|
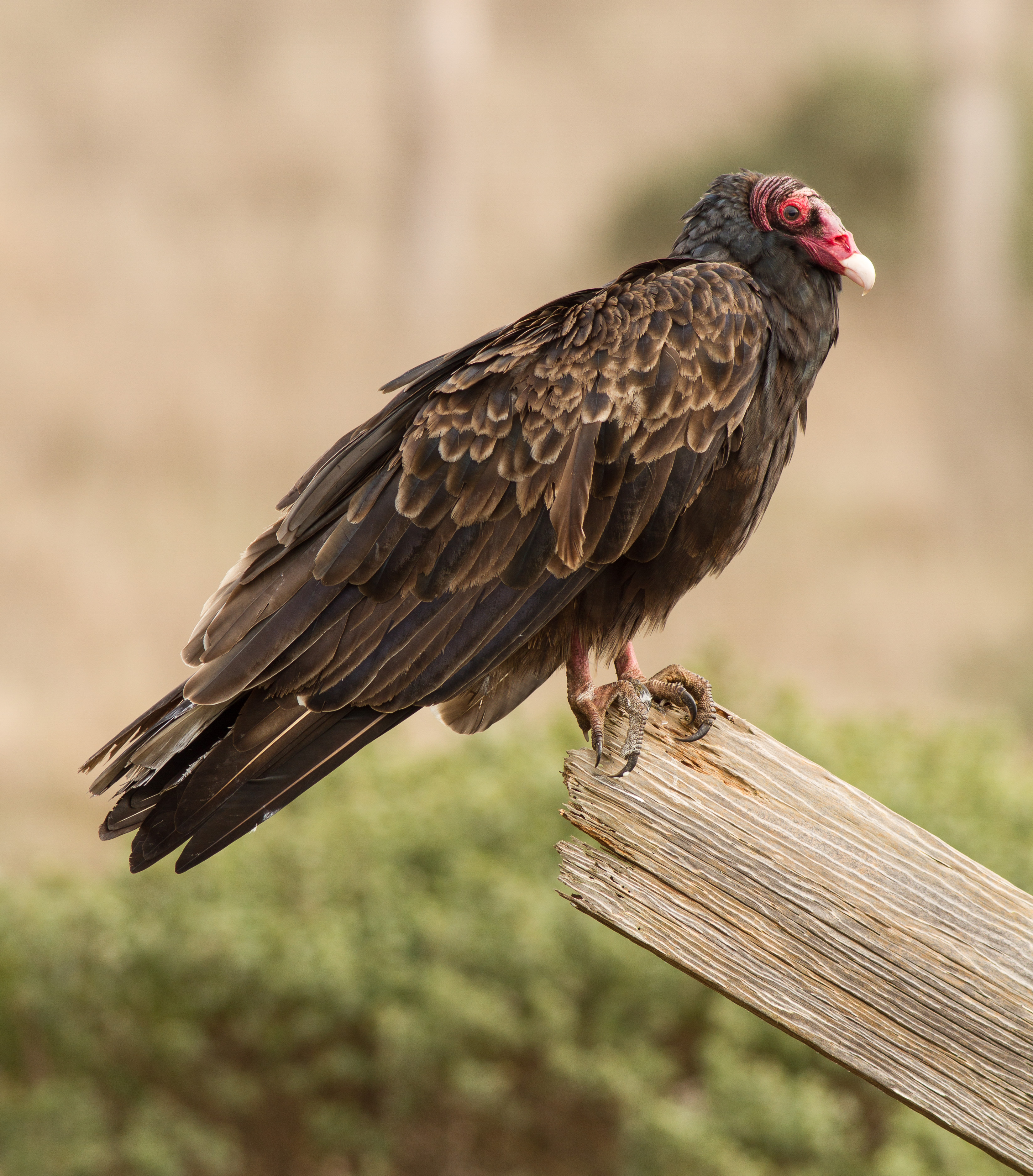
Turkey Vulture
The turkey vulture (''Cathartes aura'') is the most widespread of the New World vultures. One of three species in the genus '' Cathartes'' of the family Cathartidae, the turkey vulture ranges from southern Canada to the southernmost tip of South America. It inhabits a variety of open and semi-open areas, including subtropical forests, shrublands, pastures, and deserts. Like all New World vultures, it is not closely related to the Old World vultures of Europe, Africa, and Asia. However, the two groups strongly resemble each other due to convergent evolution. The turkey vulture is a scavenger and feeds almost exclusively on carrion. It finds its food using its keen eyes and sense of smell, flying low enough to detect the gasses produced by the early stages of decay in dead animals. In flight, it uses thermals to move through the air, flapping its wings infrequently. It roosts in large community groups. Lacking a syrinx—the vocal organ of birds—its only vocalizations are grun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Orange Walk District
Orange Walk is a Districts of Belize, district in the northwest of the nation of Belize, with its district capital in Orange Walk Town. Demographics Main settlements The Orange Walk District, with an area of 1,829 square miles (4,636 square km), is located north-northwest of the Belize District. This is the second largest district in terms of total area in comparison to other districts in Belize, and lies between the Belize and Corozal District, Corozal districts to the east, Mexico to the north and Guatemala to the west. Villages in Orange Walk District include August Pine Ridge, Blue Creek (Belize), Blue Creek, Carmelita, Belize, Carmelita, Chan Pine Ridge, Douglas, Belize, Douglas, Indian Church, Belize, Indian Church, Guinea Grass, San Antonio, Belize, San Antonio, San Carlos, Belize, San Carlos, San Estevan, Belize, San Estevan, San Felipe, Orange Walk, San Felipe, San José, Belize, San José, San Jose Palmar, Nuevo San Juan, Belize, Nuevo San Juan, San Lazaro, Belize, San L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Buteo
''Buteo'' is a genus of medium to fairly large, wide-ranging raptors with a robust body and broad wings. In the Old World, members of this genus are called " buzzards", but "hawk" is used in the New World (Etymology: ''Buteo'' is the Latin name of the common buzzard). As both terms are ambiguous, buteo is sometimes used instead, for example, by the Peregrine Fund. Characteristics Buteos are fairly large birds. Total length can vary from and wingspan can range from . The lightest known species is the roadside hawk, at an average of although the lesser known white-rumped and Ridgway's hawks are similarly small in average wingspan around , and average length around in standard measurements. The largest species in length and wingspan is the upland buzzard, which averages around in length and in wingspan. The upland is rivaled in weight and outsized in foot measurements and bill size by the ferruginous hawk. In both of these largest buteos, adults typically weigh over , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Charles Sibley
Charles Gald Sibley (August 7, 1917 – April 12, 1998) was an American ornithologist and molecular biologist. He had an immense influence on the scientific classification of birds, and the work that Sibley initiated has substantially altered our understanding of the evolutionary history of modern birds. Sibley's taxonomy has been a major influence on the sequences adopted by ornithological organizations, especially the American Ornithologists' Union. Life and work Educated in California (A.B. 1940; Ph.D. 1948 in Zoology, University of California, Berkeley. Minor fields: Paleontology, Botany), he did his first fieldwork in Mexico in 1939 and 1941, then in Solomon Islands, Bismarck Archipelago, New Guinea, and the Philippines during World War II while on leave from the U.S. Navy, in which he was Ensign to Lieutenant in the Communications and Medical Service Corps. He was based for much of the war at Emirau Island, in what is now New Ireland Province of Papua New Guinea. His first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Storks
Storks are large, long-legged, long-necked wading birds with long, stout Beak, bills. They belong to the family (biology), family Ciconiidae, and make up the order Ciconiiformes . Ciconiiformes previously included a number of other families, such as herons and ibises, but those families have been moved to other orders. Storks dwell in many regions and tend to live in drier habitats than the closely related herons, spoonbills and ibises; they also lack the powder down that those groups use to clean off fish slime. Bill-clattering is an important mode of Animal communication, communication at the nest. Many species are bird migration, migratory. Most storks eat frogs, fish, insects, earthworms, small birds and small mammals. There are 20 living species of storks in six genera. Various terms are used to refer to groups of storks, two frequently used ones being a ''muster'' of storks and a ''phalanx'' of storks. Storks tend to use Lift (soaring), soaring, gliding flight, which con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Old World Vultures
Old World vultures are vultures that are found in the Old World, i.e. the continents of Europe, Asia and Africa, and which belong to the family Accipitridae, which also includes eagles, buzzards, kites, and hawks. Old World vultures are not closely related to the superficially similar New World vultures and condors, and do not share that group's good sense of smell. The similarities between the two groups of vultures are due to convergent evolution, rather than a close relationship. They were widespread in both the Old World and North America during the Neogene. Old World vultures are probably a polyphyletic group within Accipitridae, belonging to two separate not closely related groups within the family. Most authorities refer to two major clades: Gypaetinae ('' Gypaetus, Gypohierax'' and '' Neophron'') and Aegypiinae (''Aegypius'', ''Gyps'', '' Sarcogyps'', '' Torgos'', '' Trigonoceps'' and possibly '' Necrosyrtes''). The former seem to be nested with Perninae hawks, while th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ecological Niche
In ecology, a niche is the match of a species to a specific environmental condition. Three variants of ecological niche are described by It describes how an organism or population responds to the distribution of Resource (biology), resources and competitors (for example, by growing when resources are abundant, and when predators, parasites and pathogens are scarce) and how it in turn alters those same factors (for example, limiting access to resources by other organisms, acting as a food source for predators and a consumer of prey). "The type and number of variables comprising the dimensions of an environmental niche vary from one species to another [and] the relative importance of particular environmental variables for a species may vary according to the geographic and biotic contexts". See also Chapter 2: Concepts of niches, pp. 7 ''ff'' A Grinnellian niche is determined by the habitat in which a species lives and its accompanying Behavioral ecology, behavioral adaptations. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Taxonomy (biology)
In biology, taxonomy () is the science, scientific study of naming, defining (Circumscription (taxonomy), circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxon, taxa (singular: taxon), and these groups are given a taxonomic rank; groups of a given rank can be aggregated to form a more inclusive group of higher rank, thus creating a taxonomic hierarchy. The principal ranks in modern use are domain (biology), domain, kingdom (biology), kingdom, phylum (''division'' is sometimes used in botany in place of ''phylum''), class (biology), class, order (biology), order, family (biology), family, genus, and species. The Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus is regarded as the founder of the current system of taxonomy, having developed a ranked system known as Linnaean taxonomy for categorizing organisms. With advances in the theory, data and analytical technology of biological systematics, the Linnaean system has transfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectively, in each homologous chromosome pair—the form in which chromosomes naturally exist. Somatic cells, tissues, and individual organisms can be described according to the number of sets of chromosomes present (the "ploidy level"): monoploid (1 set), diploid (2 sets), triploid (3 sets), tetraploid (4 sets), pentaploid (5 sets), hexaploid (6 sets), heptaploid or septaploid (7 sets), etc. The generic term polyploid is often used to describe cells with three or more sets of chromosomes. Virtually all sexually reproducing organisms are made up of somatic cells that are diploid or greater, but ploidy level may vary widely between different organisms, between different tissues within the same organism, and at different stages in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lesser Yellow-headed Vulture
The lesser yellow-headed vulture (''Cathartes burrovianus'') also known as the savannah vulture, is a species of bird in the New World vulture family Cathartidae. It was considered to be the same species as the greater yellow-headed vulture until they were split in 1964. It is found in Mexico, Central America, and South America in seasonally wet or flooded lowland grassland, swamps, and heavily degraded former forest. It is a large bird, with a wingspan of . The body plumage is black, and the head and neck, which are featherless, are pale orange with red or blue areas. It lacks a syrinx, so therefore its vocalizations are limited to grunts or low hisses. The lesser yellow-headed vulture feeds on carrion and locates carcasses by sight and by smell, an ability which is rare in birds. It is dependent on larger vultures, such as the king vulture, to open the hides of larger animal carcasses as its bill is not strong enough to do this. Like other New World vultures, the lesser yell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
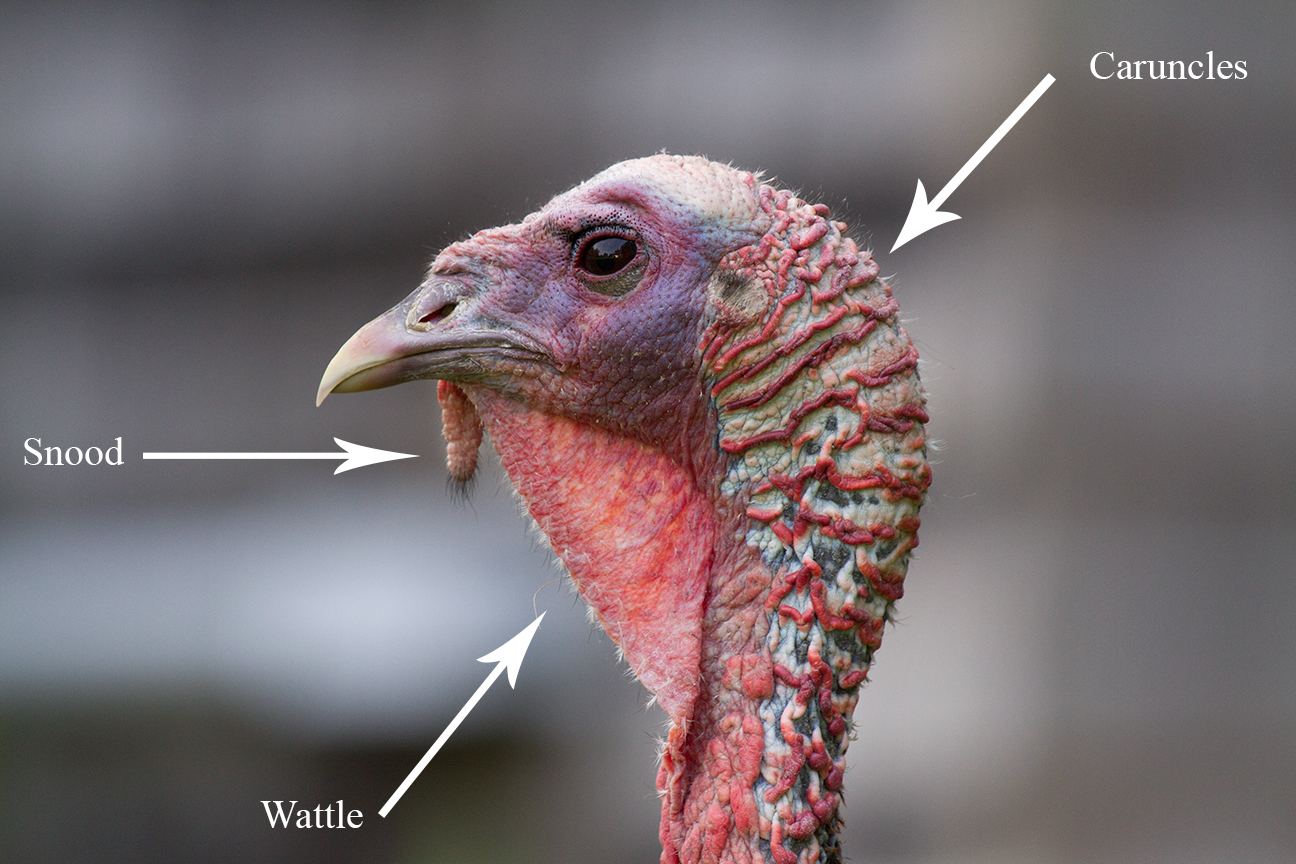
Wild Turkey
The wild turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo'') is an upland game bird native to North America, one of two extant species of Turkey (bird), turkey and the heaviest member of the order Galliformes. It is the ancestor to the domestic turkey (''M. g. domesticus''), which was originally derived from a southern Mexican subspecies of wild turkey (not the related ocellated turkey). Taxonomy The wild turkey was Species description, formally described in 1758 by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in the 10th edition of Systema Naturae, tenth edition of his ''Systema Naturae'' under its current binomial nomenclature, binomial name ''Meleagris gallopavo''. The type locality (biology), type locality is Mexico. The genus name ''Meleagris'' is from Ancient Greek μελεαγρις/''meleagris'' meaning "guineafowl". The specific epithet ''gallopavo'' is a late Medieval Latin word for a wild turkey: it combines Latin ''gallus'' meaning "fowl" and ''pavo'' meaning "peacock". The word was used in 155 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |