|
Transsulfuration Pathway
The transsulfuration pathway is a metabolic pathway involving the interconversion of cysteine and homocysteine through the intermediate cystathionine. Two transsulfurylation pathways are known: the ''forward'' and the ''reverse''. The ''forward pathway'' is present in several bacteria, such as ''Escherichia coli'' and ''Bacillus subtilis'', and involves the transfer of the thiol group from cysteine to homocysteine (methionine precursor with the S-methyl group), thanks to the γ-replacement of the acetyl or succinyl group of a homoserine with cysteine via its thiol group to form cystathionine (catalysed by cystathionine γ-synthase, which is encoded by ''metB'' in ''E. coli'' and ''metI'' in ''B. subtilis''). Cystathionine is then cleaved by means of the β-elimination of the homocysteine portion of the molecule leaving behind an unstable imino acid, which is attacked by water to form pyruvate and ammonia (catalysed by the metC-encoded cystathionine β-lyase). The production ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Met Pathway
Met, MET, The Met or The MET may refer to: Buildings Arts venues * Metropolitan Museum of Art, or the Met, in New York City * Manhattan Ensemble Theatre, or MET, in New York City * Metropolitan Opera, or the Met, in New York City * Metropolitan Opera House (other), various buildings * The Met (arts centre) in Bury, Greater Manchester * Manila Metropolitan Theater in Manila, Philippines Sports venues * Met Center in Bloomington, Minnesota * Met Park in Norfolk, Virginia * MetLife Stadium in East Rutherford, New Jersey * Metropolitan Stadium in Bloomington, Minnesota Other buildings * Metropolitan Bible Church ("The MET"), Ottawa, Canada * Metropolitan Building (Minneapolis), until 1961 * Metropolitan Miami (development), Florida, US * Metropolitan Theatre (Winnipeg), Canada * The Met (skyscraper), Bangkok, Thailand Arts, entertainment, and media * Met, a fictitious character in ''Mega Man'' (v-game) series * Met 107, a radio station in Bangkok * ''Mind's Eye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans. As the precursor of other non-essential amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine plays a critical role in the metabolism and health of many species, including humans. Methionine is also involved in angiogenesis and various processes related to DNA transcription, epigenetic expression, and gene regulation. Methionine was first isolated in 1921 by John Howard Mueller. It is Genetic code, encoded by the codon AUG. It was named by Satoru Odake in 1925, as an abbreviation of its structural description 2-amino-4-(methylthio)butanoic acid. Biochemical details Methionine (abbreviated as Met or M; encoded by the codon AUG) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological pH conditions), an amino group (which is in the proton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Nitrogen Cycle
The nitrogen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which nitrogen is converted into multiple chemical forms as it circulates among atmosphere, atmospheric, terrestrial ecosystem, terrestrial, and marine ecosystems. The conversion of nitrogen can be carried out through both biological and physical processes. Important processes in the nitrogen cycle include nitrogen fixation, fixation, ammonification, nitrification, and denitrification. The majority of Earth's atmosphere (78%) is atmospheric nitrogen, making it the largest source of nitrogen. However, atmospheric nitrogen has limited availability for biological use, leading to a scarcity of usable nitrogen in many types of ecosystems. The nitrogen cycle is of particular interest to ecologists because nitrogen availability can affect the rate of key ecosystem processes, including primary production and decomposition. Human activities such as fossil fuel combustion, use of artificial nitrogen fertilizers, and release of nitrogen in w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Cys/Met Metabolism PLP-dependent Enzyme Family
In molecular biology, the Cys/Met metabolism PLP-dependent enzyme family is a family of proteins including enzymes involved in cysteine and methionine metabolism which use PLP (pyridoxal-5'-phosphate) as a cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor. Mechanism of action PLP is employed as it binds to amino groups and stabilises carbanion intermediates. PLP enzymes exist in their resting state as a Schiff base, the aldehyde group of PLP forming a linkage with the epsilon-amino group of an active site lysine residue (chemistry), residue on the enzyme. The alpha-amino group of the Enzyme substrate, substrate displaces the lysine epsilon-amino group, in the process forming a new aldimine with the Substrate (biochemistry), substrate. This aldimine is the common central reaction intermediate, intermediate for all PLP-catalysed reactions, enzyme, enzymatic and non-enzymatic. Function PLP is the active form of vitamin B6 (pyridoxine or pyridoxal). PLP is a versatile catalyst, acting as a coenz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Pyridoxal Phosphate
Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, P5P), the active form of vitamin B6, is a coenzyme in a variety of enzymatic reactions. The International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology has catalogued more than 140 PLP-dependent activities, corresponding to ~4% of all classified activities. The versatility of PLP arises from its ability to covalently bind the substrate, and then to act as an electrophilic catalyst, thereby stabilizing different types of carbanionic reaction intermediates. Role as a coenzyme PLP acts as a coenzyme in all transamination reactions, and in certain decarboxylation, deamination, and racemization reactions of amino acids. The aldehyde group of PLP forms a Schiff-base linkage (internal aldimine) with the ε-amino group of a specific lysine group of the aminotransferase enzyme. The α-amino group of the amino acid substrate displaces the ε-amino group of the active-site lysine residue in a process known as transaldimination. The r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6 is one of the B vitamins, and is an essential nutrient for humans. The term essential nutrient refers to a group of six chemically similar compounds, i.e., "vitamers", which can be interconverted in biological systems. Its active form, pyridoxal phosphate, pyridoxal 5′-phosphate, serves as a coenzyme in more than 140 enzyme reactions in amino acid, glucose, and lipid metabolism. Plants synthesize pyridoxine as a means of protection from the UV-B, UV-B radiation found in sunlight and for the role it plays in the synthesis of chlorophyll. Animals cannot synthesize any of the various forms of the vitamin, and hence must obtain it via diet, either of plants, or of other animals. There is some absorption of the vitamin produced by intestinal bacteria, but this is not sufficient to meet dietary needs. For adult humans, recommendations from various countries' food regulatory agencies are in the range of 1.0 to 2.0 milligrams (mg) per day. These same agencies also recogni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Homocystinuria
Homocystinuria (HCU) is an inherited disorder of the metabolism of the amino acid methionine due to a deficiency of cystathionine beta synthase or methionine synthase. It is an inherited autosomal recessive trait, which means a child needs to inherit a copy of the defective gene from both parents to be affected. Symptoms of homocystinuria can also be caused by a deficiency of vitamins B6, B12, or folate. Signs and symptoms This defect leads to a multi-systemic disorder of the connective tissue, muscles, central nervous system (CNS), and cardiovascular system. Homocystinuria represents a group of hereditary metabolic disorders characterized by an accumulation of the amino acid homocysteine in the serum and an increased excretion of homocysteine in the urine. Infants appear to be normal and early symptoms, if any are present, are vague. Signs and symptoms of homocystinuria that may be seen include the following: Cause It is usually caused by the deficiency of the enzyme cyst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Auxotrophic
Auxotrophy ( "to increase"; ''τροφή'' "nourishment") is the inability of an organism to synthesize a particular organic compound required for its growth (as defined by IUPAC). An auxotroph is an organism that displays this characteristic; ''auxotrophic'' is the corresponding adjective. Auxotrophy is the opposite of prototrophy, which is characterized by the ability to synthesize all the compounds needed for growth. Prototrophic cells are self-sufficient producers of all required metabolites (e.g. amino acids, lipids, cofactors), while auxotrophs require to be on medium with the metabolite that they cannot produce. For example, a methionine auxotrophic cell could only grow on a medium that contained methionine; otherwise, it would starve. In this example, this is because it is unable to produce its own methionine. However, a methionine prototrophic cell would be able to function and replicate on a medium with or without methionine. Replica plating is a technique that transfer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Cystathionine Gamma-lyase
The enzyme cystathionine γ-lyase (EC 4.4.1.1, CTH or CSE; also cystathionase; systematic name L-cystathionine cysteine-lyase (deaminating; 2-oxobutanoate-forming)) breaks down cystathionine into cysteine, 2-oxobutanoate ( α-ketobutyrate), and ammonia: :L-cystathionine + H2O = L-cysteine + 2-oxobutanoate + NH3 (overall reaction) ::(1a) L-cystathionine = L-cysteine + 2-aminobut-2-enoate ::(1b) 2-aminobut-2-enoate = 2-iminobutanoate (spontaneous) ::(1c) 2-iminobutanoate + H2O = 2-oxobutanoate + NH3 (spontaneous) Pyridoxal phosphate is a prosthetic group of this enzyme. Cystathionine γ-lyase also catalyses the following elimination reactions: * L- homoserine to form H2O, NH3 and 2-oxobutanoate * L-cystine, producing thiocysteine, pyruvate and NH3 * L-cysteine producing pyruvate, NH3 and H2S In some bacteria and mammals, including humans, this enzyme takes part in generating hydrogen sulfide. Hydrogen sulfide is one of a few gases that was recently discovered to have a role ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Cystathionine Beta-synthase
Cystathionine is an intermediate in the synthesis of cysteine from homocysteine. It is produced by the transsulfuration pathway and is converted into cysteine by cystathionine gamma-lyase (CTH). Biosynthetically, cystathionine is generated from homocysteine and serine by cystathionine beta synthase (upper reaction in the diagram below). It is then cleaved into cysteine and α-ketobutyrate by cystathionine gamma-lyase (lower reaction). An excess of cystathionine in the urine is called cystathioninuria. Cysteine dioxygenase (CDO), and sulfinoalanine decarboxylase can turn cysteine into hypotaurine and then taurine. Alternately, the cysteine from the cystathionine gamma-lyase can be used by the enzymes glutamate–cysteine ligase (GCL) and glutathione synthetase (GSS) to produce glutathione Glutathione (GSH, ) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an antioxidant in plants, animals, fungi, and some bacteria and archaea. Glutathione is capable of preventing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
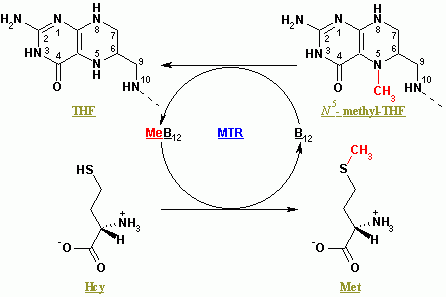 |
5-Methyltetrahydrofolate-homocysteine Methyltransferase
Methionine synthase (MS, MeSe, MTR) is primarily responsible for the regeneration of methionine from homocysteine in most individuals. In humans it is encoded by the ''MTR'' gene (5-methyltetrahydrofolate-homocysteine methyltransferase). Methionine synthase forms part of the S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe) biosynthesis and regeneration cycle, and is the enzyme responsible for linking the cycle to one-carbon metabolism via the folate cycle. There are two primary forms of this enzyme, the Vitamin B12 (cobalamin)-dependent (MetH) and independent (MetE) forms, although minimal core methionine synthases that do not fit cleanly into either category have also been described in some anaerobic bacteria. The two dominant forms of the enzymes appear to be evolutionary independent and rely on considerably different chemical mechanisms. Mammals and other higher eukaryotes express only the cobalamin-dependent form. In contrast, the distribution of the two forms in Archaeplastida (plants and algae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Cystathionine Beta-lyase
Cystathionine beta-lyase (), also commonly referred to as CBL or β-cystathionase, is an enzyme that primarily catalyzes the following α,β-elimination reaction Thus, the substrate of this enzyme is L-cystathionine, whereas its 3 products are homocysteine, pyruvate, and ammonia. Found in plants, bacteria, and yeast, cystathionine beta-lyase is an essential part of the methionine biosynthesis pathway as homocysteine can be directly converted into methionine by methionine synthase. The enzyme belongs to the γ-family of PLP-dependent enzymes due to its use of a pyridoxal-5'-phosphate (PLP) cofactor to cleave cystathionine. The enzyme also belongs to the family of lyases, specifically the class of carbon-sulfur lyases. The systematic name of this enzyme class is L-cystathionine L-homocysteine-lyase (deaminating; pyruvate-forming). This enzyme participates in 5 metabolic pathways: methionine metabolism, cysteine metabolism, selenoamino acid metabolism, nitrogen metabolism, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |