|
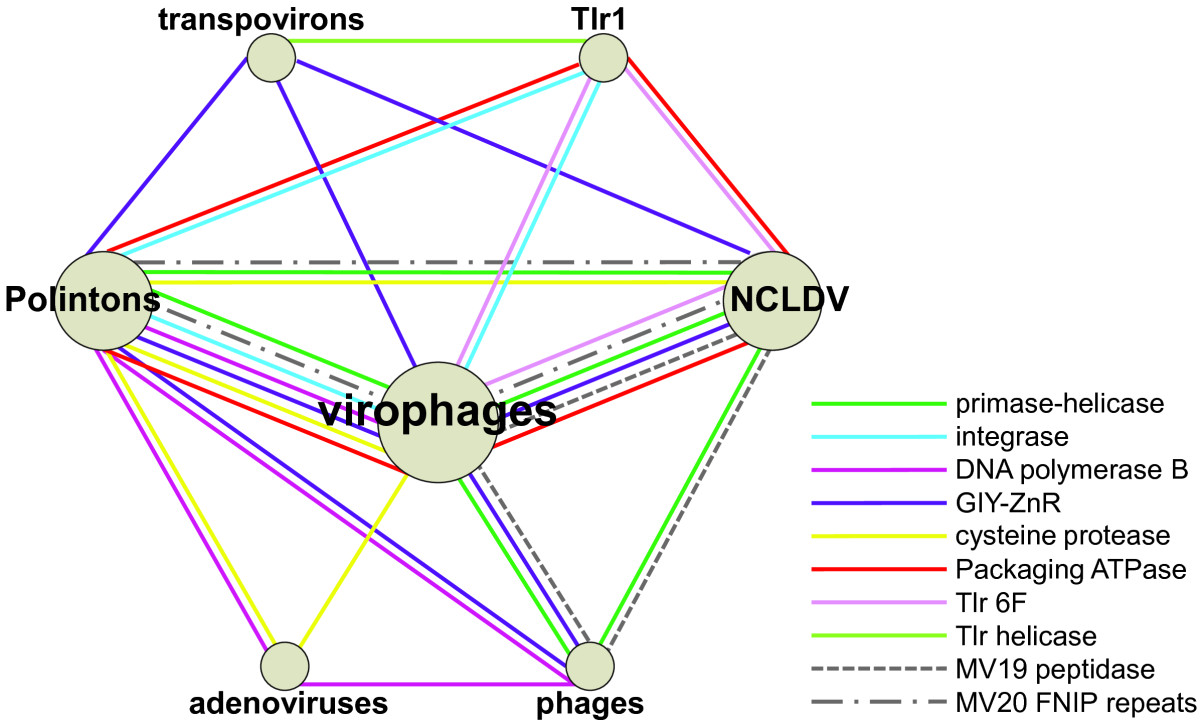
Transpoviron
A transpoviron is a plasmid-like genetic element found in the genomes of giant DNA viruses. They are linear DNA elements of approximately 7 kilobases that encompass six to eight protein encoding genes. Two of these genes are homologous to virophage genes. Transpovirons encode a superfamily 1 helicase, which encompasses an inactivated family B DNA polymerase domain. Homologs of this unique polymerase-helicase fusion protein are widespread in Polinton Polintons (also called Mavericks) are large DNA transposons which contain genes with homology to viral proteins and which are often found in eukaryotic genomes. They were first discovered in the mid-2000s and are the largest and most complex know ...-Like Viruses (PLV). Based on the phylogenetic analysis of the helicase domain the discoverers of PLVs concluded that transpovirons evolved from PLV via the loss of several genes including those encoding the morphogenetic module proteins. References {{Organisms et al. Mobile geneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polinton
Polintons (also called Mavericks) are large DNA transposons which contain genes with homology to viral proteins and which are often found in eukaryotic genomes. They were first discovered in the mid-2000s and are the largest and most complex known DNA transposons. Polintons encode up to 10 individual proteins and derive their name from two key proteins, a DNA polymerase and a retroviral-like integrase. Properties A typical polinton is around 15–20 kilobase pairs in size, though examples have been described up to 40kb. Polintons encode up to 10 proteins, the key elements being the protein-primed type B DNA polymerase and the retroviral-like integrase from which they derive their name. Polintons are sometimes referred to as "self-synthesizing" transposons, because they encode the proteins necessary to replicate themselves. Most polintons also encode an adenoviral-like cysteine protease, an FtsK-like ATPase, and proteins with homology to the jelly-roll fold structure of viral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmid
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria; however, plasmids are sometimes present in archaea and eukaryotic organisms. In nature, plasmids often carry genes that benefit the survival of the organism and confer selective advantage such as antibiotic resistance. While chromosomes are large and contain all the essential genetic information for living under normal conditions, plasmids are usually very small and contain only additional genes that may be useful in certain situations or conditions. Artificial plasmids are widely used as vectors in molecular cloning, serving to drive the replication of recombinant DNA sequences within host organisms. In the laboratory, plasmids may be introduced into a cell via transformation. Synthetic plasmids are available for procurement over the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobile Genetic Elements
Mobile genetic elements (MGEs) sometimes called selfish genetic elements are a type of genetic material that can move around within a genome, or that can be transferred from one species or replicon to another. MGEs are found in all organisms. In humans, approximately 50% of the genome is thought to be MGEs. MGEs play a distinct role in evolution. Gene duplication events can also happen through the mechanism of MGEs. MGEs can also cause mutations in protein coding regions, which alters the protein functions. These mechanisms can also rearrange genes in the host genome generating variation. These mechanism can increase fitness by gaining new or additional functions. An example of MGEs in evolutionary context are that virulence factors and antibiotic resistance genes of MGEs can be transported to share genetic code with neighboring bacteria. However, MGEs can also decrease fitness by introducing disease-causing alleles or mutations. The set of MGEs in an organism is called a mobilome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences (see non-coding DNA), and often a substantial fraction of 'junk' DNA with no evident function. Almost all eukaryotes have mitochondria and a small mitochondrial genome. Algae and plants also contain chloroplasts with a chloroplast genome. The study of the genome is called genomics. The genomes of many organisms have been sequenced and various regions have been annotated. The International Human Genome Project reported the sequence of the genome for ''Homo sapiens'' in 200The Human Genome Project although the initial "finished" sequence was missing 8% of the genome consisting mostly of repetitive sequences. With advancements in technology that could handle seq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleocytoplasmic Large DNA Viruses
''Nucleocytoviricota'' is a phylum of viruses. Members of the phylum are also known as the nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses (NCLDV), which serves as the basis of the name of the phylum with the suffix - for virus phylum. These viruses are referred to as nucleocytoplasmic because they are often able to replicate in both the host's cell nucleus and cytoplasm. The phylum is notable for containing the giant viruses. There are nine families of NCLDVs that all share certain genomic and structural characteristics; however, it is uncertain whether the similarities of the different families of this group have a common viral ancestor. One feature of this group is a large genome and the presence of many genes involved in DNA repair, DNA replication, transcription, and translation. Typically, viruses with smaller genomes do not contain genes for these processes. Most of the viruses in this family also replicate in both the host's nucleus and cytoplasm, thus the name nucleocytoplasmic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virophage
Virophages are small, double-stranded DNA viral phages that require the co-infection of another virus. The co-infecting viruses are typically giant viruses. Virophages rely on the viral replication factory of the co-infecting giant virus for their own replication. One of the characteristics of virophages is that they have a parasitic relationship with the co-infecting virus. Their dependence upon the giant virus for replication often results in the deactivation of the giant viruses. The virophage may improve the recovery and survival of the host organism. Unlike satellite viruses, virophages have a parasitic effect on their co-infecting virus. Virophages have been observed to render a giant virus inactive and thereby improve the condition of the host organism. All known virophages are grouped into the family ''Lavidaviridae'' (from "large virus dependent or associated" + -viridae). Discovery The first virophage was discovered in a cooling tower in Paris, France in 200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helicase
Helicases are a class of enzymes thought to be vital to all organisms. Their main function is to unpack an organism's genetic material. Helicases are motor proteins that move directionally along a nucleic acid phosphodiester backbone, separating two hybridized nucleic acid strands (hence '' helic- + -ase''), using energy from ATP hydrolysis. There are many helicases, representing the great variety of processes in which strand separation must be catalyzed. Approximately 1% of eukaryotic genes code for helicases. The human genome codes for 95 non-redundant helicases: 64 RNA helicases and 31 DNA helicases. Many cellular processes, such as DNA replication, transcription, translation, recombination, DNA repair, and ribosome biogenesis involve the separation of nucleic acid strands that necessitates the use of helicases. Some specialized helicases are also involved in sensing of viral nucleic acids during infection and fulfill a immunological function. Function Helicases ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |