|
Transcytosis
Transcytosis (also known as cytopempsis) is a type of transcellular transport in which various macromolecules are transported across the interior of a cell (biology), cell. Macromolecules are captured in Vesicle (biology), vesicles on one side of the cell, drawn across the cell, and ejected on the other side. Examples of macromolecules transported include immunoglobulin A, IgA, transferrin, and insulin. While transcytosis is most commonly observed in epithelium, epithelial cells, the process is also present elsewhere. Blood capillaries are a well-known site for transcytosis, though it occurs in other cells, including neurons, osteoclasts and microfold cell, M cells of the intestine. Regulation The regulation of transcytosis varies greatly due to the many different tissues in which this process is observed. Various tissue-specific mechanisms of transcytosis have been identified. Brefeldin A, a commonly used inhibitor of endoplasmic reticulum, ER-to-Golgi apparatus transport, has b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcellular Transport
Transcellular transport involves the transportation of solutes by a cell ''through'' a cell. Transcellular transport can occur in three different ways active transport, passive transport, and transcytosis. Active Transport Active transport is the process of moving molecules from an area of low concentrations to an area of high concentration. There are two types of active transport, primary active transport and secondary active transport. Primary active transport uses adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to move specific molecules and solutes against its concentration gradient. Examples of molecules that follow this process are potassium K+, sodium Na+, and calcium Ca2+. A place in the human body where this occurs is in the intestines with the uptake of glucose. Secondary active transport is when one solute moves down the electrochemical gradient to produce enough energy to force the transport of another solute from low concentration to high concentration. An example of where this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SNARE Protein-IT
SNARE proteins – " SNAP REceptors" – are a large protein family consisting of at least 24 members in yeasts and more than 60 members in mammalian and plant cells. The primary role of SNARE proteins is to mediate the fusion of vesicles with the target membrane; this notably mediates exocytosis, but can also mediate the fusion of vesicles with membrane-bound compartments (such as a lysosome). The best studied SNAREs are those that mediate the release of synaptic vesicles containing neurotransmitters in neurons. These neuronal SNAREs are the targets of the neurotoxins responsible for botulism and tetanus produced by certain bacteria. Types SNAREs can be divided into two categories: ''vesicle'' or ''v-SNAREs'', which are incorporated into the membranes of transport vesicles during budding, and ''target'' or ''t-SNAREs'', which are associated with nerve terminal membranes. Evidence suggests that t-SNAREs form stable subcomplexes which serve as guides for v-SNARE, incorpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. It consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the isthmus (: isthmi). Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical thyroid follicle, lined with follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a lumen containing colloid. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)and a peptide hormone, calcitonin. The thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis and growth and development in children. Calcitonin plays a role in calcium homeostasis. Secretion of the two thyroid hormones is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. TSH is regulated by thy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pregnancy (mammals)
In mammals, pregnancy is the period of reproduction during which a female carries one or more live offspring from implantation in the uterus through gestation. It begins when a fertilized zygote implants in the female's uterus, and ends once it leaves the uterus. Fertilization and implantation During copulation, the male inseminates the female. The spermatozoon fertilizes an ovum or various ova in the uterus or oviducts, and this results in one or multiple zygotes. Sometimes, a zygote can be created by humans outside of the animal's body in the artificial process of in-vitro fertilization. After fertilization, the newly formed zygote then begins to divide through mitosis, forming an embryo, which implants in the female's endometrium. At this time, the embryo usually consists of 50 cells. Development After implantation A blastocele is a small cavity on the center of the embryo, and the developing embryonary cells will grow around it. Then, a flat layer cell forms on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
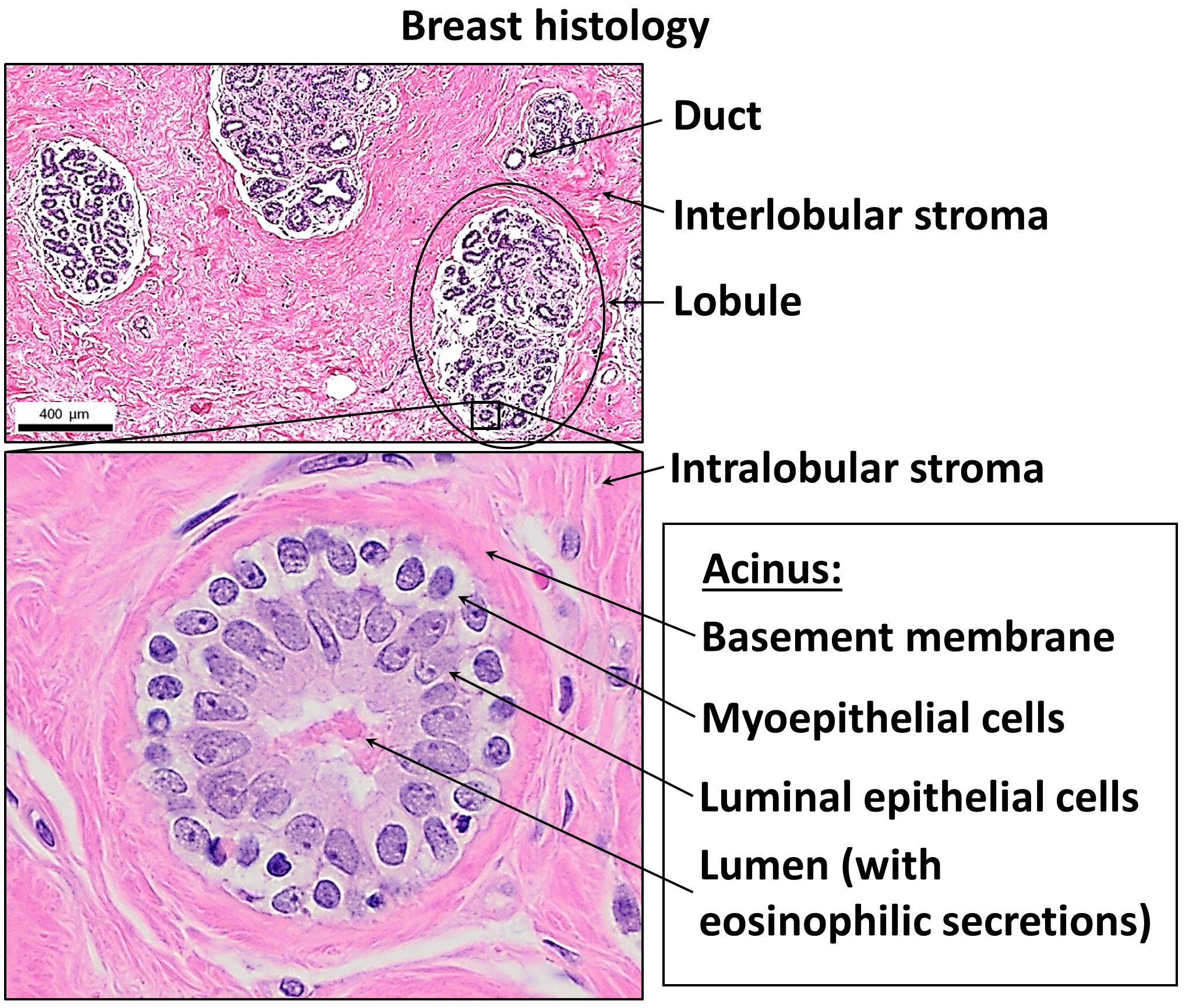
Mammary Gland
A mammary gland is an exocrine gland that produces milk in humans and other mammals. Mammals get their name from the Latin word ''mamma'', "breast". The mammary glands are arranged in organs such as the breasts in primates (for example, humans and chimpanzees), the udder in ruminants (for example, cows, goats, sheep, and deer), and the dugs of other animals (for example, dogs and cats) to feed young offspring. Lactorrhea, the occasional production of milk by the glands, can occur in any mammal, but in most mammals, lactation, the production of enough milk for nursing, occurs only in phenotypic females who have gestated in recent months or years. It is directed by hormonal guidance from sex steroids. In a few mammalian species, male lactation can occur. With humans, male lactation can occur only under specific circumstances. Mammals are divided into 3 groups: monotremes, metatherians, and eutherians. In the case of monotremes, their mammary glands are modified seba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prolactin
Prolactin (PRL), also known as lactotropin and mammotropin, is a protein best known for its role in enabling mammals to produce milk. It is influential in over 300 separate processes in various vertebrates, including humans. Prolactin is secreted from the pituitary gland in response to eating, mating, estrogen treatment, ovulation and nursing. It is secreted heavily in pulses in between these events. Prolactin plays an essential role in metabolism, regulation of the immune system and pancreatic development. Discovered in non-human animals around 1930 by Oscar Riddle and confirmed in humans in 1970 by Henry Friesen, prolactin is a peptide hormone, encoded by the ''PRL'' gene. In mammals, prolactin is associated with milk production; in fish it is thought to be related to the control of water and salt balance. Prolactin also acts in a cytokine-like manner and as an important regulator of the immune system. It has important cell cycle-related functions as a growth-, diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estradiol
Estradiol (E2), also called oestrogen, oestradiol, is an estrogen steroid hormone and the major female sex hormone. It is involved in the regulation of female reproductive cycles such as estrous and menstrual cycles. Estradiol is responsible for the development of female secondary sexual characteristics such as the breasts, widening of the hips and a female pattern of fat distribution. It is also important in the development and maintenance of female reproductive tissues such as the mammary glands, uterus and vagina during puberty, adulthood and pregnancy. It also has important effects in many other tissues including bone, fat, skin, liver, and the brain. Though estradiol levels in males are much lower than in females, estradiol has important roles in males as well. Apart from humans and other mammals, estradiol is also found in most vertebrates and crustaceans, insects, fish, and other animal species. Estradiol is produced within the follicles of the ovaries and in oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progesterone
Progesterone (; P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the major progestogen in the body. Progesterone has a variety of important functions in the body. It is also a crucial metabolic intermediate in the production of other endogenous steroids, including the sex hormones and the corticosteroids, and plays an important role in brain function as a neurosteroid. In addition to its role as a natural hormone, progesterone is also used as a medication, such as in combination with estrogen for contraception, to reduce the risk of Uterine cancer, uterine or cervical cancer, in hormone replacement therapy, and in feminizing hormone therapy. It was first prescribed in 1934. Biological activity Progesterone is the most important progestogen in the body. As a potent agonist of the progesterone receptor, nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAPK1
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (MAPK 1), also known as ERK2, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAPK1'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the MAP kinase family. MAP kinases, also known as extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs), act as an integration point for multiple biochemical signals, and are involved in a wide variety of cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, transcription regulation and development. The activation of this kinase requires its phosphorylation by upstream kinases. Upon activation, this kinase translocates to the nucleus of the stimulated cells, where it phosphorylates nuclear targets. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein, but differing in the UTRs, have been reported for this gene. MAPK1 contains multiple amino acid sites that are phosphorylated and ubiquitinated. Interactions MAPK1 has been shown to interact with: * ADAM17, * CIITA, * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAB11FIP5
Rab11 family-interacting protein 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RAB11FIP5'' gene. Interactions RAB11FIP5 has been shown to interact with RAB11A and RAB25. Vesicle trafficking Rab11FIP5 is one of the many proteins that have been shown to interact with the Rab11 protein. Rab GTPases, such as Rab11, are enzymes that are involved in vesicular trafficking. Rab11 specifically plays a key role in endocytic trafficking and recycling through guiding early endosomes to endosome recycling complexes. Rab11FIP5, like most other Rab11FIP proteins, interacts with Rab11 by serving as an adaptor protein. This leads to downstream changes with regards to which proteins can interact. This is a result of the various Rab11FIP proteins that each have different binding partners. This process allows for the coordination and organization of endosomal transport and ultimately gives Rab11 its versatile function in the cell. It is believed that Rab11 recruits specific Rab11FIP prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
YES1
Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes is a Enzyme, non-receptor tyrosine kinase that in humans is encoded by the ''YES1'' gene. This gene is the cellular homolog of the Yamaguchi sarcoma virus oncogene. The encoded protein has tyrosine kinase activity and belongs to the Src family kinase, src family. This gene lies in close proximity to thymidylate synthase gene on chromosome 18, and a corresponding pseudogene has been found on chromosome 22. Interactions YES1 has been shown to Protein-protein interaction, interact with Janus kinase 2, CTNND1, RPL10 and Occludin. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * {{gene-18-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR; ErbB-1; HER1 in humans) is a transmembrane protein that is a receptor (biochemistry), receptor for members of the epidermal growth factor family (EGF family) of extracellular protein ligand (biochemistry), ligands. The epidermal growth factor receptor is a member of the ErbB, ErbB family of receptors, a subfamily of four closely related receptor tyrosine kinases: EGFR (ErbB-1), HER2/neu (ErbB-2), ERBB3, Her 3 (ErbB-3) and Her 4 (ErbB-4). In many cancer types, mutations affecting EGFR expression or activity could result in cancer. Epidermal growth factor and its receptor was discovered by Stanley Cohen (biochemist), Stanley Cohen of Vanderbilt University. Cohen shared the 1986 Nobel Prize in Medicine with Rita Levi-Montalcini for their discovery of growth factors. Deficient signaling of the EGFR and other receptor tyrosine kinases in humans is associated with diseases such as Alzheimer's, while over-expression is associated with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |