|
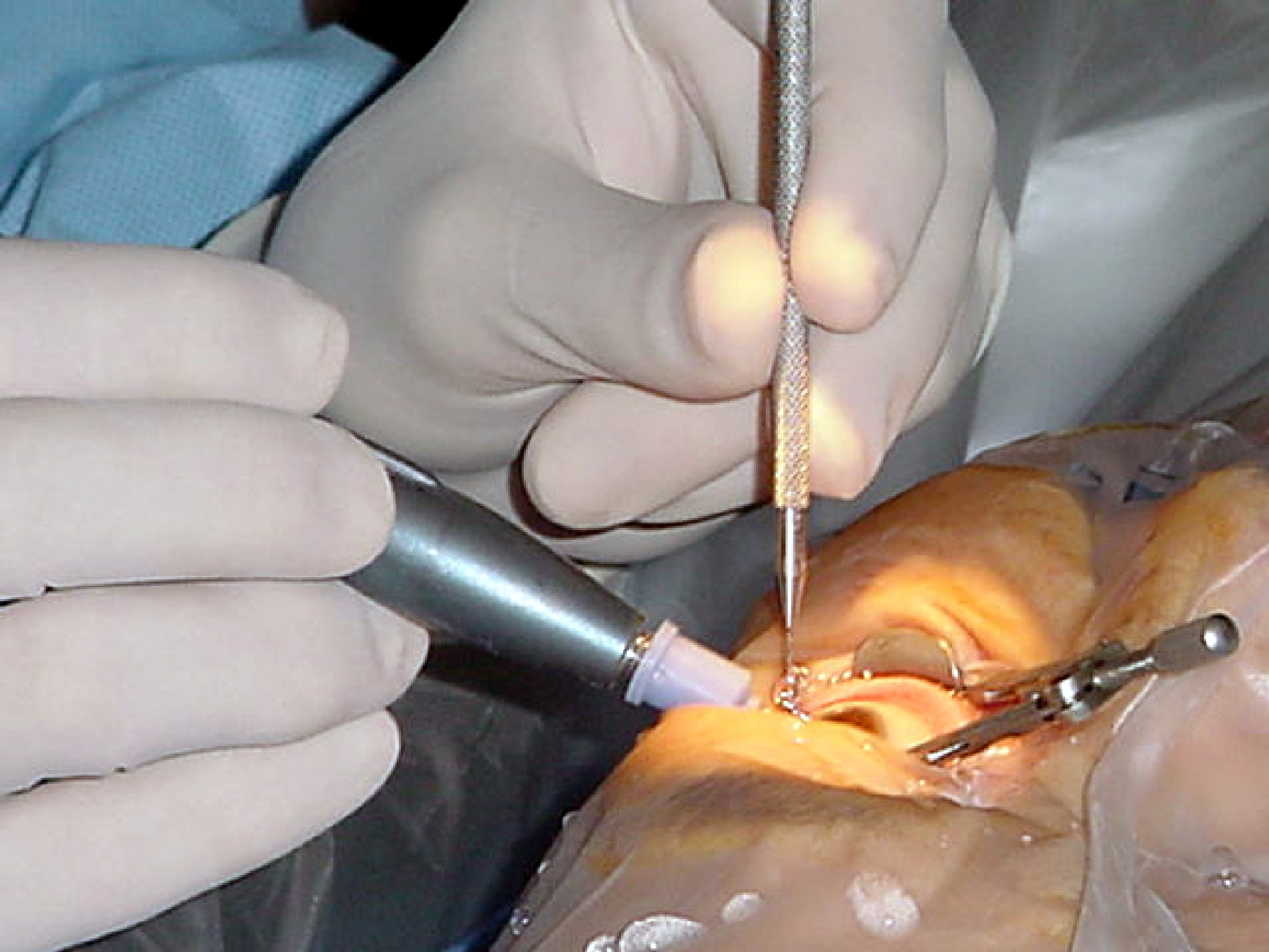
Trepanotrabeculectomy
Trabeculectomy is a surgical procedure used in the treatment of glaucoma to relieve intraocular pressure by removing part of the eye's trabecular meshwork and adjacent structures. It is the most common glaucoma surgery performed and allows drainage of aqueous humor from within the eye to underneath the conjunctiva where it is absorbed. This outpatient procedure was most commonly performed under monitored anesthesia care using a retrobulbar block or peribulbar block or a combination of topical and subtenon (Tenon's capsule) anesthesia. Due to the higher risks associated with bulbar blocks, topical analgesia with mild sedation is becoming more common. Rarely general anesthesia will be used, in patients with an inability to cooperate during surgery. Procedure An initial pocket is created under the conjunctiva and Tenon's capsule and the wound bed is treated for several seconds to minutes with mitomycin C (MMC, 0.5–0.2 mg/ml) or 5-fluorouracil (5-FU, 50 mg/ml) soaked spo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Surgery
Eye surgery, also known as ophthalmic surgery or ocular surgery, is surgery performed on the eye or its adnexa. Eye surgery is part of ophthalmology and is performed by an ophthalmologist or eye surgeon. The eye is a fragile organ, and requires due care before, during, and after a surgical procedure to minimize or prevent further damage. An eye surgeon is responsible for selecting the appropriate surgical procedure for the patient, and for taking the necessary safety precautions. Mentions of eye surgery can be found in several ancient texts dating back as early as 1800 BC, with cataract treatment starting in the fifth century BC. It continues to be a widely practiced class of surgery, with various techniques having been developed for treating eye problems. Preparation and precautions Since the eye is heavily supplied by nerves, anesthesia is essential. Local anesthesia is most commonly used. Topical anesthesia using lidocaine topical gel is often used for quick procedures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that can lead to damage of the optic nerve. The optic nerve transmits visual information from the eye to the brain. Glaucoma may cause vision loss if left untreated. It has been called the "silent thief of sight" because the loss of vision usually occurs slowly over a long period of time. A major risk factor for glaucoma is increased pressure within the eye, known as Intraocular pressure, intraocular pressure (IOP). It is associated with old age, a family history of glaucoma, and certain medical conditions or the use of some medications. The word ''glaucoma'' comes from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning 'gleaming, blue-green, gray'. Of the different types of glaucoma, the most common are called open-angle glaucoma and closed-angle glaucoma. Inside the eye, a liquid called Aqueous humour, aqueous humor helps to maintain shape and provides nutrients. The aqueous humor normally drains through the trabecular meshwork. In open-angle glaucoma, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iridectomy
An iridectomy, also known as a surgical iridectomy or corectomy, is the surgical removal of part of the iris.Cline D; Hofstetter HW; Griffin JR. ''Dictionary of Visual Science''. 4th ed. Butterworth-Heinemann, Boston 1997. Surgery Encyclopedia - "Iridectomy." Encyclopedia of Surgery: A Guide for Patients and Caregivers. Retrieved May 20, 2006. These procedures are most frequently performed in the treatment of closed-angle glaucoma and iris . Comparison with Nd:YAG laser iridotomy In[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Gordon Watson
Peter Gordon Watson (30 April 1930 – 31 January 2017) was a British ophthalmologist, professor and researcher better known as the inventor of surgical procedure trabeculectomy. With John Cairns, in the 1970s, Watson developed trabeculectomy, the most common form of surgery for glaucoma today. His 1977 textbook, ''The Sclera and Systemic Disorders'' (third edition published in 2012) is still considered the only comprehensive textbook on disease of the sclera. Biography Peter Gordon Watson was born on April 30, 1930, in Newport, Wales, United Kingdom, the son of Ralph and Renée née Smith. He studied and trained in ophthalmology at University College Hospital, London, Moorfields Eye Hospital, London and the Institute of Ophthalmology. Watson held several positions including president of the Academia Ophthalmology Internationalis, member of the International Council of Ophthalmology, Editor of ''Eye'' magazine, Founder and Chair of the Cambridge Eye Trust, and Deputy Hospitaller ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trabectome
The Trabectome is a surgical device that can be used for ab interno trabeculotomy, a minimally invasive glaucoma surgery for the surgical management of adult, juvenile, and infantile glaucoma. The trabecular meshwork is a major site of resistance to aqueous humor outflow. As angle surgeries such as Trabectome follow the physiologic outflow pathway, the risk of complications is significantly lower than filtering surgeries. Hypotony with damage to the macula (hypotony maculopathy), can occur with pressures below 5 mmHg, for instance, after traditional trabeculectomy, because of the episcleral venous pressure limit. The Trabectome handpiece is inserted into the anterior chamber, its tip positioned into Schlemm's canal, and advanced to the left and to the right. Different from cautery, the tip generates plasma to molecularize the trabecular meshwork and remove it drag-free and with minimal thermal effect. Active irrigation of the trabectome surgery system helps to keep the anterior c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polytetrafluoroethylene
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer of tetrafluoroethylene, and has numerous applications because it is chemically inert. The commonly known brand name of PTFE-based composition is Teflon by Chemours, a corporate spin-off, spin-off from DuPont (1802–2017), DuPont, which originally invented the compound in 1938. Polytetrafluoroethylene is a fluorocarbon solid, as it is a high-molecular-weight polymer consisting wholly of carbon and fluorine. PTFE is hydrophobic: neither water nor water-containing substances Wetting, wet PTFE, as fluorocarbons exhibit only small London dispersion forces due to the low polarizability, electric polarizability of fluorine. PTFE has one of the lowest Friction#Coefficient of friction, coefficients of friction of any solid. Polytetrafluoroethylene is used as a non-stick coating for Cookware and bakeware, pans and other Cookware and bakeware, cookware. It is Chemically inert, non-reactive, partly because of the strength of car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antifibrotic
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is the development of fibrous connective tissue in response to an injury. Fibrosis can be a normal connective tissue deposition or excessive tissue deposition caused by a disease. Repeated injuries, chronic inflammation and repair are susceptible to fibrosis, where an accidental excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix components, such as the collagen, is produced by fibroblasts, leading to the formation of a permanent fibrotic scar. In response to injury, this is called scarring, and if fibrosis arises from a single cell line, this is called a fibroma. Physiologically, fibrosis acts to deposit connective tissue, which can interfere with or totally inhibit the normal architecture and function of the underlying organ or tissue. Fibrosis can be used to describe the pathological state of excess deposition of fibrous tissue, as well as the process of connective tissue deposition in healing. Defined by the pathological accumulation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaucoma Valve
A glaucoma valve is a medical shunt used in the treatment of glaucoma to reduce the eye's intraocular pressure (IOP). Mechanism The device works by bypassing the trabecular meshwork and redirecting the outflow of aqueous humour through a small tube into an outlet chamber or bleb. The IOP generally decreases from around 33 to 10 mmHg by removing aqueous on average 2.75 microliters/min. Types The first glaucoma drainage implant was developed in 1966. Following on the success of the Molteno implant, several varieties of device have been developed from the original, the Baerveldt tube shunt, or the valved implants, such as the Ahmed glaucoma valve implant and the later generation pressure ridge Molteno implants. These are indicated for glaucoma patients not responding to maximal medical therapy, with previous failed guarded filtering surgery (trabeculectomy). The flow tube is inserted into the anterior chamber of the eye and the plate is implanted underneath the conjunctiva to all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypotony
Ocular hypotony, or ocular hypotension, or shortly hypotony, is the medical condition in which intraocular pressure (IOP) of the eye is very low. Description Normal IOP ranges between 10–20 mm Hg. The eye is considered hypotonous if the IOP is ≤5 mm Hg (some sources say IOP less than 6.5 mmHg). Types Ocular hypotony is divided into statistical and clinical types. If intraocular pressure is low (less than 6.5 mm Hg) it is called statistical hypotony, and if the reduced IOP causes a decrease in vision, it is called clinical. Causes Hypotony may occur either due to decreased production of aqueous humor or due to increased outflow. Hypotony has many causes including post-surgical wound leak from the eye, chronic inflammation within the eye including iridocyclitis, hypoperfusion, tractional ciliary body detachment or retinal detachment. Eye inflammation, medications including anti glaucoma drugs, or proliferative vitreoretinopathy causes decreased production. Increased outflow or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endophthalmitis
Endophthalmitis, or endophthalmia, is inflammation of the interior cavity of the eye, usually caused by an infection. It is a possible complication of all intraocular surgeries, particularly cataract surgery, and can result in loss of vision or loss of the eye itself. Infection can be caused by bacteria or fungi, and is classified as exogenous (infection introduced by direct inoculation as in surgery or penetrating trauma), or endogenous (organisms carried by blood vessels to the eye from another site of infection and is more common in people who have an immunocompromised state). Other non-infectious causes include toxins, allergic reactions, and retained intraocular foreign bodies. Intravitreal injections are a rare cause, with an incidence rate usually less than 0.05%. Endophthalmitis requires immediate medical attention to ensure the condition is diagnosed as soon as possible and treatment is started in order to reduce the risk of the person losing vision in the eye. Treatment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciliary Body
The ciliary body is a part of the eye that includes the ciliary muscle, which controls the shape of the lens, and the ciliary epithelium, which produces the aqueous humor. The aqueous humor is produced in the non-pigmented portion of the ciliary body. The ciliary body is part of the uvea, the layer of tissue that delivers oxygen and nutrients to the eye tissues. The ciliary body joins the ora serrata of the choroid to the root of the iris.Cassin, B. and Solomon, S. ''Dictionary of Eye Terminology''. Gainesville, Florida: Triad Publishing Company, 1990. Structure The ciliary body is a ring-shaped thickening of tissue inside the eye that divides the posterior chamber from the vitreous body. It contains the ciliary muscle, vessels, and fibrous connective tissue. Folds on the inner ciliary epithelium are called ciliary processes, and these secrete aqueous humor into the posterior chamber. The aqueous humor then flows through the iris into the anterior chamber. The ciliary bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intraocular Pressure
Intraocular pressure (IOP) is the fluid pressure inside the eye. Tonometry is the method eye care professionals use to determine this. IOP is an important aspect in the evaluation of patients at risk of glaucoma. Most tonometers are calibrated to measure pressure in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). Physiology Intraocular pressure is determined by the production and drainage of aqueous humour by the ciliary body and its drainage via the trabecular meshwork and uveoscleral outflow. The reason for this is because the vitreous humour in the posterior segment has a relatively fixed volume and thus does not affect intraocular pressure regulation. An important quantitative relationship (Goldmann's equation) is as follows: :P_o = \frac + P_v Where: * P_o is the IOP in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) * F the rate of aqueous humour formation in microliters per minute (μL/min) * U the resorption of aqueous humour through the uveoscleral route (μL/min) * C is the facility of outflow in mic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |