|
Trellis (graph)
A trellis is a graph whose nodes are ordered into vertical slices (''time'') with every node at almost every time connected to at least one node at an earlier and at least one node at a later time. The earliest and latest times in the trellis have only one node (hence the "almost" in the preceding sentence). Trellises are used in encoders and decoders for communication theory and encryption. They are also the central datatype used in Baum–Welch algorithm or the Viterbi AlgorithmRyan, M. S., & Nudd, G. R. (1993). The viterbi algorithm. University of Warwick, Department of Computer Science. for Hidden Markov Models. The trellis graph is named for its similar appearance to an architectural trellis. References See also * Trellis modulation Trellis coded modulation (TCM) is a modulation scheme that transmits information with high efficiency over band-limited channels such as telephone lines. Gottfried Ungerboeck invented trellis modulation while working for IBM in the 1970 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graph (discrete Mathematics)
In discrete mathematics, particularly in graph theory, a graph is a structure consisting of a Set (mathematics), set of objects where some pairs of the objects are in some sense "related". The objects are represented by abstractions called ''Vertex (graph theory), vertices'' (also called ''nodes'' or ''points'') and each of the related pairs of vertices is called an ''edge'' (also called ''link'' or ''line''). Typically, a graph is depicted in diagrammatic form as a set of dots or circles for the vertices, joined by lines or curves for the edges. The edges may be directed or undirected. For example, if the vertices represent people at a party, and there is an edge between two people if they shake hands, then this graph is undirected because any person ''A'' can shake hands with a person ''B'' only if ''B'' also shakes hands with ''A''. In contrast, if an edge from a person ''A'' to a person ''B'' means that ''A'' owes money to ''B'', then this graph is directed, because owing mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communication Theory
Communication theory is a proposed description of communication phenomena, the relationships among them, a storyline describing these relationships, and an argument for these three elements. Communication theory provides a way of talking about and analyzing key events, processes, and commitments that together form communication. Theory can be seen as a way to map the world and make it navigable; communication theory gives us tools to answer empirical, conceptual, or practical communication questions. Communication is defined in both commonsense and specialized ways. Communication theory emphasizes its symbolic and social process aspects as seen from two perspectives—as exchange of information (the transmission perspective), and as work done to connect and thus enable that exchange (the ritual perspective). Sociolinguistic research in the 1950s and 1960s demonstrated that the level to which people change their formality of their language depends on the social context that they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encryption
In Cryptography law, cryptography, encryption (more specifically, Code, encoding) is the process of transforming information in a way that, ideally, only authorized parties can decode. This process converts the original representation of the information, known as plaintext, into an alternative form known as ciphertext. Despite its goal, encryption does not itself prevent interference but denies the intelligible content to a would-be interceptor. For technical reasons, an encryption scheme usually uses a pseudo-random encryption Key (cryptography), key generated by an algorithm. It is possible to decrypt the message without possessing the key but, for a well-designed encryption scheme, considerable computational resources and skills are required. An authorized recipient can easily decrypt the message with the key provided by the originator to recipients but not to unauthorized users. Historically, various forms of encryption have been used to aid in cryptography. Early encryption ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baum–Welch Algorithm
In electrical engineering, statistical computing and bioinformatics, the Baum–Welch algorithm is a special case of the expectation–maximization algorithm used to find the unknown parameters of a hidden Markov model (HMM). It makes use of the forward-backward algorithm to compute the statistics for the expectation step. The Baum–Welch algorithm, the primary method for inference in hidden Markov models, is numerically unstable due to its recursive calculation of joint probabilities. As the number of variables grows, these joint probabilities become increasingly small, leading to the forward recursions rapidly approaching values below machine precision. History The Baum–Welch algorithm was named after its inventors Leonard E. Baum and Lloyd R. Welch. The algorithm and the Hidden Markov models were first described in a series of articles by Baum and his peers at the IDA Center for Communications Research, Princeton in the late 1960s and early 1970s. One of the first major a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viterbi Algorithm
The Viterbi algorithm is a dynamic programming algorithm for obtaining the maximum a posteriori probability estimate of the most likely sequence of hidden states—called the Viterbi path—that results in a sequence of observed events. This is done especially in the context of Markov information sources and hidden Markov models (HMM). The algorithm has found universal application in decoding the convolutional codes used in both CDMA and GSM digital cellular, dial-up modems, satellite, deep-space communications, and 802.11 wireless LANs. It is now also commonly used in speech recognition, speech synthesis, diarization, keyword spotting, computational linguistics, and bioinformatics. For example, in speech-to-text (speech recognition), the acoustic signal is treated as the observed sequence of events, and a string of text is considered to be the "hidden cause" of the acoustic signal. The Viterbi algorithm finds the most likely string of text given the acoustic signal. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
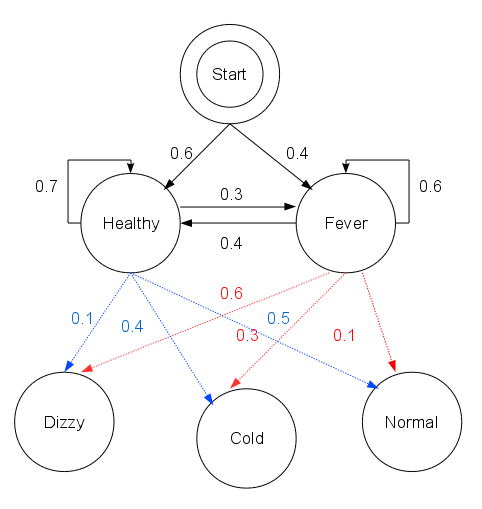
Hidden Markov Models
A hidden Markov model (HMM) is a Markov model in which the observations are dependent on a latent (or ''hidden'') Markov process (referred to as X). An HMM requires that there be an observable process Y whose outcomes depend on the outcomes of X in a known way. Since X cannot be observed directly, the goal is to learn about state of X by observing Y. By definition of being a Markov model, an HMM has an additional requirement that the outcome of Y at time t = t_0 must be "influenced" exclusively by the outcome of X at t = t_0 and that the outcomes of X and Y at t < t_0 must be conditionally independent of at given at time . Estimation of the parameters in an HMM can be performed using . For linear chain HMMs, the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trellis (architecture)
A trellis (French: ''treillage'') is an architectural structure, usually made from an open framework or lattice of interwoven or intersecting pieces of wood, bamboo or metal that is normally made to support and display climbing plants, especially shrubs.The Book of Garden Furniture C. Thonger, 1903 Types There are many types of trellis for different places and for different plants, from agricultural types, especially in , which are covered at , to garden uses for climbers such as |
Trellis Modulation
Trellis coded modulation (TCM) is a modulation scheme that transmits information with high efficiency over band-limited channels such as telephone lines. Gottfried Ungerboeck invented trellis modulation while working for IBM in the 1970s, and first described it in a conference paper in 1976. It went largely unnoticed, however, until he published a new, detailed exposition in 1982 that achieved sudden and widespread recognition. In the late 1980s, modems operating over plain old telephone service (''POTS'') typically achieved 9.6 kbit/s by employing four bits per symbol QAM modulation at 2,400 baud (symbols/second). This bit rate ceiling existed despite the best efforts of many researchers, and some engineers predicted that without a major upgrade of the public phone infrastructure, the maximum achievable rate for a POTS modem might be 14 kbit/s for two-way communication (3,429 baud × 4 bits/symbol, using QAM). 14 kbit/s is only 40% of the theoretical maximum bit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trellis Quantization
Trellis quantization is an algorithm that can improve data compression in DCT-based encoding methods. It is used to optimize residual DCT coefficients after motion estimation in lossy video compression encoders such as Xvid and x264. Trellis quantization reduces the size of some DCT coefficients while recovering others to take their place. This process can increase quality because coefficients chosen by Trellis have the lowest rate-distortion ratio. Trellis quantization effectively finds the optimal quantization for each block to maximize the PSNR relative to bitrate In telecommunications and computing, bit rate (bitrate or as a variable ''R'') is the number of bits that are conveyed or processed per unit of time. The bit rate is expressed in the unit bit per second (symbol: bit/s), often in conjunction .... It has varying effectiveness depending on the input data and compression method. ReferencesVirtualDub/Xvid guide mentioning Trellis quantization [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |