|
Tracking Trial
Tracking may refer to: Science and technology Computing * Tracking, in computer graphics, in match moving (insertion of graphics into footage) * Tracking, composing music with music tracker software * Eye tracking, measuring the position of the eye relative to the head * Finger tracking, measuring the positions of the fingers * Optical motion tracking, or motion capture, recording the precise movements of objects or people * Position tracking, monitoring the location of a mechanical system in real-time by counting pulses; see * Positional tracking, an essential component of augmented reality * Video tracking, locating an object in each frame of a video sequence * Mobile phone tracking, monitoring the physical location of a mobile phone * Internet tracking, analyzing online activity * Web visitor tracking, the analysis of visitor behavior on a website * Sleep tracking, monitoring sleeping experience (deep, REM, duration etc.) Life sciences * Animal migration tracking, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Match Moving
In visual effects, match moving is a technique that allows the insertion of 2D elements, other live action elements or CG computer graphics into live-action footage with correct position, scale, orientation, and motion relative to the photographed objects in the Shot (filmmaking), shot. It also allows for the removal of live action elements from the live action shot. The term is used loosely to describe several different methods of extracting camera motion information from a motion picture. Also referred to as motion tracking or camera solving, match moving is related to rotoscoping and photogrammetry. Match moving is sometimes confused with motion capture, which records the motion of objects, often human actors, rather than the camera. Typically, motion capture requires special cameras and sensors and a controlled environment (although recent developments such as the Kinect camera and Apple Inc., Apple's Face ID have begun to change this). Match moving is also distinct from motio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asset Tracking
Asset tracking refers to the method of tracking physical assets, either by scanning barcode labels attached to the assets or by using tags using GPS, BLE, LoRa, or RFID which broadcast their location. These technologies can also be used for indoor tracking of persons wearing a tag. RFID 'Passive' RFID tags broadcast their location but have limited transmission range (typically a few meters). Longer-range "smart tags" use 'active' RFID -where a radio transmitter is powered by a battery and can transmit up to 2000 meters (6,600 feet) in optimum conditions. RFID-based Asset Tracking requires an infrastructure to be put in place before the whereabouts of tags may be ascertained. An asset tracking system can record the location and usage of the assets and generate various reports. Unlike traditional barcode labels, RFID tags can be read faster and have higher durability. RFID is integrated in smart warehousing to track inventory and other assets. Realtime information of the tagged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multitrack Recording
Multitrack recording (MTR), also known as multitracking, is a method of sound recording developed in 1955 that allows for the separate recording of multiple sound sources or of sound sources recorded at different times to create a cohesive whole. Multitracking became possible in the mid-1950s when the idea of simultaneously recording different audio channels to separate discrete ''tracks'' on the same reel-to-reel tape was developed. A ''track'' was simply a different channel recorded to its own discrete area on the tape whereby their relative sequence of recorded events would be preserved, and playback would be simultaneous or Synchronization, synchronized. A multitrack recorder allows one or more sound sources to different tracks to be simultaneously recorded, which may subsequently be processed and mixed separately. Take, for example, a band with vocals, guitars, a keyboard, bass, and drums that are to be recorded. The singer's microphone, the output of the guitars and keys, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Surveillance
Mass surveillance is the intricate surveillance of an entire or a substantial fraction of a population in order to monitor that group of citizens. The surveillance is often carried out by Local government, local and federal governments or intelligence agency, governmental organizations, but it may also be carried out by corporations (either on behalf of governments or at their own initiative). Depending on each nation's laws and Judiciary, judicial systems, the legality of and the permission required to engage in mass surveillance varies. It is the single most indicative distinguishing trait of Totalitarianism, totalitarian regimes. It is often distinguished from targeted surveillance. Mass surveillance has often been cited by agencies like the National Security Agency (NSA) as necessary to fight terrorism, prevent crime and social unrest, protect national security, and control the population. At the same time, mass surveillance has equally often been criticized for violating pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surveillance
Surveillance is the monitoring of behavior, many activities, or information for the purpose of information gathering, influencing, managing, or directing. This can include observation from a distance by means of electronic equipment, such as closed-circuit television (CCTV), or interception of electronically transmitted information like Internet traffic. Increasingly, Government, governments may also obtain Customer data, consumer data through the purchase of online information, effectively expanding surveillance capabilities through commercially available digital records. It can also include simple technical methods, such as Human intelligence (intelligence gathering), human intelligence gathering and postal interception. Surveillance is used by citizens, for instance for protecting their neighborhoods. It is widely used by governments for intelligence gathering, including espionage, prevention of crime, the protection of a process, person, group or object, or the investigat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missile Guidance
Missile guidance refers to a variety of methods of guiding a missile or a guided bomb to its intended target. The missile's target accuracy is a critical factor for its effectiveness. Guidance systems improve missile accuracy by improving its Probability of Guidance (Pg). These guidance technologies can generally be divided up into a number of categories, with the broadest categories being "active", "passive", and "preset" guidance. Missiles and guided bombs generally use similar types of guidance system, the difference between the two being that missiles are powered by an onboard engine, whereas guided bombs rely on the speed and height of the launch aircraft for propulsion. History The concept of unmanned guidance originated at least as early as World War I, with the idea of remotely guiding an airplane bomb onto a target, such as the systems developed for the R.F.C. World War I Drone Weapons, first powered drones by Archibald Low (the father of radio guidance). In World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracking Transmitter
A tracking transmitter broadcasts a radio signal which can be detected by a directional antenna (typically a Radio Direction Finder). By rotating the antenna one can determine the direction the signal lies in and of course whatever it may be attached to. The EPIRB is an example of a similar device. It is commonly used in model rocketry and remote control aircraft to locate lost equipment. See also * Homing beacon * Emergency locator beacon An emergency locator beacon is a radio beacon, a portable battery powered radio transmitter, used to geolocalization, locate airplanes, vessels, and persons in distress and in need of immediate rescue. Various types of emergency locator beacons ar ... External links1.5 volt example transmitter Wireless transmitters {{radio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracking System
A tracking system or locating system is used for Surveillance, tracking persons or objects that do not stay in a fixed location, and supplying a time-ordered sequence of positions (track). Applications A myriad of tracking systems exist. Some are 'lag time' indicators, that is, the data is collected after an item has passed a point for example, a bar code or choke point or gate. Others are 'real-time' or 'near real-time' like Global Positioning Systems (GPS) depending on how often the data is refreshed. There are bar-code systems which require items to be scanned and other which have Automatic identification and data capture, automatic identification (RFID auto-id). For the most part, the tracking worlds are composed of discrete hardware and software systems for different applications. That is, bar-code systems are separate from Electronic Product Code (EPC) systems and GPS systems are separate from active real time locating systems or Real-time locating, RTLS. For example ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar Tracker
A radar tracker is a component of a radar system, or an associated command and control (C2) system, that associates consecutive radar observations of the same target into Track (navigation), tracks. It is particularly useful when the radar system is reporting data from several different targets or when it is necessary to combine the data from several different radars or other sensors for data fusion. Role of the radar tracker A classical rotating air surveillance radar system detects target echoes against a background of noise. It reports these detections (known as "plots") in Polar coordinate system, polar coordinates representing the range and bearing of the target. In addition, noise in the radar receiver will occasionally exceed the detection threshold of the radar's constant false alarm rate detector and be incorrectly reported as targets (known as false alarms). The role of the radar tracker is to monitor consecutive updates from the radar system (which typically occur once ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Tape Tracking
In a video tape recorder, tracking is a calibration adjustment which ensures that the spinning playback head is properly aligned with the helical scan signal written onto the tape. In the case of VHS, a linear control track A control track is a track that runs along an outside edge of a standard analog videotape (including VHS). The control track encodes a series of pulses, each pulse corresponding to the beginning of each frame. This allows the video tape player ... at the tape's lower edge holds pulses that mark the beginning of every frame of video; these are used to fine-tune the tape speed during playback and to get the rotating heads exactly on their helical tracks rather than having them end up somewhere between two adjacent tracks. However, the exact distance between the rotating video head and the fixed head reading the linear track can vary by a couple of micrometers between machines due to manufacturing tolerances, so most machines offer a manual or automatic tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toe (automotive)
In automotive engineering, toe, also known as tracking, is the symmetric angle that each wheel makes with the longitudinal axis of the vehicle, as a function of static geometry, and kinematic and compliant effects. This can be contrasted with steer, which is the antisymmetric angle, i.e. both wheels point to the left or right, in parallel (roughly). Negative toe, or toe out, is the front of the wheel pointing away from the centreline of the vehicle. Positive toe, or toe in, is the front of the wheel pointing towards the centreline of the vehicle. Historically, and still commonly in the United States, toe was specified as the linear difference (either inches or millimeters) of the distance between the two front-facing and rear-facing tire centerlines at the outer diameter and axle-height; since the toe angle in that case depends on the tire diameter, the linear dimension toe specification for a particular vehicle is for specified tires. Description In a rear-wheel drive vehicl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
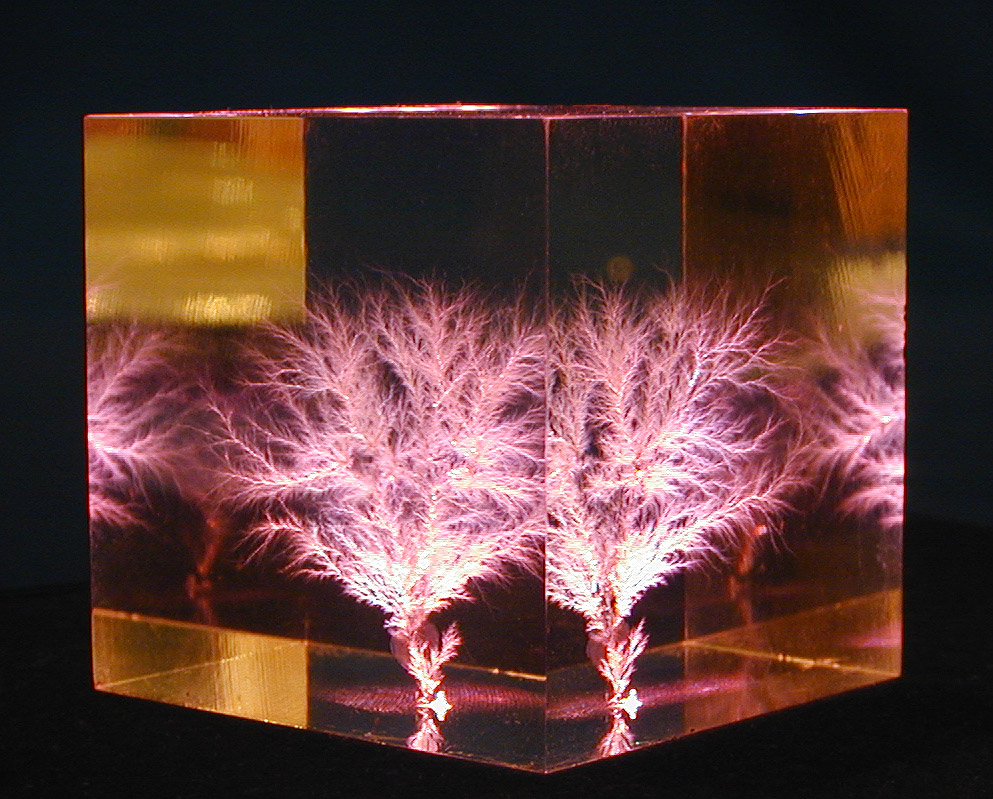
Electrical Treeing
In electrical engineering, treeing is an electrical pre-breakdown phenomenon in solid insulation. It is a damaging process due to partial discharges and progresses through the stressed dielectric insulation, in a path resembling the branches of a tree. Treeing of solid high-voltage cable insulation is a common breakdown mechanism and source of electrical faults in underground power cables. Other occurrences and causes Electrical treeing is typically initiated and then propagates when a dry dielectric material is subjected to high and divergent electrical field stress over a long period of time. Electrical treeing is observed to originate at points where impurities, gas voids, mechanical defects, or conducting projections cause excessive electrical field stress within small regions of the dielectric. This can ionize gases within voids inside the bulk dielectric, creating small electrical discharges between the walls of the void. An impurity or defect may even result in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |