|
Trigonitis
Trigonitis is a condition of inflammation of the trigone region of the bladder. It is more common in women. The cause of trigonitis is not known, and there is no solid treatment. Electrocautery is sometimes used, but is generally unreliable as a treatment, and typically does not have quick results. Several drugs, such as muscle relaxants including urinary antispasmodics, antibiotics, and antiseptics have varied and unreliable results. Other forms of treatment include urethrotomy, cryosurgery, and neurostimulation Neurostimulation is the purposeful modulation of the nervous system's activity using invasive (e.g. microelectrodes) or Non-invasive procedure, non-invasive means (e.g. transcranial magnetic stimulation, transcranial electric stimulation such as .... References External links Urinary bladder disorders Inflammations {{genitourinary-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
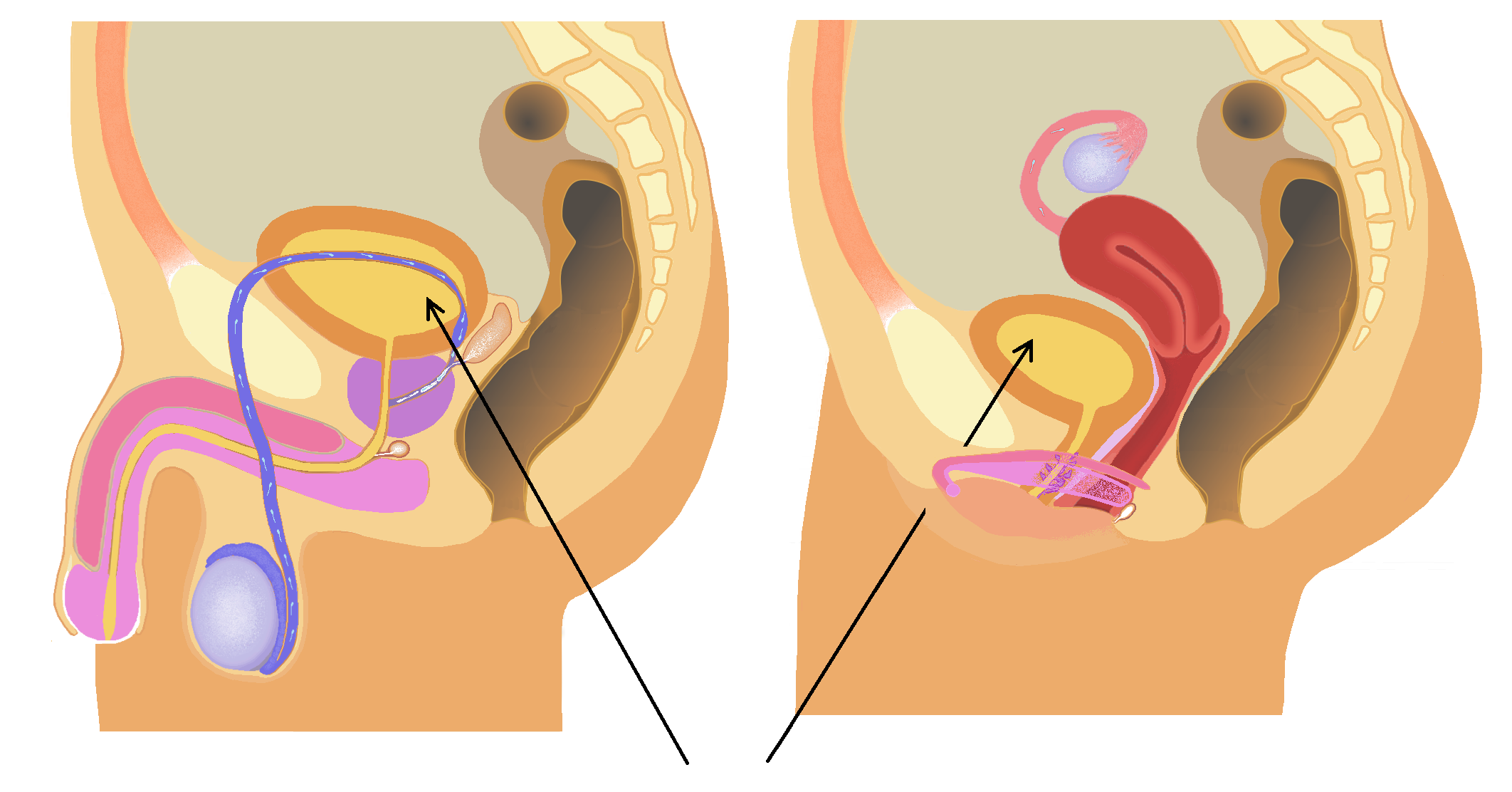
Trigone Of Urinary Bladder
The trigone of urinary bladder (also known as the vesical trigone) is a smooth triangular region of the urinary bladder formed by the two ureteric orifices and the internal urethral orifice. Between the ureteric openings, there is a fold of mucous membrane called the ''interureteric crest'' or ''Mercier bar''. The trigone lies between the crest or ridge, and the neck of the bladder. The area is very sensitive to expansion and once stretched to a certain degree, stretch receptors in the urinary bladder signal the brain of its need to empty. The signals become stronger as the bladder continues to fill. Embryologically, the trigone of the bladder is derived from the caudal end of mesonephric ducts, which is of intermediate mesodermal origin (the rest of the bladder is endodermal). In the female the mesonephric ducts regress, causing the trigone to be less prominent, but still present. Clinical significance The trigone can become irritated in a condition known as trigonitis Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', ''dolor'', ''rubor'', ''tumor'', and ''functio laesa''). Inflammation is a generic response, and therefore is considered a mechanism of innate immunity, whereas adaptive immunity is specific to each pathogen. Inflammation is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. The function of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear out damaged cells and tissues, and initiate tissue repair. Too little inflammation could lead to progressive tissue destruction by the harmful stimulus (e.g. bacteria) and compromise the survival of the organism. However inflammation can also have negative effects. Too much inflammation, in the form of chronic inflammation, is associated with variou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. The typical adult human bladder will hold between 300 and (10 and ) before the urge to empty occurs, but can hold considerably more. The Latin phrase for "urinary bladder" is ''vesica urinaria'', and the term ''vesical'' or prefix ''vesico-'' appear in connection with associated structures such as vesical veins. The modern Latin word for "bladder" – ''cystis'' – appears in associated terms such as cystitis (inflammation of the bladder). Structure In humans, the bladder is a hollow muscular organ situated at the base of the pelvis. In gross anatomy, the bladder can be divided into a broad (base), a body, an apex, and a neck. The apex (also called the vertex) is directed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrocautery
Cauterization (or cauterisation, or cautery) is a medical practice or technique of burning a part of a body to remove or close off a part of it. It destroys some tissue in an attempt to mitigate bleeding and damage, remove an undesired growth, or minimize other potential medical harm, such as infections when antibiotics are unavailable. The practice was once widespread for treatment of wounds. Its utility before the advent of antibiotics was said to be effective at more than one level: *To prevent exsanguination *To close amputations Cautery was historically believed to prevent infection, but current research shows that cautery actually increases the risk for infection by causing more tissue damage and providing a more hospitable environment for bacterial growth. Actual cautery refers to the metal device, generally heated to a dull red glow, that a physician applies to produce blisters, to stop bleeding of a blood vessel, and for other similar purposes., page 16. The main fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Relaxants
A muscle relaxant is a drug that affects skeletal muscle function and decreases the muscle tone. It may be used to alleviate symptoms such as muscle spasms, pain, and hyperreflexia. The term "muscle relaxant" is used to refer to two major therapeutic groups: Neuromuscular-blocking drugs, neuromuscular blockers and Antispasmodic, spasmolytics. Neuromuscular blockers act by interfering with transmission at the neuromuscular end plate and have no central nervous system (CNS) activity. They are often used during surgical procedures and in intensive care and emergency medicine to cause temporary paralysis. Spasmolytics, also known as "centrally acting" muscle relaxant, are used to alleviate musculoskeletal pain and spasms and to reduce spasticity in a variety of neurological conditions. While both neuromuscular blockers and spasmolytics are often grouped together as muscle relaxant, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antispasmodics
An antispasmodic (synonym: spasmolytic) is a pharmaceutical drug or other agent that suppresses muscle spasms. Smooth muscle spasm One type of antispasmodics is used for smooth muscle relaxation, especially in tubular organs of the gastrointestinal tract. The effect is to prevent spasms of the stomach, intestine or urinary bladder. Both dicyclomine and hyoscyamine are antispasmodic due to their anticholinergic action. Both of these drugs have side effects common to anticholinergics and can worsen gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Papaverine is an opium alkaloid used to treat visceral spasms, particularly those of the intestines. Mebeverine is a papaverine analog and spasmolytic with a strong and selective action on the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract, particularly of the colon. Despite being anticholinergic, it does not have the systemic anticholinergic side effects seen in other such drugs. Peppermint oil has been traditionally used as an antispasmodic, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, treatment and antibiotic prophylaxis, prevention of such infections. They may either bactericide, kill or bacteriostatic agent, inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the ones which cause the common cold or influenza. Drugs which inhibit growth of viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals. Antibiotics are also not effective against fungi. Drugs which inhibit growth of fungi are called antifungal drugs. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek language, Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiseptics
An antiseptic ( and ) is an antimicrobial substance or compound that is applied to living tissue to reduce the possibility of sepsis, infection, or putrefaction. Antiseptics are generally distinguished from ''antibiotics'' by the latter's ability to safely destroy bacteria within the body, and from ''disinfectants'', which destroy microorganisms found on non-living objects. Antibacterials include antiseptics that have the proven ability to act against bacteria. Microbicides which destroy virus particles are called viricides or antivirals. Antifungals, also known as antimycotics, are pharmaceutical fungicides used to treat and prevent mycosis (fungal infection). Surgery Antiseptic practices evolved in the 19th century through multiple individuals. Ignaz Semmelweis showed already in 1847-1848 that hand washing prior to delivery reduced puerperal fever. Despite this, many hospitals continued to practice surgery in unsanitary conditions, with some surgeons taking pride in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urethrotomy
A urethrotomy is an operation which involves incision of the urethra, especially for relief of a stricture. It is most often performed in the outpatient setting, with the patient (usually) being discharged from the hospital or surgery center within six hours from the procedure's inception. Urethrotomy (also referred to as DVIU, or Direct Visual Internal Urethrotomy) is a popular treatment for male urethral strictures. However, the performance characteristics are poor. Success is less than 9% for the first or subsequent urethrotomies. Most patients will be expected to experience failure with longer followup and the expected long-term success rate from any urethrotomy approach is 0%. Beginning in 2003, several urology residency programs in the northeastern section of the United States began advocating the use of urethrotomy as initial treatment in the young stricture patient, versus urethral dilatation. It is theorized that the one-to-two years of relief from stricture disease will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryosurgery
Cryosurgery (with ''cryo'' from the Ancient Greek ) is the use of extreme cold in surgery to destroy abnormal or diseased tissue; thus, it is the surgical application of cryoablation. Cryosurgery has been historically used to treat a number of diseases and disorders, especially a variety of benign and malignant skin conditions. History In 1841, English physician James Arnott described therapeutic applications of extremely cold temperatures, namely a mixture of crushed ice and salt applied locally (to skin or mucous membrane). He theorized his technique was capable of "arresting the accompanying inflammation, and perhaps destroying the vitality of the cancer cell." His works were the first to hypothesize that extreme cold could be used to selectively damage or destroy harmful tissue. Uses Warts, moles, skin tags, solar keratoses, molluscum, Morton's neuroma and small skin cancers are candidates for cryosurgical treatment. Several internal disorders are also treat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
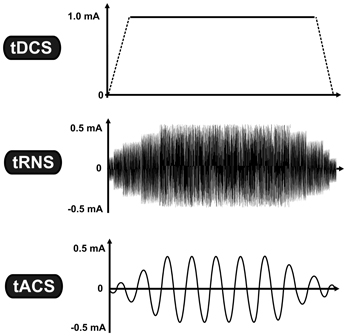
Neurostimulation
Neurostimulation is the purposeful modulation of the nervous system's activity using invasive (e.g. microelectrodes) or Non-invasive procedure, non-invasive means (e.g. transcranial magnetic stimulation, transcranial electric stimulation such as transcranial direct-current stimulation, tDCS or transcranial alternating current stimulation, tACS). Neurostimulation usually refers to the electromagnetic approaches to Neuromodulation (medicine), neuromodulation. Neurostimulation technology can improve the life quality of those who are severely paralyzed or have profound losses to various sense organs, as well as for permanent reduction of severe, chronic pain which would otherwise require constant (around-the-clock), high-dose opioid therapy (such as neuropathic pain and spinal-cord injury). It serves as the key part of neural prosthetics for hearing aids, artificial vision, artificial limbs, and brain-machine interfaces. In the case of neural stimulation, mostly an electrical stimulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Bladder Disorders
Urinary bladder disease includes urinary bladder inflammation such as cystitis, bladder rupture and bladder obstruction (tamponade). Cystitis is common, sometimes referred to as urinary tract infection (UTI) caused by bacteria, bladder rupture occurs when the bladder is overfilled and not emptied while bladder tamponade is a result of blood clot formation near the bladder outlet. Cystitis Cystitis is a urinary bladder inflammation that results from any one of a number of distinct syndromes. It is most commonly caused by a bacterial infection in which case it is referred to as a urinary tract infection. Bladder trauma Bladder rupture (rupture of bladder, ) may occur if the bladder is overfilled and not emptied. This can occur in the case of binge drinkers who have consumed large quantities of fluids, but are not conscious of the need to urinate due to stupor. This condition is very rare in women, but does occur. Signs and symptoms include localized pain and uraemia (poisoning due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |