|
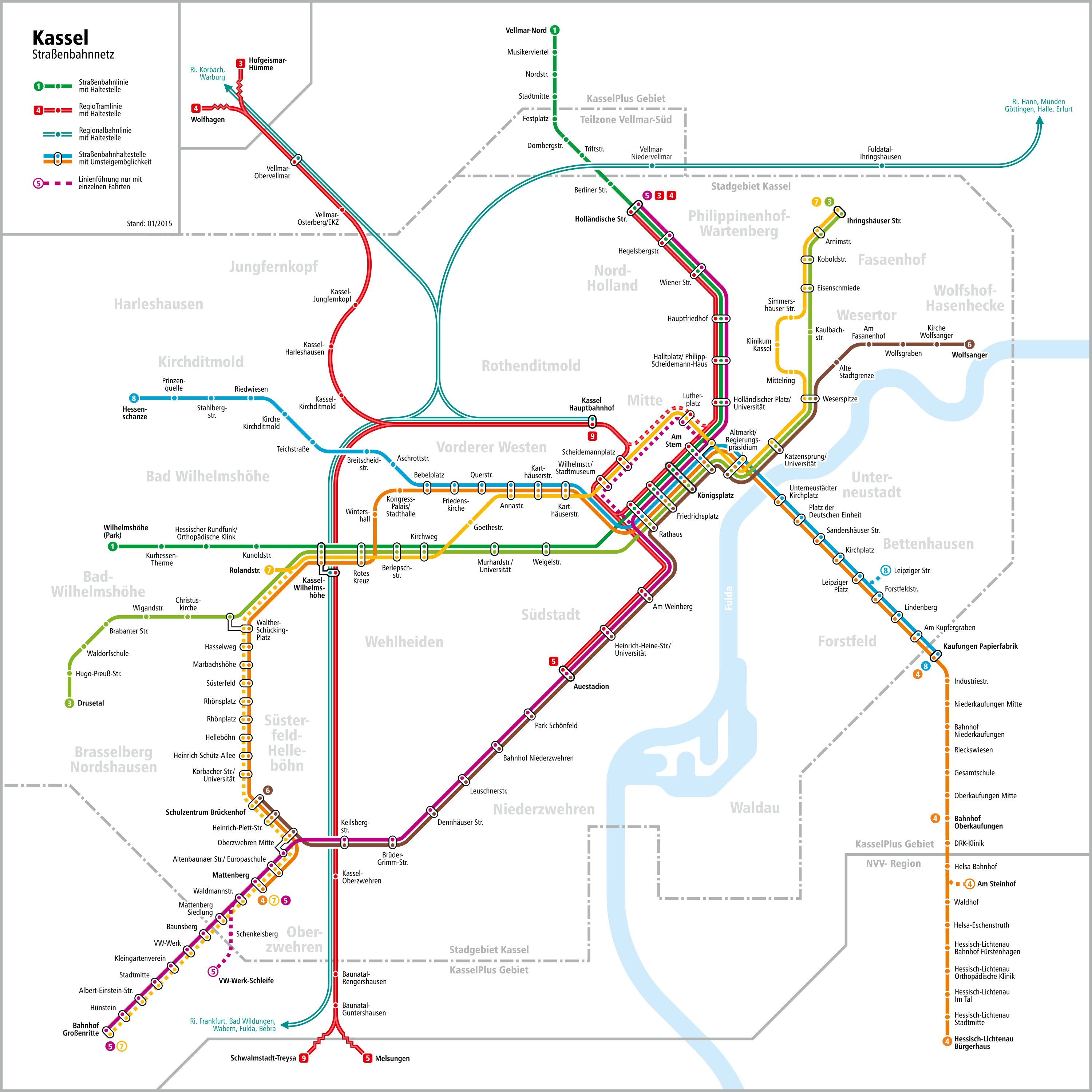
Trams In Kassel
The Kassel tramway network is a network of tramways, forming part of the public transport system in Kassel, a city in the north of the federal state of Hesse, Germany. , the Kassel tram network is made up of seven regular tramlines. Opened in 1877 as a steam tramway from Wilhelmshöhe the Königsplatz (Royal Square), the network has been operated since 1897 by Kasseler Verkehrs-Gesellschaft (KVG), and is integrated in the Nordhessischer Verkehrsverbund (NVV). The track gauge is . There existed also a narrow gauge network to the Hercules monument. The network was extended gradually into the surrounding area, partly as conventional tramways, and partly as a tram-train '' RegioTram'' network. History In the summer of 1870 a horse-drawn omnibus line opened as part of an industrial exhibition from 1 June to 5 October 1870. The growth of the city made it attractive to operate a steam tram which was opened in 1877 by the English company "Jay & Comp. London". With the first two s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kassel
Kassel (; in Germany, spelled Cassel until 1926) is a city on the Fulda River in North Hesse, northern Hesse, in Central Germany (geography), central Germany. It is the administrative seat of the Regierungsbezirk Kassel (region), Kassel and the district Kassel (district), of the same name, and had 201,048 inhabitants in December 2020. The former capital of the States of Germany, state of Hesse-Kassel, it has many palaces and parks, including the Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe, which is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Kassel is also known for the ''documenta'' Art exhibition, exhibitions of contemporary art. Kassel has a Public university, public University of Kassel, university with 25,000 students (2018) and a multicultural population (39% of the citizens in 2017 had a migration background). History Kassel was first mentioned in 913 AD, as the place where two deeds were signed by King Conrad of Franconia, Conrad I. The place was called ''Chasella'' or ''Chassalla'' and was a fortifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Track Gauge
In rail transport, track gauge is the distance between the two rails of a railway track. All vehicles on a rail network must have Wheelset (rail transport), wheelsets that are compatible with the track gauge. Since many different track gauges exist worldwide, gauge differences often present a barrier to wider operation on railway networks. The term derives from the metal bar, or gauge, that is used to ensure the distance between the rails is correct. Railways also deploy two other gauges to ensure compliance with a required standard. A ''loading gauge'' is a two-dimensional profile that encompasses a cross-section of the track, a rail vehicle and a maximum-sized load: all rail vehicles and their loads must be contained in the corresponding envelope. A ''structure gauge'' specifies the outline into which structures (bridges, platforms, lineside equipment etc.) must not encroach. Uses of the term The most common use of the term "track gauge" refers to the transverse distance be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Town Tramway Systems In Germany
This is a list of town tramway systems in Germany by ''Land''. It includes all tram systems, past and present. Cities with currently operating systems, and those systems themselves, are indicated in bold and blue background colored rows. Those tram systems that operated on other than standard gauge track (where known) are indicated in the 'Notes' column. Baden-Württemberg Bavaria (Bayern) Berlin Brandenburg Bremen Hamburg Hessen Lower Saxony (Niedersachsen) Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania (Mecklenburg-Vorpommern) North Rhine-Westphalia (Nordrhein-Westfalen) Rhine-Ruhr (Rhein-Ruhr) '' Ruhrgebiet (Ruhr Area)'' towns in geographic order, west to east: '' ''Bezirksregierung Düsseldorf'' (Düsseldorf Region) and '' ''Bezirksregierung Arnsberg'' (Arnsberg Region) towns not tabulated above, in geographic order, west to east: Note for Rheydt: Amalgamated with Mönchengladbach from 29 July 1929 to 31 July 1933, and again from 1 January 1975. Note f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Documenta
Documenta (often stylized documenta) is an Art exhibition, exhibition of contemporary art which takes place every five years in Kassel, Germany. Documenta was founded by artist, teacher and curator Arnold Bode in 1955 as part of the Bundesgartenschau (Federal Horticultural Show) which took place in Kassel at that time. It was an attempt to bring Germany up to speed with modern art, both banishing and repressing the cultural darkness of Nazism. This first Documenta featured many artists who are generally considered to have had a significant influence on modern art (such as Pablo Picasso, Picasso and Wassily Kandinsky, Kandinsky). The more recent editions of the event feature artists based across the world, but much of the art is Site-specific art, site-specific. Every Documenta is limited to 100 days of exhibition, which is why it is often referred to as the "museum of 100 days". Documenta is not a selling exhibition. Etymology ''Documenta'', an invented word, reflects the int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wrap Advertising
A vehicle vinyl wrap is the automotive aftermarket practice of completely or partially covering a vehicle's original paint with a vinyl wrap. Generally this vinyl wrap will be a different color or finish like a gloss, matte, chrome or clear protective layer. The purpose may be for a color change, advertising or custom livery. Vinyl wraps were first used for advertising, resulting in vehicle becoming essentially mobile billboards. The vinyl sheets can later be removed with relative ease, drastically reducing the costs associated with changing advertisements. History Vehicle vinyl wrap and color change wrap grew in popularity out of the wrap advertising business. The first attempts at using the plastic in commercial applications failed as a result of being too fragile. In 1926, Waldo Semon invented the vinyl still used today by introducing additives to PVC that made it flexible and easier to process. One of the earliest cosmetic vinyl treatments dates to the 1950s and an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Art – Das Kunstmagazin
''Art – Das Kunstmagazin'' is a monthly art magazine founded by Wolf Uecker and first published by Gruner + Jahr in 1979. Its original editor-in-chief, Axel Hecht, was replaced by Tim Sommer in 2005. The magazine features both new and established contemporary artists across all disciplines (including painting, sculpture, design, and video art) as well as reports on exhibitions and projects. In 2001, ''Art'' assimilated the Swiss monthly art magazine ''Artis – Zeitschrift für neue Kunst'' (), which had been published by Hallwag, Bern and Stuttgart-Ostfildern since 1950. References Further reading * External links * Publisher's profile {{DEFAULTSORT:Art Das Kunstmagazin Visual arts magazines published in Germany Monthly magazines published in Germany Gruner + Jahr Magazines published in Hamburg Magazines established in 1979 German-language magazines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexity Classic
The Bombardier Flexity Classic is a model of light-rail tram manufactured by Bombardier Transportation (now merged into Alstom). Although it is marketed as the most traditionally designed member of the Flexity family, it is still a modern bi-directional articulated tram with a low-floor section allowing good accessibility, especially to passengers in wheelchairs. Flexity Classic trams run on in Australia, in Essen, in Dresden, and in Leipzig. Flexity models operate in a number of German cities, as well as in Stockholm (2010–2020), Norrköping and Gothenburg (Sweden), Kraków and Gdańsk (Poland), and Adelaide in South Australia. Along with Bombardier's other Flexity trams, the Flexity Classic's closest competitors are Alstom's Citadis and Siemens' Combino, Avenio and Avanto. Adelaide In 2006 TransAdelaide began to replace the Type H cars operating on the Glenelg tram line with 11 Flexity Classic trams built in Bautzen, Germany by Bombardier Transportation. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trams In Gdańsk
A tram (also known as a streetcar or trolley in Canada and the United States) is an urban rail transit in which vehicles, whether individual railcars or multiple-unit trains, run on tramway tracks on urban public streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or tram networks operated as public transport Public transport (also known as public transit, mass transit, or simply transit) are forms of transport available to the general public. It typically uses a fixed schedule, route and charges a fixed fare. There is no rigid definition of whic ... are called tramways or simply trams/streetcars. Because of their close similarities, trams are commonly included in the wider term ''light rail'', which also includes systems separated from other traffic. Tram vehicles are usually lighter and shorter than Main line (railway), main line and rapid transit trains. Most trams use electrical power, usually fed by a Pantograph (transport), pantograph sl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duewag
Düwag or Duewag (stylised in all caps), formerly Waggonfabrik Uerdingen, was a German manufacturer of rail vehicles. It was sold in 1999 to Siemens with the brand later retired. History Duewag was founded in March 1898 as Waggonfabrik Uerdingen in Uerdingen and produced rail vehicles under the Düwag brand. After merging with Düsseldorfer Waggonfabrik in 1935, railway vehicles were built in Uerdingen, while the Düsseldorf plant produced mainly local traffic vehicles, namely tramway and light rail vehicles. In 1981, the company changed its name from Waggonfabrik Uerdingen to Duewag. Siemens acquired a 60% shareholding in 1989 before taking full ownership in April 1999. In 2001, the Düsseldorf plant was closed with production transferred to Uerdingen. Duewag vehicles were close to a monopoly market in West Germany, as nearly every tram and light rail vehicle purchased from the 1960s onward was built by Duewag. Products Train * Uerdingen railbus * Düwag Wadloper * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stadtbahnwagen M/N
The Stadtbahnwagen Typ M/N (translation ''Type "M/N" Light Rail Vehicle'') is a light rail vehicle used by several Stadtbahn and tram networks in Germany and Austria plus second hand in Poland, Romania and Turkey. It was mainly developed by Düsseldorf-based Duewag, who also built most of the vehicles. As the type evolved over two decades of production, some vehicles have little more in common than their outer dimensions and the basic configuration of a two or thee-part vehicle on three or four bogies with both outer ones powered. History Development started when the transport authorities from Bochum, Essen and Mülheim asked Duewag to develop a standardised vehicle for their meter gauge tram networks, soon followed by Bielefeld and Krefeld. Initially the tramcar was designated ''Stadtbahnwagen R'' (R = Ruhr), but the definitive name became ''Stadtbahn M'' (M = Meterspur (meter gauge)). In 1976, the ''Stadtbahnwagen N'' (N = Normalspur (standard gauge)) for Nuremberg was introduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hauptbahnhof
Central stations or central railway stations emerged in the second half of the nineteenth century as railway stations that had initially been built on the edge of city centres were enveloped by urban expansion and became an integral part of the city centres themselves.Kellerman, Aharon. "Central railway stations" in ''Daily Spatial Mobilities: Physical and Virtual'', Oxford: Routledge, 2012. pp. 159-161. Bán, D. ''The railway station in the social science.'' The Journal of Transport History, 28, 289-93, 2007. As a result, "Central Station" is often, but not always, part of the proper name for a railway station that is the central or primary railway hub for a city. Development Emergence and growth Central stations emerged in the second half of the nineteenth century during what has been termed the "Railway Age".Richards, Jeffrey and John M. MacKenzie, ''The Railway Station'', Oxford: OUP, 1986. Initially railway stations were built on the edge of city centres but, subsequent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe
Bergpark Wilhelmshöhe is a landscape park in Kassel, Germany. The area of the park is , making it the largest European hillside park, and second largest park on a hill slope in the world. Construction of the ''Bergpark'', or "mountain park", began in 1689 at the behest of the Landgraves of Hesse-Kassel and took about 150 years. The park is open to the public today. Since 2013, it has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site because of its monumental Baroque architecture and its unique fountains and water features. Geography Location , a ''Stadtteil'' of Kassel in northern Hesse, is situated west of the city centre at the foot of the Habichtswald hill range. It is also known for Kassel-Wilhelmshöhe station on the Hanover–Würzburg high-speed railway line. Description The park comprises an area of about , stretching from Kassel up to the Karlsberg mountain at . At the summit of the park stands the Hercules monument, a 40-meter high pyramid with a 8.5-meter bronze statue of Hercu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |