|
Trusted Computing
Trusted Computing (TC) is a technology developed and promoted by the Trusted Computing Group. The term is taken from the field of trusted systems and has a specialized meaning that is distinct from the field of confidential computing. With Trusted Computing, the computer will consistently behave in expected ways, and those behaviors will be enforced by computer hardware and software. Enforcing this behavior is achieved by loading the hardware with a unique encryption key that is inaccessible to the rest of the system and the owner. TC is controversial as the hardware is not only secured for its owner, but also against its owner, leading opponents of the technology like free software activist Richard Stallman to deride it as "treacherous computing", and certain scholarly articles to use scare quotes when referring to the technology. Trusted Computing proponents such as International Data Corporation, the Enterprise Strategy Group and Endpoint Technologies Associates state that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trusted Computing Group
The Trusted Computing Group is a group formed in 2003 as the successor to the Trusted Computing Platform Alliance which was previously formed in 1999 to implement Trusted Computing concepts across personal computers. Members include Intel, AMD, IBM, Microsoft, and Cisco. The core idea of trusted computing is to give hardware manufacturers control over what software does and does not run on a system by refusing to run unsigned software. History On October 11, 1999, the Trusted Computing Platform Alliance (abbreviated as TCPA), a consortium of various technology companies including Compaq, Hewlett-Packard, IBM, Intel, and Microsoft, was formed in an effort to promote trust and security in the personal computing platform. In November 1999, the TCPA announced that over 70 leading hardware and software companies joined the alliance in the first month. On January 30, 2001, version 1.0 of the Trusted Computing Platform Specifications was released IBM was the first original equipment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hewlett-Packard
The Hewlett-Packard Company, commonly shortened to Hewlett-Packard ( ) or HP, was an American multinational information technology company. It was founded by Bill Hewlett and David Packard in 1939 in a one-car garage in Palo Alto, California, where the company would remain headquartered for the remainder of its lifetime; this HP Garage is now a designated landmark and marked with a plaque calling it the "Birthplace of 'Silicon Valley. HP developed and provided a wide variety of hardware components, as well as software and related services, to consumers, small and medium-sized businesses (small and medium-sized enterprises, SMBs), and fairly large companies, including customers in government sectors, until the company officially split into Hewlett Packard Enterprise and HP Inc. in 2015. HP initially produced a line of electronic test and measurement equipment. It won its first big contract in 1938 to provide the HP 200B, a variation of its first product, the HP 200A low-distor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows Vista
Windows Vista is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was the direct successor to Windows XP, released five years earlier, which was then the longest time span between successive releases of Microsoft Windows. It was Software release life cycle#Release to manufacturing (RTM), released to manufacturing on November 8, 2006, and over the following two months, it was released in stages to business customers, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), and retail channels. On January 30, 2007, it was released internationally and was made available for purchase and download from the Windows Marketplace; it is the first release of Windows to be made available through a digital distribution platform. Development of Windows Vista began in 2001 under the codename "Longhorn"; originally envisioned as a minor successor to Windows XP, it feature creep, gradually included numerous new features from the then-next major release of Windows codenamed "Blackc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proof Of Space
Proof of space (PoS) is a type of consensus algorithm achieved by demonstrating one's legitimate interest in a service (such as sending an email) by allocating a non-trivial amount of Computer memory, memory or disk space to solve a challenge presented by the service provider. The concept was formulated in 2013 by Dziembowski ''et al.'' and (with a different formulation) by Ateniese ''et al.''. Proofs of space are very similar to proof-of-work system, proofs of work (PoW), except that instead of computation, storage is used to earn cryptocurrency. Proof-of-space is different from memory-hard functions in that the Bottleneck (software), bottleneck is not in the number of memory access events, but in the amount of memory required. After the release of Bitcoin, alternatives to its PoW Cryptocurrency mining, mining mechanism were researched, and PoS was studied in the context of cryptocurrencies. Proofs of space are seen as fairer and Green computing, greener alternatives by blockch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Anonymous Attestation
Direct Anonymous Attestation (DAA) is a cryptographic primitive which enables remote authentication of a trusted computer whilst preserving privacy of the platform's user. The protocol has been adopted by the Trusted Computing Group (TCG) in the latest version of its Trusted Platform Module (TPM) specification to address privacy concerns (see also Loss of Internet anonymity). ISO/IEC 20008 specifies DAA, as well, and Intel's Enhanced Privacy ID (EPID) 2.0 implementation for microprocessors is available for licensing RAND-Z along with an open source SDK. Historical perspective In principle the privacy issue could be resolved using any standard signature scheme (or public key encryption) and a single key pair. Manufacturers would embed the private key into every TPM produced and the public key would be published as a certificate. Signatures produced by the TPM must have originated from the private key, by the nature of the technology, and since all TPMs use the same private ke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trusted Computing
Trusted Computing (TC) is a technology developed and promoted by the Trusted Computing Group. The term is taken from the field of trusted systems and has a specialized meaning that is distinct from the field of confidential computing. With Trusted Computing, the computer will consistently behave in expected ways, and those behaviors will be enforced by computer hardware and software. Enforcing this behavior is achieved by loading the hardware with a unique encryption key that is inaccessible to the rest of the system and the owner. TC is controversial as the hardware is not only secured for its owner, but also against its owner, leading opponents of the technology like free software activist Richard Stallman to deride it as "treacherous computing", and certain scholarly articles to use scare quotes when referring to the technology. Trusted Computing proponents such as International Data Corporation, the Enterprise Strategy Group and Endpoint Technologies Associates state that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Protection
Memory protection is a way to control memory access rights on a computer, and is a part of most modern instruction set architectures and operating systems. The main purpose of memory protection is to prevent a process from accessing memory that has not been allocated to it. This prevents a bug or malware within a process from affecting other processes, or the operating system itself. Protection may encompass all accesses to a specified area of memory, write accesses, or attempts to execute the contents of the area. An attempt to access unauthorized memory results in a hardware fault, e.g., a segmentation fault, storage violation exception, generally causing abnormal termination of the offending process. Memory protection for computer security includes additional techniques such as address space layout randomization and executable-space protection. Methods Segmentation Segmentation refers to dividing a computer's memory into segments. A reference to a memory locatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamper Resistance
Tamperproofing is a methodology used to hinder, deter or detect unauthorised access to a device or circumvention of a security system. Since any device or system can be foiled by a person with sufficient knowledge, equipment, and time, the term "tamperproof" is a misnomer unless some limitations on the tampering party's resources is explicit or assumed. Tamper resistance is resistance to intentional malfunction or sabotage by either the normal users of a product, package, or system or others with physical access to it. Tamper resistance ranges from simple features like screws with special drives and tamper-evident seals to more complex devices that render themselves inoperable or encrypt all data transmissions between individual chips, use of materials needing special tools and knowledge. Tamper-resistant devices or features are common on packages to deter package or product tampering or enable its detection. Anti-tamper devices have one or more components: tamper resistance, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Anonymous Attestation
Direct Anonymous Attestation (DAA) is a cryptographic primitive which enables remote authentication of a trusted computer whilst preserving privacy of the platform's user. The protocol has been adopted by the Trusted Computing Group (TCG) in the latest version of its Trusted Platform Module (TPM) specification to address privacy concerns (see also Loss of Internet anonymity). ISO/IEC 20008 specifies DAA, as well, and Intel's Enhanced Privacy ID (EPID) 2.0 implementation for microprocessors is available for licensing RAND-Z along with an open source SDK. Historical perspective In principle the privacy issue could be resolved using any standard signature scheme (or public key encryption) and a single key pair. Manufacturers would embed the private key into every TPM produced and the public key would be published as a certificate. Signatures produced by the TPM must have originated from the private key, by the nature of the technology, and since all TPMs use the same private ke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RSA (algorithm)
The RSA (Rivest–Shamir–Adleman) cryptosystem is a public-key cryptosystem, one of the oldest widely used for secure data transmission. The initialism "RSA" comes from the surnames of Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir and Leonard Adleman, who publicly described the algorithm in 1977. An equivalent system was developed secretly in 1973 at Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ), the British signals intelligence agency, by the English mathematician Clifford Cocks. That system was declassified in 1997. In a public-key cryptosystem, the encryption key is public and distinct from the decryption key, which is kept secret (private). An RSA user creates and publishes a public key based on two large prime numbers, along with an auxiliary value. The prime numbers are kept secret. Messages can be encrypted by anyone via the public key, but can only be decrypted by someone who knows the private key. The security of RSA relies on the practical difficulty of factoring the product of two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
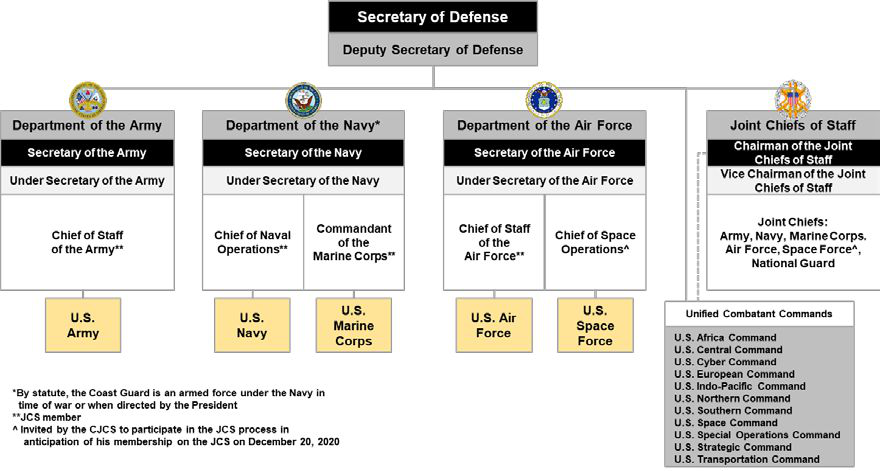
United States Department Of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD, or DOD) is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government charged with coordinating and supervising the six U.S. armed services: the United States Army, Army, United States Navy, Navy, United States Marine Corps, Marines, United States Air Force, Air Force, United States Space Force, Space Force, the United States Coast Guard, Coast Guard for some purposes, and related functions and agencies. As of November 2022, the department has over 1.4 million active-duty uniformed personnel in the six armed services. It also supervises over 778,000 National Guard (United States), National Guard and reservist personnel, and over 747,000 civilians, bringing the total to over 2.91 million employees. Headquartered at the Pentagon in Arlington County, Virginia, just outside Washington, D.C., the Department of Defense's stated mission is "to provid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trusted Platform Module
A Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a secure cryptoprocessor that implements the ISO/IEC 11889 standard. Common uses are verifying that the boot process starts from a trusted combination of hardware and software and storing disk encryption keys. A TPM 2.0 implementation is part of the Windows 11 system requirements. History The first TPM version that was deployed was 1.1b in 2003. Trusted Platform Module (TPM) was conceived by a computer industry consortium called Trusted Computing Group (TCG). It evolved into ''TPM Main Specification Version 1.2'' which was standardized by International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) in 2009 as ISO/IEC 11889:2009. ''TPM Main Specification Version 1.2'' was finalized on 3 March 2011 completing its revision. On April 9, 2014, the Trusted Computing Group announced a major upgrade to their specification entitled ''TPM Library Specification 2.0''. The group continues work on the standard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |