|
Treponema Pallidum
''Treponema pallidum'', formerly known as ''Spirochaeta pallida'', is a Microaerophile, microaerophilic, Gram-negative bacteria, gram-negative, spirochaete bacterium with subspecies that cause the diseases syphilis, bejel (also known as endemic syphilis), and yaws. It is known to be transmitted only among humans and baboons. ''T. pallidum'' can enter the host through mucosal membranes or open lesions in the skin and is primarily spread through sexual contact. It is a helically coiled microorganism usually 6–15 μm long and 0.1–0.2 μm wide. ''T. pallidum'''s lack of both a Citric acid cycle, tricarboxylic acid cycle and processes for oxidative phosphorylation results in minimal metabolic activity. As a Chemoorganoheterotrophic, chemoorganoheterotroph, ''Treponema pallidum'' is an obligate parasite that acquires its glucose carbon source from its host. Glucose can be used not only as a primary carbon source but also in glycolytic mechanisms to generate ATP needed to power the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fritz Schaudinn
Fritz Richard Schaudinn (19 September 1871 – 22 June 1906) was a German zoologist. Born in Röseningken (now in Ozyorsky District) in the Province of Prussia, he co-discovered, with Erich Hoffmann in 1905, the causative agent of syphilis, ''Spirochaeta pallida'' (also known as ''Treponema pallidum''). The work was carried out at the Berlin Charité. Among Schaudinn's other contributions to medicine include his work in the field of amoebic dysentery, sleeping sickness and his confirmation of the work of Sir Ronald Ross and Giovanni Battista Grassi (1854–1925) in the field of malaria research. He also demonstrated that human hookworm infection is contracted through the skin of the feet. He made noted contributions to zoology and was one of the developers of protozoology as an experimental science. Schaudinn was a graduate in zoology of the Friedrich Wilhelm University in Berlin. Since 2002 an annual medical prize has been awarded in his name. In 1898 with zoologist F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dark-field Illumination
Dark-field microscopy, also called dark-ground microscopy, describes microscopy methods, in both light and electron microscopy, which exclude the unscattered beam from the image. Consequently, the field around the specimen (i.e., where there is no specimen to scatter the beam) is generally dark. In optical microscopes a darkfield condenser lens must be used, which directs a cone of light away from the objective lens. To maximize the scattered light-gathering power of the objective lens, oil immersion is used and the numerical aperture (NA) of the objective lens must be less than 1.0. Objective lenses with a higher NA can be used but only if they have an adjustable diaphragm, which reduces the NA. Often these objective lenses have a NA that is variable from 0.7 to 1.25. Light microscopy applications In optical microscopy, dark-field describes an illumination technique used to enhance the contrast in unstained samples. It works by illuminating the sample with light that wil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dieterle Stain
The Dieterle stain is a way of marking tissue for microscopic examination. The key reagent of Dieterle stain is silver nitrate. It can stain microbes like ''Treponema pallidum'' in grey or black and background in yellow. It is used to find the organisms that cause cat-scratch disease ''(Bartonella henselae'') and syphilis (''Treponema pallidum'') and sensitive for ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''. Additional images Image:Treponema pallidum - very high mag.jpg See also *Staining Staining is a technique used to enhance contrast in samples, generally at the Microscope, microscopic level. Stains and dyes are frequently used in histology (microscopic study of biological tissue (biology), tissues), in cytology (microscopic ... * Warthin–Starry stain References External linksDieterle stain{{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160303194222/http://www.mondofacto.com/facts/dictionary?Dieterle%27s+stain , date=2016-03-03 - mondofacto.com. Staining ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charité
The Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin (Charité – Berlin University of Medicine; ) is Europe's List of hospitals by capacity, largest university hospital, affiliated with Humboldt University of Berlin, Humboldt University and the Free University of Berlin. The Charité traces its origins to 1710. The complex is spread over four campuses and comprises around 3,000 beds, 15,500 staff, 8,000 students, and more than 60 operating theaters, and has a turnover of two billion euros annually. The modern history of medicine has been significantly influenced by scientists who worked at the Charité. Rudolf Virchow was the founder of cellular pathology, while Robert Koch developed vaccines for anthrax, cholera, and tuberculosis. For his life's work Koch is seen as one of the founders of modern medicine. More than half of all German Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, Nobel Prize winners in Physiology or Medicine, including Emil von Behring, Robert Koch, and Paul Ehrlich, have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinta (disease)
Pinta (also known as azul, carate, empeines, lota, mal del pinto, and tina) is a human skin disease caused by infection with the spirochete '' Treponema carateum'', which is morphologically and serologically indistinguishable from the bacterium that causes syphilis and bejel. The disease was previously known to be endemic to Mexico, Central America, and South America; it may have been eradicated since, with the latest case occurring in Brazil in 2020. Signs and symptoms Pinta, the least severe of the treponemal infections being limited to the skin, is thought to be transmitted by skin-to-skin contact (similar to bejel and yaws), and after an incubation period of two to three weeks, produces a raised papule, which enlarges and becomes hyperkeratotic (scaly/flaky). Lesions are usually present on the exposed surface of arms and legs. Local lymph nodes might be enlarged. Three to nine months later, further thickened and flat lesions (pintids) appear all over the body. These gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
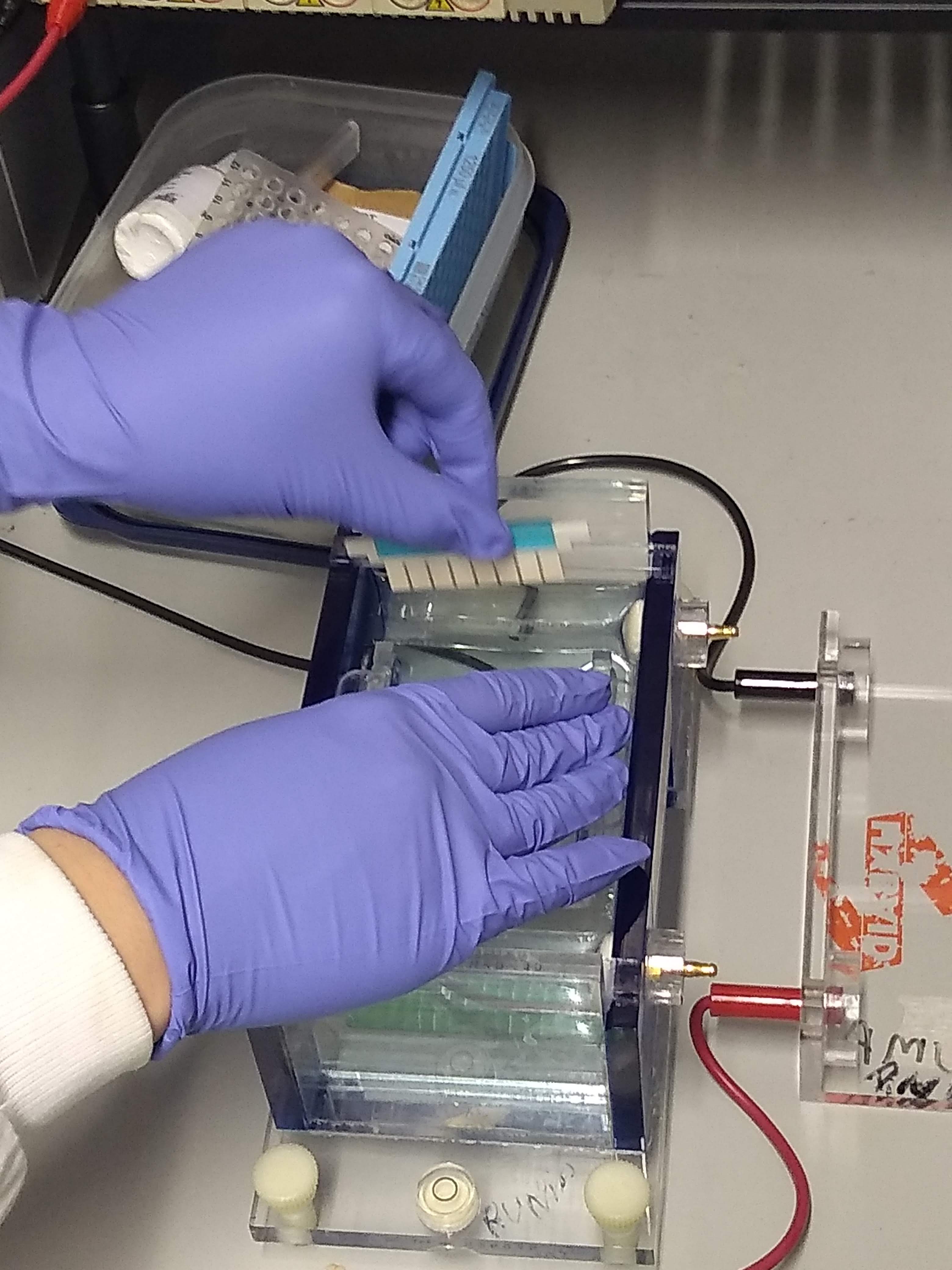
Gel Electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is an electrophoresis method for separation and analysis of biomacromolecules (DNA, RNA, proteins, etc.) and their fragments, based on their size and charge through a gel. It is used in clinical chemistry to separate proteins by charge or size (IEF agarose, essentially size independent) and in biochemistry and molecular biology to separate a mixed population of DNA and RNA fragments by length, to estimate the size of DNA and RNA fragments, or to separate proteins by charge. Nucleic acid molecules are separated by applying an electric field to move the negatively charged molecules through a gel matrix of agarose, polyacrylamide, or other substances. Shorter molecules move faster and migrate farther than longer ones because shorter molecules migrate more easily through the pores of the gel. This phenomenon is called sieving. Proteins are separated by the charge in agarose because the pores of the gel are too large to sieve proteins. Gel electrophoresi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Restriction Digest
In molecular biology, a restriction digest is a procedure used to prepare DNA for analysis or other processing. It is sometimes termed ''DNA fragmentation'', though this term is used for other procedures as well. In a restriction digest, DNA molecules are cleaved at specific regions of 4-12 nucleotides in length (restriction sites) by use of restriction enzymes which recognize these sequences. Hartl, Daniel L., Jones, Elizabeth W. (2001), ''Genetics: Analysis of Genes and Genomes'', Fifth Edition. The resulting digested DNA is very often selectively amplified using polymerase chain reaction (PCR), making it more suitable for analytical techniques such as agarose gel electrophoresis, and chromatography. It is used in genetic fingerprinting, plasmid subcloning, and RFLP analysis. Restriction site A given restriction enzyme cuts DNA segments within a specific nucleotide sequence, at what is called a restriction site. These ''recognition sequences'' are typically four, six, eig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymerase Chain Reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to make millions to billions of copies of a specific DNA sample rapidly, allowing scientists to amplify a very small sample of DNA (or a part of it) sufficiently to enable detailed study. PCR was invented in 1983 by American biochemist Kary Mullis at Cetus Corporation. Mullis and biochemist Michael Smith (chemist), Michael Smith, who had developed other essential ways of manipulating DNA, were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993. PCR is fundamental to many of the procedures used in genetic testing and research, including analysis of Ancient DNA, ancient samples of DNA and identification of infectious agents. Using PCR, copies of very small amounts of DNA sequences are exponentially amplified in a series of cycles of temperature changes. PCR is now a common and often indispensable technique used in medical laboratory research for a broad variety of applications including biomedical research and forensic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
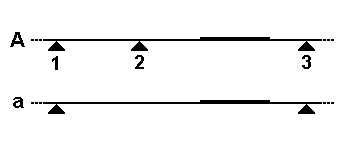
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism
In molecular biology, restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) is a technique that exploits variations in homologous DNA sequences, known as polymorphisms, populations, or species or to pinpoint the locations of genes within a sequence. The term may refer to a polymorphism itself, as detected through the differing locations of restriction enzyme sites, or to a related laboratory technique by which such differences can be illustrated. In RFLP analysis, a DNA sample is digested into fragments by one or more restriction enzymes, and the resulting ''restriction fragments'' are then separated by gel electrophoresis according to their size. RFLP analysis is now largely obsolete due to the emergence of inexpensive DNA sequencing technologies, but it was the first DNA profiling technique inexpensive enough to see widespread application. RFLP analysis was an important early tool in genome mapping, localization of genes for genetic disorders, determination of risk for disease, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serology
Serology is the scientific study of Serum (blood), serum and other body fluids. In practice, the term usually refers to the medical diagnosis, diagnostic identification of Antibody, antibodies in the serum. Such antibodies are typically formed in response to an infection (against a given microorganism), against other foreign proteins (in response, for example, to a Acute hemolytic transfusion reaction, mismatched blood transfusion), or to one's own proteins (in instances of autoimmune disease). In either case, the procedure is simple. Serological tests Serological tests are diagnostic methods that are used to identify antibodies and antigens in a patient's sample. Serological tests may be performed to diagnose infections and autoimmune illnesses, to check if a person has immunity (medical), immunity to certain diseases, and in many other situations, such as determining an individual's blood type. Serological tests may also be used in forensic serology to investigate crime scene evid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparative Anatomy
Comparative anatomy is the study of similarities and differences in the anatomy of different species. It is closely related to evolutionary biology and phylogeny (the evolution of species). The science began in the classical era, continuing in the early modern period with work by Pierre Belon who noted the similarities of the skeletons of birds and humans. Comparative anatomy has provided evidence of common descent, and has assisted in the classification of animals. History The first specifically anatomical investigation separate from a surgical or medical procedure is associated by Alcmaeon of Croton. Leonardo da Vinci made notes for a planned anatomical treatise in which he intended to compare the hands of various animals including bears. Pierre Belon, a French naturalist born in 1517, conducted research and held discussions on dolphin embryos as well as the comparisons between the skeletons of birds to the skeletons of humans. His research led to modern comparative a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |