|
Trifluridine Tipiracil
Trifluridine (also called trifluorothymidine; abbreviation TFT or FTD) is an anti-herpesvirus antiviral drug, used primarily on the eye. It was sold under the trade name Viroptic by Glaxo Wellcome, now merged into GlaxoSmithKline. The brand is now owned by Monarch Pharmaceuticals, which is wholly owned by King Pharmaceuticals. Trifluridine was approved for medical use in 1980. It is also a component of the anti-cancer drug trifluridine/tipiracil, which is taken by mouth. Medical uses Trifluridine eye drops are used for the treatment of keratitis and keratoconjunctivitis caused by the herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2, as well as for prevention and treatment of vaccinia virus infections of the eye. A Cochrane Systematic Review showed that trifluridine and aciclovir were a more effective treatment than idoxuridine or vidarabine, significantly increasing the relative number of successfully healed eyes in one to two weeks. For cancer treatment, the combination trifluridine/tipira ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tipiracil
Tipiracil is a drug used in the treatment of cancer. It is approved for use in form of the combination drug trifluridine/tipiracil for the treatment of unresectable advanced or recurrent colorectal cancer. Tipiracil helps maintain the blood concentration of trifluridine by inhibiting the enzyme thymidine phosphorylase which metabolizes trifluridine. Adverse effects Adverse effects were not assessed independently of trifluridine, but only in the combination drug. Interactions Only ''in vitro'' interaction studies are available. In these, tipiracil was transported by the solute carrier proteins SLC22A2 and SLC47A1. Drugs that interact with these transporters could influence blood plasma concentrations of tipiracil. Pharmacology Mechanism of action Tipiracil is a thymidine phosphorylase (TPase) inhibitor and inhibits degradation of trifluridine by inhibiting TPase, thus increasing systemic exposure to trifluridine when tipiracil is given together with trifluridine. Phar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edema
Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels tight, the area may feel heavy, and joint stiffness. Other symptoms depend on the underlying cause. Causes may include venous insufficiency, heart failure, kidney problems, low protein levels, liver problems, deep vein thrombosis, infections, angioedema, certain medications, and lymphedema. It may also occur after prolonged sitting or standing and during menstruation or pregnancy. The condition is more concerning if it starts suddenly, or pain or shortness of breath is present. Treatment depends on the underlying cause. If the underlying mechanism involves sodium retention, decreased salt intake and a diuretic may be used. Elevating the legs and support stockings may be useful for edema of the legs. Older people are more commonly affected. The wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and lens, the cornea refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical power. In humans, the refractive power of the cornea is approximately 43 dioptres. The cornea can be reshaped by surgical procedures such as LASIK. While the cornea contributes most of the eye's focusing power, its focus is fixed. Accommodation (the refocusing of light to better view near objects) is accomplished by changing the geometry of the lens. Medical terms related to the cornea often start with the prefix "'' kerat-''" from the Greek word κέρας, ''horn''. Structure The cornea has unmyelinated nerve endings sensitive to touch, temperature and chemicals; a touch of the cornea causes an involuntary reflex to close the eyelid. Because transparency is of prime importance, the healthy cornea does not have or need blood vess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA and RNA. Dictated by specific hydrogen bonding patterns, "Watson–Crick" (or "Watson–Crick–Franklin") base pairs ( guanine– cytosine and adenine– thymine) allow the DNA helix to maintain a regular helical structure that is subtly dependent on its nucleotide sequence. The complementary nature of this based-paired structure provides a redundant copy of the genetic information encoded within each strand of DNA. The regular structure and data redundancy provided by the DNA double helix make DNA well suited to the storage of genetic information, while base-pairing between DNA and incoming nucleotides provides the mechanism through which DNA polymerase replicates DNA and RNA polymerase transcribes DNA into RNA. Many DNA-binding p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uracil
Uracil () (symbol U or Ura) is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid RNA. The others are adenine (A), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). In RNA, uracil binds to adenine via two hydrogen bonds. In DNA, the uracil nucleobase is replaced by thymine (T). Uracil is a demethylated form of thymine. Uracil is a common and naturally occurring pyrimidine derivative. The name "uracil" was coined in 1885 by the German chemist Robert Behrend, who was attempting to synthesize derivatives of uric acid. Originally discovered in 1900 by Alberto Ascoli, it was isolated by hydrolysis of yeast nuclein; it was also found in bovine thymus and spleen, herring sperm, and wheat germ. It is a planar, unsaturated compound that has the ability to absorb light. Based on 12C/13C isotopic ratios of organic compounds found in the Murchison meteorite, it is believed that uracil, xanthine, and related molecules can also be formed extraterrestrially. Data from the Cassini mission, orbitin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritance. This is essential for cell division during growth and repair of damaged tissues, while it also ensures that each of the new cells receives its own copy of the DNA. The cell possesses the distinctive property of division, which makes replication of DNA essential. DNA is made up of a double helix of two complementary strands. The double helix describes the appearance of a double-stranded DNA which is thus composed of two linear strands that run opposite to each other and twist together to form. During replication, these strands are separated. Each strand of the original DNA molecule then serves as a template for the production of its counterpart, a process referred to as semiconservative replication. As a result of semi-conservativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deoxyuridine
Deoxyuridine (dU) is a compound and a nucleoside.It belongs to a class of compounds known as Pyrimidine 2'-deoxyribonucleosides and closely resembles the chemical composition of uridine but without the presence of the 2' hydroxyl group. Idoxuridine and Trifluridine are variants of deoxyuridine used as antiviral drugs. They are similar enough to be incorporated as part of DNA replication, but they possess side groups on the uracil component (an iodine and a CF3 group, respectively), that prevent base pair A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA ...ing. A known use of dU is as a precursor in the synthesis of Edoxudine. This compound exists in all living organisms and can become part of DNA in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells through two mechanisms. The first is the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
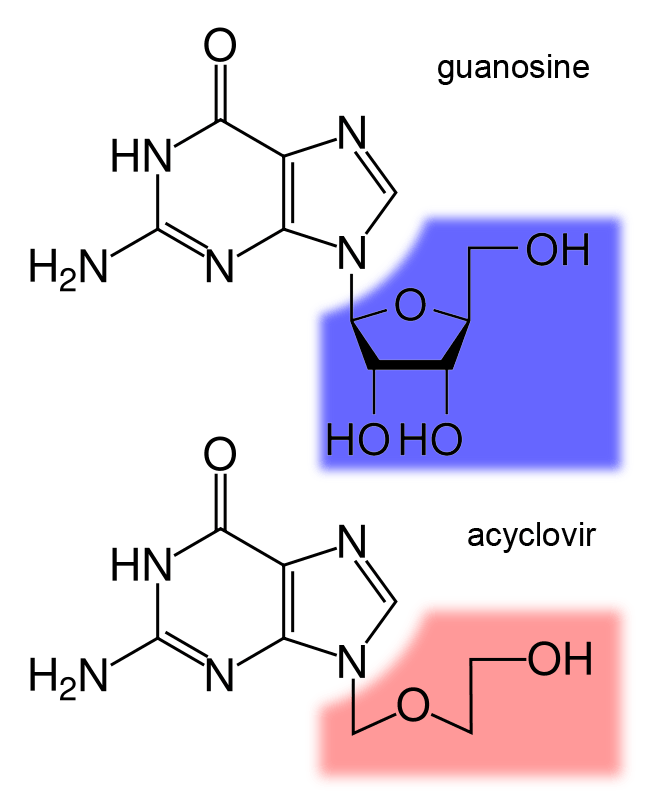
Nucleoside Analogue
Nucleoside analogues are nucleosides which contain a nucleic acid analogue and a sugar. Nucleotide analogs are nucleotides which contain a nucleic acid analogue, a sugar, and a phosphate group with one to three phosphates. Nucleoside and nucleotide analogues can be used in therapeutic drugs, including a range of antiviral products used to prevent viral replication in infected cells. The most commonly used is acyclovir, although its inclusion in this category is uncertain, because it acts as a nucleoside but contains no actual sugar, as the sugar ring is replaced by an open-chain structure. Nucleotide and nucleoside analogues can also be found naturally. Examples include ddhCTP (3ʹ-deoxy-3′,4ʹdidehydro-CTP) produced by the human antiviral protein viperin and sinefungin (a S-Adenosyl methionine analogue) produced by some ''Streptomyces''. Function These agents can be used against hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, herpes simplex, and HIV. Once they are phosphorylated, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drugs
A drug is any chemical substance that causes a change in an organism's physiology or psychology when consumed. Drugs are typically distinguished from food and substances that provide nutritional support. Consumption of drugs can be via inhalation, injection, smoking, ingestion, absorption via a patch on the skin, suppository, or dissolution under the tongue. In pharmacology, a drug is a chemical substance, typically of known structure, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. A pharmaceutical drug, also called a medication or medicine, is a chemical substance used to treat, cure, prevent, or diagnose a disease or to promote well-being. Traditionally drugs were obtained through extraction from medicinal plants, but more recently also by organic synthesis. Pharmaceutical drugs may be used for a limited duration, or on a regular basis for chronic disorders. Pharmaceutical drugs are often classified into drug classes—groups of r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zidovudine
Zidovudine (ZDV), also known as azidothymidine (AZT), is an antiretroviral medication used to prevent and treat HIV/AIDS. It is generally recommended for use in combination with other antiretrovirals. It may be used to prevent mother-to-child spread during birth or after a needlestick injury or other potential exposure. It is sold both by itself and together as lamivudine/zidovudine and abacavir/lamivudine/zidovudine. It can be used by mouth or by slow injection into a vein. Common side effects include headaches, fever, and nausea. Serious side effects include liver problems, muscle damage, and high blood lactate levels. It is commonly used in pregnancy and appears to be safe for the baby. ZDV is of the nucleoside analog reverse-transcriptase inhibitor (NRTI) class. It works by inhibiting the enzyme reverse transcriptase that HIV uses to make DNA and therefore decreases replication of the virus. Zidovudine was first described in 1964. It was approved in the United St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Plasma
Blood plasma is a light amber-colored liquid component of blood in which blood cells are absent, but contains proteins and other constituents of whole blood in suspension. It makes up about 55% of the body's total blood volume. It is the intravascular part of extracellular fluid (all body fluid outside cells). It is mostly water (up to 95% by volume), and contains important dissolved proteins (6–8%; e.g., serum albumins, globulins, and fibrinogen), glucose, clotting factors, electrolytes (, , , , , etc.), hormones, carbon dioxide (plasma being the main medium for excretory product transportation), and oxygen. It plays a vital role in an intravascular osmotic effect that keeps electrolyte concentration balanced and protects the body from infection and other blood-related disorders. Blood plasma is separated from the blood by spinning a vessel of fresh blood containing an anticoagulant in a centrifuge until the blood cells fall to the bottom of the tube. The bloo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equilibrative Nucleoside Transporter 2
Equilibrative nucleoside transporter 2 (ENT2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC29A2'' gene. See also * Solute carrier family * Equilibrative nucleoside transporters * Nucleoside transporter Nucleoside transporters (NTs) are a group of membrane transport proteins which transport nucleoside substrates like adenosine Adenosine ( symbol A) is an organic compound that occurs widely in nature in the form of diverse derivatives. The ...s References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Solute carrier family Neurotransmitter transporters {{membrane-protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |