|
Treaty Of Dresden
The Treaty of Dresden was signed on 25 December 1745 at the Saxon capital of Dresden between Austria, Saxony and Prussia, ending the Second Silesian War. In the 1742 Treaty of Breslau, Maria Theresa of Austria, struggling for the succession after her father Emperor Charles VI according to the Pragmatic Sanction of 1713, had to cede most of the Bohemian province of Silesia to the attacking King Frederick II of Prussia. In the following years, however, she was able to strengthen her position. She attacked the Electorate of Bavaria and in January 1745 achieved the support of Great Britain, the Dutch Republic and Saxony to reconquer Silesia. Furthermore, her rival, Emperor Charles VII, died a few days later, and on 22 April 1745 his son and successor, Elector Maximilian III Joseph of Bavaria, concluded the Treaty of Füssen with her. By the end of May 1745, Austrian and Saxon troops invaded Prussian Silesia but were halted by Prussian forces at the Battle of Hohenfriedberg o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canaletto
Giovanni Antonio Canal (18 October 1697 – 19 April 1768), commonly known as Canaletto (), was an Italian painter from the Republic of Venice, considered an important member of the 18th-century Venetian school. Painter of cityscapes or '' vedute'', of Venice, Rome, and London, he also painted imaginary views (referred to as capricci), although the demarcation in his works between the real and the imaginary is never quite clearcut.Alice Binion and Lin Barton. "Canaletto." Grove Art Online. Oxford Art Online. Oxford University Press. Web. 6 Jan. 2017 He was further an important printmaker using the etching technique. In the period from 1746 to 1756, he worked in England, where he painted many views of London and other sites, including Warwick Castle and Alnwick Castle. He was highly successful in England, thanks to the British merchant and connoisseur Joseph "Consul" Smith, whose large collection of Canaletto's works was sold to King George III in 1762. Early career ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electorate Of Bavaria
The Electorate of Bavaria () was a quasi-independent hereditary electorate of the Holy Roman Empire from 1623 to 1806, when it was succeeded by the Kingdom of Bavaria. The Wittelsbach dynasty which ruled the Duchy of Bavaria was the younger branch of the family which also ruled the Electoral Palatinate. The head of the elder branch was one of the seven prince-electors of the Holy Roman Empire according to the Golden Bull of 1356, but Bavaria was excluded from the electoral dignity. In 1621, Frederick V, Elector Palatine was put under the imperial ban for his role in the Bohemian Revolt against Ferdinand II, Holy Roman Emperor, and the electoral dignity and territory of the Upper Palatinate was conferred upon his loyal cousin, Duke Maximilian I of Bavaria. Although the Peace of Westphalia would create a new electoral title for Frederick V's son, with the exception of a brief period during the War of the Spanish Succession, Maximilian's descendants would continue to h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rixdollar
Rixdollar is the English term for silver coinage used throughout the European continent (, , , ). The same term was also used of currency in Cape Colony and Ceylon. However, the Rixdollar only existed as a coin in Ceylon. Unissued remainder banknotes for the Cape of Good Hope The Cape of Good Hope ( ) is a rocky headland on the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa. A List of common misconceptions#Geography, common misconception is that the Cape of Good Hope is the southern tip of Afri ... denominated in Rixdollars exist, but these are very rare. Rixdollars were used throughout 17th century America in most Dutch colonies. References {{money-stub Coins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Status Quo
is a Latin phrase meaning the existing state of affairs, particularly with regard to social, economic, legal, environmental, political, religious, scientific or military issues. In the sociological sense, the ''status quo'' refers to the current state of social structure or values. With regard to policy debate, it means how conditions are contrasted with a possible change. For example: "The countries are now trying to maintain the ''status quo'' with regard to their nuclear arsenals." To maintain the ''status quo'' is to keep things the way they presently are. The related phrase '' status quo ante'', literally 'the status before', refers to the state of affairs that existed previously. Political usage The status quo may be changed via social movements. These seek to alleviate or prevent a particular issue and often to shape social feeling and cultural expression of a society or nation. Advocating to improve the status quo is a persuasive rhetorical device. This is sometimes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elizabeth Of Russia
Elizabeth or Elizaveta Petrovna (; ) was Empress of Russia from 1741 until her death in 1762. She remains one of the most popular List of Russian rulers, Russian monarchs because of her decision not to execute a single person during her reign, her numerous construction projects, and her strong opposition to Prussian policies. She was the last person on the agnatic line of the Romanovs as Peter III of Russia, her nephew ascended, thus creating the house of Holstein-Gottorp-Romanov. The second-eldest daughter of Tsar Peter the Great (), Elizabeth lived through the confused successions of her father's descendants following her half-brother Alexei Petrovich, Tsarevich of Russia, Alexei's death in 1718. The throne first passed to her mother Catherine I of Russia (), then to her nephew Peter II of Russia, Peter II, who died in 1730 and was succeeded by Elizabeth's first cousin Anna of Russia, Anna (). After the brief rule of Anna's infant great-nephew, Ivan VI of Russia, Ivan VI, Eliz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
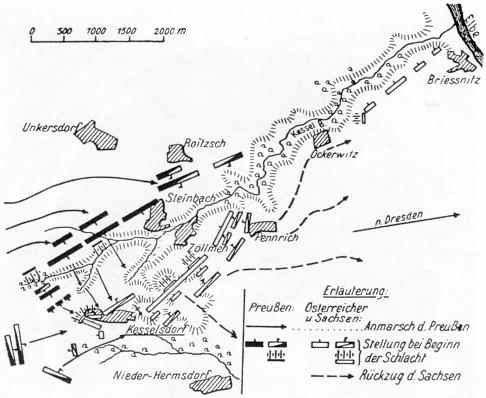
Battle Of Kesselsdorf
The Battle of Kesselsdorf was fought on 15 December 1745, between the Kingdom of Prussia and the combined forces of the Archduchy of Austria and the Electorate of Saxony during the part of the War of the Austrian Succession known as the Second Silesian War. The Prussians were led by Leopold I, Prince of Anhalt-Dessau, while the Austrians and Saxons were led by Field Marshal Rutowsky. The Prussians were victorious over the Royal Saxon Army and the Imperial Army of the Holy Roman Emperor. Preliminary maneuvers Two Prussian columns, one led by Frederick, the second by Leopold the 'Old Dessauer' were converging on Dresden, the capital of Saxony, which was at that time an Austrian ally. Interposed between Leopold and Dresden was Rutowsky with an army of Saxons and Austrians. Leopold moved slowly and deliberately forward entering Saxon territory on the 29 November and advanced on Rutowsky at Leipzig, whereupon Rutowsky retired towards Dresden. By the 12 December, Leopold reached Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Soor
The Battle of Soor (30 September 1745) was a battle between Frederick the Great's Prussian army and an Austro-Saxon army led by Prince Charles Alexander of Lorraine during the Second Silesian War (part of the War of the Austrian Succession). The battle occurred in the vicinity of Soor, also known as Hajnice, in the modern day Czech Republic. The battle started with a failed Austrian surprise attack on the outnumbered Prussians. Despite initial setbacks the Prussian army managed to defeat the Austrians, due to an unexpected attack from a reserve regiment that refused to follow Frederick's orders. Background Three months after the battle of Hohenfriedberg, Frederick laid the "Camp of Staudenz", initially planning to return to Berlin, in order to inspect the building work on his new palace of Sans Souci. Having stripped off many detachments during his march through Bohemia, Frederick's numbers had been reduced to 22,500 men. Prince Charles then discovered that Frederick had fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans (other), Emperor of the Romans (; ) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period (; ), was the ruler and head of state of the Holy Roman Empire. The title was held in conjunction with the title of King of Italy#Kingdom of Italy (781–962), King of Italy (''Rex Italiae'') from the 8th to the 16th century, and, almost without interruption, with the title of King of Germany (''Rex Teutonicorum'', ) throughout the 12th to 18th centuries. The Holy Roman Emperor title provided the highest prestige among Christianity in the Middle Ages, medieval Catholic monarchs, because the empire was considered by the Catholic Church to be Translatio imperii, the only successor of the Roman Empire during the Middle Ages and the early modern period. Thus, in theory and diplomacy, the emperors were considered first among equalsamong other Catholic monarchs across E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis I, Holy Roman Emperor
Francis I (Francis Stephen; ; ; ; 8 December 1708 – 18 August 1765) was Holy Roman Emperor from 1745 to 1765, List of rulers of Austria#Dukes and archdukes of Austria under the House of Habsburg, Archduke of Austria from 1740 to 1765, List of kings and dukes of Lorraine#House of Lorraine, Duke of Lorraine and Duchy of Bar, Bar from 1729 to 1737, and List of grand dukes of Tuscany#Habsburg-Lorraine grand dukes of Tuscany, 1737–1801, Grand Duke of Tuscany from 1737 to 1765. He became the ruler of the Holy Roman Empire, Habsburg monarchy, Austria, and Grand Duchy of Tuscany, Tuscany through his marriage to his second cousin Maria Theresa of Austria, daughter of Emperor Charles VI. Francis was the last non-Habsburg monarch of the Empire. The couple were the founders of the Habsburg-Lorraine dynasty, and their marriage produced sixteen children. Francis was the oldest surviving son of Leopold, Duke of Lorraine, and the French princess Élisabeth Charlotte d'Orléans. Duke Leopo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Hohenfriedberg
The Battle of Hohenfriedberg or Hohenfriedeberg (now Dobromierz, Poland), also known as the Battle of Striegau (now Strzegom, Poland) was one of Frederick the Great's most admired victories. Frederick's Prussian army decisively defeated an Austrian army under Prince Charles Alexander of Lorraine on June 4, 1745, during the Second Silesian War – part of the War of the Austrian Succession. Background Austria sought to regain Silesia, which had been lost to Prussia in the Battle of Mollwitz. An Austrian army of about 62,500, including allied Saxon troops, marched to Silesia. The commander was Prince Charles Alexander of Lorraine, brother-in-law of Empress Maria Theresa. Johann Adolf II, Duke of Saxe-Weissenfels commanded the Saxons. Frederick had a very low opinion of his counterpart, saying of Prince Charles Alexander that "there will be some stupid mistakes." In fact, Frederick was counting on Charles entering Silesia by crossing the Giant Mountains. If he did, Frede ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Füssen
The Peace of Füssen () was a peace treaty signed at Füssen, between the Electorate of Bavaria and Habsburg Austria. Signed on 22 April 1745, it ended the participation of Bavaria on the French side in the War of the Austrian Succession. Background After the conquest of Prague by Bavarian and French troops on 26 November 1741, Elector Charles Albert of Bavaria, with French and Prussian support, declared himself King of Bohemia and was elected Emperor Charles VII on 24 January 1742. Charles Albert was then crowned on 12 February. On the same day as his coronation in Frankfurt, however, Austrian troops occupied Bavaria and Hungarian hussars plundered Munich and the Bavarians were forced also to evacuate Bohemia which they had occupied for a few months. With French assistance, Charles VII fought Austria for three years, but was unable to secure victory. When Charles VII died in Munich on 20 January 1745, his successor as Elector of Bavaria, Maximilian III Joseph, signed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximilian III Joseph Of Bavaria
Maximilian III Joseph (28 March 1727 – 30 December 1777), also known by his epithet "the much beloved" was a Prince-elector of the Holy Roman Empire and Duke of Bavaria from 1745 to 1777. He was the last of the Bavarian branch of the House of Wittelsbach and because of his death, the War of Bavarian Succession broke out. Biography Born in Munich, Maximilian was the eldest son of Holy Roman Emperor Charles VII and his wife, Maria Amalia of Austria, daughter of Joseph I, Holy Roman Emperor. Upon his father's death in January 1745, he inherited a country in the process of being invaded by Austrian armies (see War of the Austrian Succession). The 18-year-old Maximilian Joseph wavered between the ''Peace-party'', led by his mother Maria Amalia and Army Commander Friedrich Heinrich von Seckendorff and the ''War-party'', led by Foreign Minister General Ignaz Count of Törring and the French envoy Chavigny. After the decisive defeat in the Battle of Pfaffenhofen on 15 April Max ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |