|
Transcranial Stimulation (other)
Transcranial stimulation may refer to: *Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS or rTMS or deep TMS) *Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) *Transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) * Transcranial pulsed ultrasound(TPU) * Transcranial focused ultrasound stimulation (tFUS) *Cranial electrotherapy stimulation Cranial electrotherapy stimulation (CES) is a form of neurostimulation that delivers a small, pulsed, alternating current via electrodes on the head. CES is used with the intention of treating a variety of conditions such as anxiety, clinical depr ... (CES), also called ''transcranial electrotherapy'' See also * Electro stimulation (other) {{Disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a noninvasive neurostimulation technique in which a changing magnetic field is used to induce an electric current in a targeted area of the brain through electromagnetic induction. A device called a stimulator generates electric pulses that are delivered to a magnetic coil placed against the scalp. The resulting magnetic field penetrates the skull and induces a secondary electric current in the underlying brain tissue, modulating neural activity. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) is a safe, effective, and FDA-approved treatment for major depressive disorder (approved in 2008), chronic pain (2013), and obsessive-compulsive disorder (2018). It has strong evidence for certain neurological and psychiatric conditions—especially depression (with a large effect size), neuropathic pain, and stroke recovery—and emerging advancements like iTBS and image-guided targeting may improve its efficacy and efficiency. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
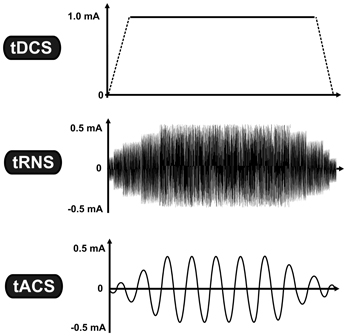
Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) is a form of neuromodulation that uses constant, low direct current delivered via electrodes on the head. This type of neurotherapy was originally developed to help patients with brain injuries or neuropsychiatric conditions such as major depressive disorder. It can be contrasted with cranial electrotherapy stimulation, which generally uses alternating current the same way, as well as transcranial magnetic stimulation. Research shows increasing evidence for tDCS as a treatment for depression. There is mixed evidence about whether tDCS is useful for cognitive enhancement in healthy people. There is no strong evidence that tDCS is useful for memory deficits in Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease, non-neuropathic pain, nor for improving arm or leg functioning and muscle strength in people recovering from a stroke. There is emerging supportive evidence for tDCS in the management of schizophreniaespecially for negative symptoms. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation
Cranial electrotherapy stimulation (CES) is a form of neurostimulation that delivers a small, pulsed, alternating current via electrodes on the head. CES is used with the intention of treating a variety of conditions such as anxiety, depression and insomnia. CES has been suggested as a possible treatment for headaches, fibromyalgia, smoking cessation, and opiate withdrawal, but there is little evidence of effectiveness for many of these conditions and the evidence for use in acute depression is not sufficient to justify it. Medical uses A 2014 Cochrane review found insufficient evidence to determine whether or not CES with alternating current is safe and effective for treating depression. The FDA came to the same conclusion in December 2019. A 2018 systematic review found that evidence is insufficient that CES has clinically important effects on fibromyalgia, headache, neuromusculoskeletal pain, degenerative joint pain, depression, or insomnia; low-strength evidence suggests mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcranial Focused Ultrasound Stimulation
Transcranial focused ultrasound (tFUS) is a form of focused ultrasound (FUS) which is being investigated for the potential non-invasive treatment of psychiatric and neurological disorders. It differs from other non-invasive brain stimulation methods such as magnetic (transcranial magnetic stimulation or TMS) and electrical (transcranial direct-current stimulation or tDCS) in that it has higher spatial resolution and precision (millimetric) and is able to reach deep brain structures. Depending on the parameters, tFUS can inhibit, stimulate, and even ablate brain tissue. Only a handful of clinical studies Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, drugs, dietar ... of tFUS for psychiatric conditions have been conducted as of 2024. References Experimental medical treatments Neurostimulati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cranial Electrotherapy Stimulation
Cranial electrotherapy stimulation (CES) is a form of neurostimulation that delivers a small, pulsed, alternating current via electrodes on the head. CES is used with the intention of treating a variety of conditions such as anxiety, clinical depression, depression and insomnia. CES has been suggested as a possible treatment for headaches, fibromyalgia, smoking cessation, and opiate withdrawal, but there is little evidence of effectiveness for many of these conditions and the evidence for use in acute depression (mood), depression is not sufficient to justify it. Medical uses A 2014 Cochrane review found insufficient evidence to determine whether or not CES with alternating current is safe and effective for treating depression. The FDA came to the same conclusion in December 2019. A 2018 systematic review found that evidence is insufficient that CES has clinically important effects on fibromyalgia, headache, neuromusculoskeletal pain, degenerative joint pain, depression, or insomn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |