that already existed in the eighteenth century, when there were ten positions of the feet in classical ballet. Five basic positions The first basic position requires the feet to be flat on the floor and turnout (ballet), turned out (pointing in opposite directions as a result of rotating t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Pelvic Tilt
Pelvic tilt is the orientation of the pelvis in respect to the thighbones and the rest of the body. The pelvis can tilt towards the front, back, or either side of the body. Anterior pelvic tilt and posterior pelvic tilt are very common abnormalities in regard to the orientation of the pelvis. Forms *Anterior pelvic tilt (APT) is when the front of the pelvis drops in relationship to the back of the pelvis. For example, this happens when the hip flexors shorten and the hip extensors lengthen. It is also called lumbar hyperlordosis, which is characterized by an exaggerated curve in the lower back. *Posterior pelvic tilt (PPT) is the opposite, when the front of the pelvis rises and the back of the pelvis drops. For example, this happens when the hip flexors lengthen and the hip extensors shorten, particularly the gluteus maximus which is the primary extensor of the hip. *Lateral pelvic tilt (LPT) describes tilting toward either right or left and is associated with scoliosis or peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femur
The femur (; : femurs or femora ), or thigh bone is the only long bone, bone in the thigh — the region of the lower limb between the hip and the knee. In many quadrupeds, four-legged animals the femur is the upper bone of the hindleg. The Femoral head, top of the femur fits into a socket in the pelvis called the hip joint, and the bottom of the femur connects to the shinbone (tibia) and kneecap (patella) to form the knee. In humans the femur is the largest and thickest bone in the body. Structure The femur is the only bone in the upper Human leg, leg. The two femurs converge Anatomical terms of location, medially toward the knees, where they articulate with the Anatomical terms of location, proximal ends of the tibiae. The angle at which the femora converge is an important factor in determining the femoral-tibial angle. In females, thicker pelvic bones cause the femora to converge more than in males. In the condition genu valgum, ''genu valgum'' (knock knee), the femurs conve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hip (anatomy)
In vertebrate anatomy, the hip, or coxaLatin ''coxa'' was used by Celsus in the sense "hip", but by Pliny the Elder in the sense "hip bone" (Diab, p 77) (: ''coxae'') in medical terminology, refers to either an anatomical region or a joint on the outer (lateral) side of the pelvis. The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest, and lateral to the obturator foramen, with muscle tendons and soft tissues overlying the greater trochanter of the femur. In adults, the three pelvic bones ( ilium, ischium and pubis) have fused into one hip bone, which forms the superomedial/deep wall of the hip region. The hip joint, scientifically referred to as the acetabulofemoral joint (''art. coxae''), is the ball-and-socket joint between the pelvic acetabulum and the femoral head. Its primary function is to support the weight of the torso in both static (e.g. standing) and dynamic (e.g. walking or running) postures. The hip joints have very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iliofemoral Ligament
The iliofemoral ligament is a thick and very tough triangular capsular ligament of the hip joint situated anterior to this joint. It attaches superiorly at the inferior portion of the anterior inferior iliac spine and adjacent portion of the margin of the acetabulum; it attaches inferiorly at the intertrochanteric line. It is also referred to as the Y-ligament (see below). the ligament of Bigelow, the ligament of Bertin and any combinations of these names. With a force strength exceeding 350 kg (772 lbs), the iliofemoral ligament is not only stronger than the two other ligaments of the hip joint, the ischiofemoral and the pubofemoral, but also the strongest ligament in the human body and as such is an important constraint to the hip joint. Structure The ligament is triangular in shape, with its apex represented by its pelvic attachment. The ligament has two though outer bands; it is thinner and weaker centrally. As the lateral portion is twisted like a screw, the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |