|
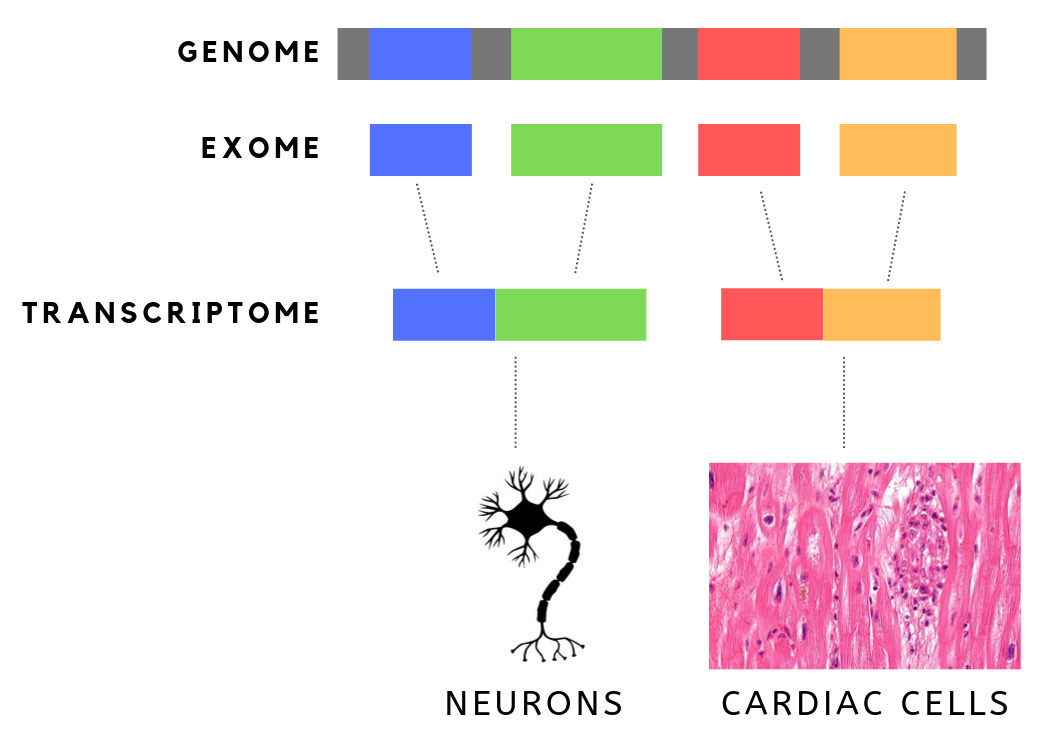
Transcriptomes
The transcriptome is the set of all RNA transcripts, including coding and non-coding RNA, non-coding, in an individual or a population of cell (biology), cells. The term can also sometimes be used to refer to RNA#Types of RNA, all RNAs, or just Messenger RNA, mRNA, depending on the particular experiment. The term ''transcriptome'' is a portmanteau of the words ''transcript'' and ''genome''; it is associated with the process of transcript production during the biological process of Transcription (biology), transcription. The early stages of transcriptome annotations began with cDNA libraries published in the 1980s. Subsequently, the advent of high-throughput technology led to faster and more efficient ways of obtaining data about the transcriptome. Two biological techniques are used to study the transcriptome, namely DNA microarray, a hybridization-based technique and RNA-seq, a sequence-based approach. RNA-seq is the preferred method and has been the dominant transcriptomics techniq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcriptomics Technique
Transcriptomics technologies are the techniques used to study an organism's transcriptome, the sum of all of its RNA, RNA transcripts. The information content of an organism is recorded in the DNA of its genome and Gene expression, expressed through Transcription (genetics), transcription. Here, mRNA serves as a transient intermediary molecule in the information network, whilst non-coding RNAs perform additional diverse functions. A transcriptome captures a snapshot in time of the total transcripts present in a cell (biology), cell. Transcriptomics technologies provide a broad account of which cellular processes are active and which are dormant. A major challenge in molecular biology is to understand how a single genome gives rise to a variety of cells. Another is how gene expression is regulated. The first attempts to study whole transcriptomes began in the early 1990s. Subsequent technological advances since the late 1990s have repeatedly transformed the field and made transcript ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
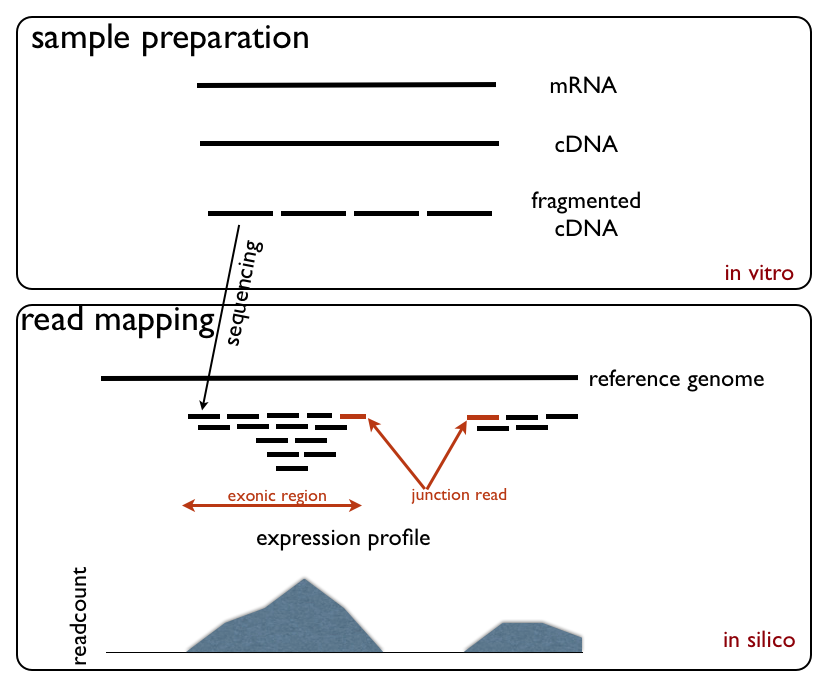
RNA-seq
RNA-Seq (named as an abbreviation of RNA sequencing) is a technique that uses next-generation sequencing to reveal the presence and quantity of RNA molecules in a biological sample, providing a snapshot of gene expression in the sample, also known as transcriptome. RNA-Seq facilitates the ability to look at alternative gene spliced transcripts, post-transcriptional modifications, gene fusion, mutations/ SNPs and changes in gene expression over time, or differences in gene expression in different groups or treatments. In addition to mRNA transcripts, RNA-Seq can look at different populations of RNA to include total RNA, small RNA, such as miRNA, tRNA, and ribosomal profiling. RNA-Seq can also be used to determine exon/intron boundaries and verify or amend previously annotated 5' and 3' gene boundaries. Recent advances in RNA-Seq include single cell sequencing, bulk RNA sequencing, 3' mRNA-sequencing, in situ sequencing of fixed tissue, and native RNA molecule sequencin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omics
Omics is the collective characterization and quantification of entire sets of biological molecules and the investigation of how they translate into the structure, function, and dynamics of an organism or group of organisms. The branches of science known informally as ''omics'' are various disciplines in biology whose names end in the suffix ''wikt:-omics, -omics'', such as genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, metagenomics, phenomics and transcriptomics. The related suffix -ome is used to address the objects of study of such fields, such as the genome, proteome or metabolome respectively. The suffix ''-ome'' as used in molecular biology refers to a ''totality'' of some sort; it is an example of a "neo-suffix" formed by abstraction from various Greek terms in , a sequence that does not form an identifiable suffix in Greek. Functional genomics aims at identifying the functions of as many genes as possible of a given organism. It combines different -omics techniques such as transcr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetic Inference Using Transcriptomic Data
In molecular phylogenetics, relationships among individuals are determined using character traits, such as DNA, RNA or protein, which may be obtained using a variety of sequencing technologies. High-throughput next-generation sequencing has become a popular technique in transcriptomics, which represent a snapshot of gene expression. In eukaryotes, making phylogenetic inferences using RNA is complicated by alternative splicing, which produces multiple transcripts from a single gene. As such, a variety of approaches may be used to improve phylogenetic inference using transcriptomic data obtained from RNA-Seq and processed using computational phylogenetics. Sequence acquisition There have been several transcriptomics technologies used to gather sequence information on transcriptomes. However the most widely used is RNA-Seq. RNA-Seq RNA reads may be obtained using a variety of RNA-seq methods. Public databases There are a number of public databases that contain freely available RNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-cell Transcriptomics
Single-cell transcriptomics examines the gene expression level of individual Cell (biology), cells in a given population by simultaneously measuring the RNA concentration (conventionally only messenger RNA (mRNA)) of hundreds to thousands of genes. Single-cell transcriptomics makes it possible to unravel Heterogenous, heterogeneous cell populations, reconstruct cellular developmental pathways, and model transcriptional dynamics — all previously masked in bulk RNA sequencing. Background The development of high-throughput RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) and microarrays has made gene expression analysis a routine. RNA analysis was previously limited to tracing individual Transcription (biology), transcripts by Northern blots or quantitative PCR. Higher throughput and speed allow researchers to frequently characterize the expression profiles of populations of thousands of cells. The data from bulk assays has led to identifying genes differentially expressed in distinct cell populations, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thanatotranscriptome
The thanatotranscriptome denotes all ribonucleic acid, RNA transcripts produced from the portions of the genome still active or awakened in the internal organs of a body following its death. It is relevant to the study of the biochemistry, microbiology, and biophysics of thanatology, in particular within forensic science. Some genes may continue to be expressed in cells for up to 48 hours after death, producing new mRNA. Certain genes that are generally inhibited since the end of fetal development may be expressed again at this time. Scientific history Clues to the existence of a post-mortem transcriptome existed at least since the beginning of the 21st century, but the word ''thanatotranscriptome'' (from (''thanatos-,'' Greek for "death") seems to have been first used in the scientific literature by Javan et al. in 2015, following the introduction of the concept of the human thanatomicrobiome in 2014 at the 66th Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Forensic Sciences in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Microarray
A DNA microarray (also commonly known as a DNA chip or biochip) is a collection of microscopic DNA spots attached to a solid surface. Scientists use DNA microarrays to measure the expression levels of large numbers of genes simultaneously or to genotype multiple regions of a genome. Each DNA spot contains picomoles (10−12 moles) of a specific DNA sequence, known as '' probes'' (or ''reporters'' or '' oligos''). These can be a short section of a gene or other DNA element that are used to hybridize a cDNA or cRNA (also called anti-sense RNA) sample (called ''target'') under high-stringency conditions. Probe-target hybridization is usually detected and quantified by detection of fluorophore-, silver-, or chemiluminescence-labeled targets to determine relative abundance of nucleic acid sequences in the target. The original nucleic acid arrays were macro arrays approximately 9 cm × 12 cm and the first computerized image based analysis was published in 1981. It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CDNA
In genetics, complementary DNA (cDNA) is DNA that was reverse transcribed (via reverse transcriptase) from an RNA (e.g., messenger RNA or microRNA). cDNA exists in both single-stranded and double-stranded forms and in both natural and engineered forms. In engineered forms, it often is a copy (replicate) of the naturally occurring DNA from any particular organism's natural genome; the organism's own mRNA was naturally transcribed from its DNA, and the cDNA is reverse transcribed from the mRNA, yielding a duplicate of the original DNA. Engineered cDNA is often used to express a specific protein in a cell that does not normally express that protein (i.e., heterologous expression), or to sequence or quantify mRNA molecules using DNA based methods (qPCR, RNA-seq). cDNA that codes for a specific protein can be transferred to a recipient cell for expression as part of recombinant DNA, often bacterial or yeast expression systems. cDNA is also generated to analyze transcriptomic pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription (biology)
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA for the purpose of gene expression. Some segments of DNA are transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins, called messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are transcribed into RNA molecules called non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a Complementarity (molecular biology), complementary language. During transcription, a DNA sequence is read by an RNA polymerase, which produces a complementary, Antiparallel (biochemistry), antiparallel RNA strand called a primary transcript. In virology, the term transcription is used when referring to mRNA synthesis from a viral RNA molecule. The genome of many Orthornavirae, RNA viruses is composed of Sense (molecular biology), negative-sense RNA which acts as a template for positive sense viral messenger RNA - a necessary step in the synthesis of viral proteins needed for viral replication. This process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exome
The exome is composed of all of the exons within the genome, the sequences which, when transcribed, remain within the mature RNA after introns are removed by RNA splicing. This includes untranslated regions of messenger RNA (mRNA), and coding regions. Exome sequencing has proven to be an efficient method of determining the genetic basis of more than two dozen Mendelian or single gene disorders. Statistics The human exome consists of roughly 233,785 exons, about 80% of which are less than 200 base pairs in length, constituting a total of about 1.1% of the total genome, or about 30 megabases of DNA. Though composing a very small fraction of the genome, mutations in the exome are thought to harbor 85% of mutations that have a large effect on disease. Definition It is important to note that the exome is distinct from the transcriptome, which is all of the transcribed RNA within a cell type. While the exome is constant from cell-type to cell-type, the transcriptome changes ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expressed Sequence Tag
In genetics, an expressed sequence tag (EST) is a short sub-sequence of a cDNA sequence. ESTs may be used to identify gene transcripts, and were instrumental in gene discovery and in gene-sequence determination. The identification of ESTs has proceeded rapidly, with approximately 74.2 million ESTs now available in public databases (e.g. GenBank 1 January 2013, all species). EST approaches have largely been superseded by whole genome and transcriptome sequencing and metagenome sequencing. An EST results from one-shot sequencing of a cloned cDNA. The cDNAs used for EST generation are typically individual clones from a cDNA library. The resulting sequence is a relatively low-quality fragment whose length is limited by current technology to approximately 500 to 800 nucleotides. Because these clones consist of DNA that is complementary to mRNA, the ESTs represent portions of expressed genes. They may be represented in databases as either cDNA/mRNA sequence or as the reverse compleme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics () is an interdisciplinary field of science that develops methods and Bioinformatics software, software tools for understanding biological data, especially when the data sets are large and complex. Bioinformatics uses biology, chemistry, physics, computer science, data science, computer programming, information engineering, mathematics and statistics to analyze and interpret biological data. The process of analyzing and interpreting data can sometimes be referred to as computational biology, however this distinction between the two terms is often disputed. To some, the term ''computational biology'' refers to building and using models of biological systems. Computational, statistical, and computer programming techniques have been used for In silico, computer simulation analyses of biological queries. They include reused specific analysis "pipelines", particularly in the field of genomics, such as by the identification of genes and single nucleotide polymorphis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |