|
Turbosail
The turbosail or French is a marine propulsion system using a sail-like vertical surface and a powered boundary layer control system to improve lift across a wide angle of attack. This allows the sail to power the boat in any direction simply by moving a single flap at the back of the sail, unlike conventional sails which have to be continually adjusted to react to changes in the relative wind. The turbosail was first developed in a large scale application by Jacques-Yves Cousteau who commissioned the ''Alcyone'' to test the concept in production. The larger ''Calypso II'' was also designed to use a turbosail, but that design was not built. Technical design Concept In 1980, Jacques Cousteau dreamed of creating a ship with a modern engine that would be powered, at least in part, by the wind, a clean, free, renewable energy source. Aerodynamics Cousteau and his associates, Professor Lucien Malavard and Dr. Bertrand Charrier, used a fixed cylinder that looked like a smoke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Alcyone (1985 Ship)
''Alcyone'' is a ship launched at La Rochelle in 1985 for the Cousteau Society. ''Alcyone'' was created as an expedition ship and to test the operation of a new kind of marine propulsion system, the turbosail. ''Alcyone''s two turbosails augment its diesel engines. Since the accidental sinking of , ''Alcyone'' has been the Cousteau Society's expedition vessel. ''Alcyone'' in popular culture * John Denver Henry John Deutschendorf Jr. (December 31, 1943 – October 12, 1997), known professionally as John Denver, was an American Country music, country and Folk music, folk singer, songwriter, and actor. He was one of the most popular acoustic m ... wrote a short song called "Alcyone The Wind" as a tribute to ''Alcyone''. The song was sung in the 1993 documentary '' Secret Societies of Dolphins and Whales''. References External links Cousteau Society's ship page for the ''Alcyone''* Jean-Charles Nahon (Naval Architect Bureau Mauric) and Bernard Deguy (First captain of ''A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Boundary Layer Control
In engineering, boundary layer control refers to methods of controlling the behaviour of fluid flow boundary layers. It may be desirable to reduce flow separation on fast vehicles to reduce the size of the wake (streamlining), which may reduce drag. Boundary layer separation is generally undesirable in aircraft high lift coefficient systems and jet engine intakes. Laminar flow produces less skin friction than turbulent but a turbulent boundary layer transfers heat better. Turbulent boundary layers are more resistant to separation. The energy in a boundary layer may need to be increased to keep it attached to its surface. Fresh air can be introduced through slots or mixed in from above. The low momentum layer at the surface can be sucked away through a perforated surface or bled away when it is in a high pressure duct. It can be scooped off completely by a diverter or internal bleed ducting. Its energy can be increased above that of the free stream by introducing high velocity a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Flap (aircraft)
A flap is a high-lift device used to reduce the stall (flight), stalling speed of an aircraft wing at a given weight. Flaps are usually mounted on the wing trailing edges of a fixed-wing aircraft. Flaps are used to reduce the take-off distance and the landing distance. Flaps also cause an increase in Drag (physics), drag so they are retracted when not needed. The flaps installed on most aircraft are partial-span flaps; spanwise from near the wing root to the inboard end of the ailerons. When partial-span flaps are extended they alter the spanwise lift distribution on the wing by causing the inboard half of the wing to supply an increased proportion of the lift, and the outboard half to supply a reduced proportion of the lift. Reducing the proportion of the lift supplied by the outboard half of the wing is accompanied by a reduction in the angle of attack on the outboard half. This is beneficial because it increases the margin above the Stall (fluid dynamics), stall of the outbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Marine Propulsion
Marine propulsion is the mechanism or system used to generate thrust to move a watercraft through water. While paddles and sails are still used on some smaller boats, most modern ships are propelled by mechanical systems consisting of an electric motor or internal combustion engine driving a propeller, or less frequently, in pump-jets, an impeller. Marine engineering is the discipline concerned with the engineering design process of marine propulsion systems. Human-powered watercraft, Human-powered paddles and oars, and later, sails were the first forms of marine propulsion. Rowed galleys, some equipped with sail, played an important early role in early human seafaring and naval warfare, warfare. The first advanced mechanical means of marine propulsion was the marine steam engine, introduced in the early 19th century. During the 20th century it was replaced by two-stroke diesel engine, two-stroke or four-stroke diesel engines, outboard motors, and gas turbine engines on faster sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Alcyone
In Greek mythology, Alcyone (or dubiously Halcyone) (; ) and Ceyx (; ) were a wife and husband who incurred the wrath of the god Zeus for their romantic hubris. Etymology Alkyóne comes from alkyón (), which refers to a sea-bird with a mournful song or to a kingfisher bird in particular. The meaning(s) of the words is uncertain because ''alkyón'' is considered to be of pre-Greek, non-Indo-European origin. However, folk etymology related them to the ''háls'' (, "brine, sea, salt") and ''kyéo'' (, "I conceive"). Alkyóne originally is written with a smooth breathing mark, but this false origin beginning with a rough breathing mark (transliterated as the letter H) led to the common misspellings ''halkyón'' () and ''Halkyóne'' (), and thus the name of one of the kingfisher bird genus' in English Halcyon. It is also speculated that Alkyóne is derived from ''alké'' (, "prowess, battle, guard") and ''onéo'' (, from , ''onínemi'', "to help, to please"). Kéyx as referring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
America's Cup
The America's Cup is a sailing competition and the oldest international competition still operating in any sport. America's Cup match races are held between two sailing yachts: one from the yacht club that currently holds the trophy (known as the defender) and the other from the yacht club that is challenging for the cup (the challenger). The winner is awarded the America's Cup trophy, informally known as the Auld Mug. Matches are held several years apart on dates agreed between the defender and the challenger. There is no fixed schedule, but the races have generally been held every three to four years. Any yacht club that meets the requirements specified in the Deed of Gift of the America's Cup has the right to challenge the yacht club that currently holds the cup. If the challenging club wins the match, it gains stewardship of the cup. From the first defence of the cup in 1870 until the twentieth defence in 1967, there was always only one challenger. In 1970 multiple ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Square Sail
Square rig is a generic type of sail and rigging arrangement in which a sailing vessel's primary driving sails are carried on horizontal spars that are perpendicular (or square) to the median plane of the keel and masts of the vessel. These spars are called and their tips, outside the lifts, are called the . A ship mainly rigged so is called a square-rigger. In " Jackspeak" (Royal Navy slang), it also refers to the dress uniform of Junior Ratings. History Single sail square rigs were used by the ancient Egyptians, the Phoenicians, the Greeks, the Romans, and the Celts. Later the Scandinavians, the Germanic peoples, and the Slavs adopted the single square-rigged sail, with it becoming one of the defining characteristics of the classic “Viking” ships.The Viking ship's single square-rigged sail. http://Longshipco.org/sail.html Retrieved 2018-8-20 See also * Glossary of nautical terms (A-L) * Glossary of nautical terms (M-Z) * Fore-and-aft rig A fore-and-aft rig is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Marconi Sail
Guglielmo Giovanni Maria Marconi, 1st Marquess of Marconi ( ; ; 25 April 1874 – 20 July 1937) was an Italian electrical engineer, inventor, and politician known for his creation of a practical radio wave-based Wireless telegraphy, wireless telegraph system. This led to Marconi being credited as the inventor of radio and sharing the 1909 Nobel Prize in Physics with Karl Ferdinand Braun "in recognition of their contributions to the development of wireless telegraphy". His work laid the foundation for the development of radio, television, and all modern wireless communication systems. Marconi was also an entrepreneur and businessman who founded the Wireless Telegraph & Signal Company (which became the Marconi Company) in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom in 1897. In 1929, Marconi was ennobled as a marchese, marquess (''marchese'') by Victor Emmanuel III. In 1931, he set up Vatican Radio for Pope Pius XI. Biography Early years Guglielmo Giovanni Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Aspirator (pump)
A vacuum ejector, or simply ejector, or aspirator, is a type of vacuum pump, which produces vacuum by means of the Venturi effect. In an ejector, a working fluid (liquid or gaseous) flows through a jet nozzle into a tube that first narrows and then expands in cross-sectional area. The fluid leaving the jet is flowing at a high velocity which due to Bernoulli's principle results in it having low pressure, thus generating a vacuum. The outer tube then narrows into a mixing section where the high velocity working fluid mixes with the fluid that is drawn in by the vacuum, imparting enough velocity for it to be ejected, the tube then typically expands in order to decrease the velocity of the ejected stream, allowing the pressure to smoothly increase to the external pressure. The strength of the vacuum produced depends on the velocity and shape of the fluid jet and the shape of the constriction and mixing sections, but if a liquid is used as the working fluid, the strength of the va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Wing
A wing is a type of fin that produces both Lift (force), lift and drag while moving through air. Wings are defined by two shape characteristics, an airfoil section and a planform (aeronautics), planform. Wing efficiency is expressed as lift-to-drag ratio, which compares the benefit of lift with the air resistance of a given wing shape, as it flies. Aerodynamics is the study of wing performance in air. Equivalent Foil (fluid mechanics), foils that move through water are found on Hydrofoil, hydrofoil power vessels and Sailing hydrofoil, foiling sailboats that lift out of the water at speed and on submarines that use diving planes to point the boat upwards or downwards, while running submerged. Hydrodynamics is the study of foil performance in water. Etymology and usage The word "wing" from the Old Norse ''vængr'' for many centuries referred mainly to the foremost limb (anatomy), limbs of birds (in addition to the architectural aisle). But in recent centuries the word's meaning ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
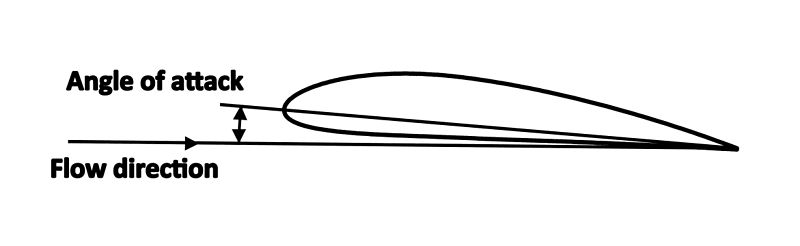
Angle Of Attack
In fluid dynamics, angle of attack (AOA, α, or \alpha) is the angle between a Airfoil#Airfoil terminology, reference line on a body (often the chord (aircraft), chord line of an airfoil) and the vector (geometry), vector representing the relative motion between the body and the fluid through which it is moving. Angle of attack is the angle between the body's reference line and the oncoming flow. This article focuses on the most common application, the angle of attack of a wing or airfoil moving through air. In aerodynamics, angle of attack specifies the angle between the chord line of the wing of a fixed-wing aircraft and the vector representing the relative motion between the aircraft and the atmosphere. Since a wing can have twist, a chord line of the whole wing may not be definable, so an alternate reference line is simply defined. Often, the chord line of the Wing root, root of the wing is chosen as the reference line. Another choice is to use a horizontal line on the fuse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |