|
Tourism In Tanzania
Tanzania is a country with many tourist attractions. Approximately 38 percent of Tanzania's land area is set aside in protected areas for conservation. There are List of protected areas of Tanzania, 17 national parks, 29 game reserves, 40 controlled conservation areas (including the Ngorongoro Conservation Area) and marine parks. Tanzania is also home to Mount Kilimanjaro, the highest point in Africa. Travel and tourism contributed 17.5 percent of Tanzania's gross domestic product in 2016 and employed 11.0 percent of the country's labour force (1,189,300 jobs) in 2013. The sector is growing rapidly, rising from US$1.74 billion in 2004 to US$4.48 billion in 2013. In 2016, 1,284,279 tourists arrived at Tanzania's borders compared to 590,000 in 2005. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elephant And Tourists At Ngorongoro Crater
Elephants are the Largest and heaviest animals, largest living land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant (''Loxodonta africana''), the African forest elephant (''L. cyclotis''), and the Asian elephant (''Elephas maximus''). They are the only surviving members of the Family (biology), family Elephantidae and the Order (biology), order Proboscidea; extinct relatives include mammoths and mastodons. Distinctive features of elephants include a long proboscis called a trunk, tusks, large ear flaps, pillar-like legs, and tough but sensitive grey skin. The trunk is Prehensility, prehensile, bringing food and water to the mouth and grasping objects. Tusks, which are derived from the incisor teeth, serve both as weapons and as tools for moving objects and digging. The large ear flaps assist in maintaining a constant body temperature as well as in communication. African elephants have larger ears and concave backs, whereas Asian elephants hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
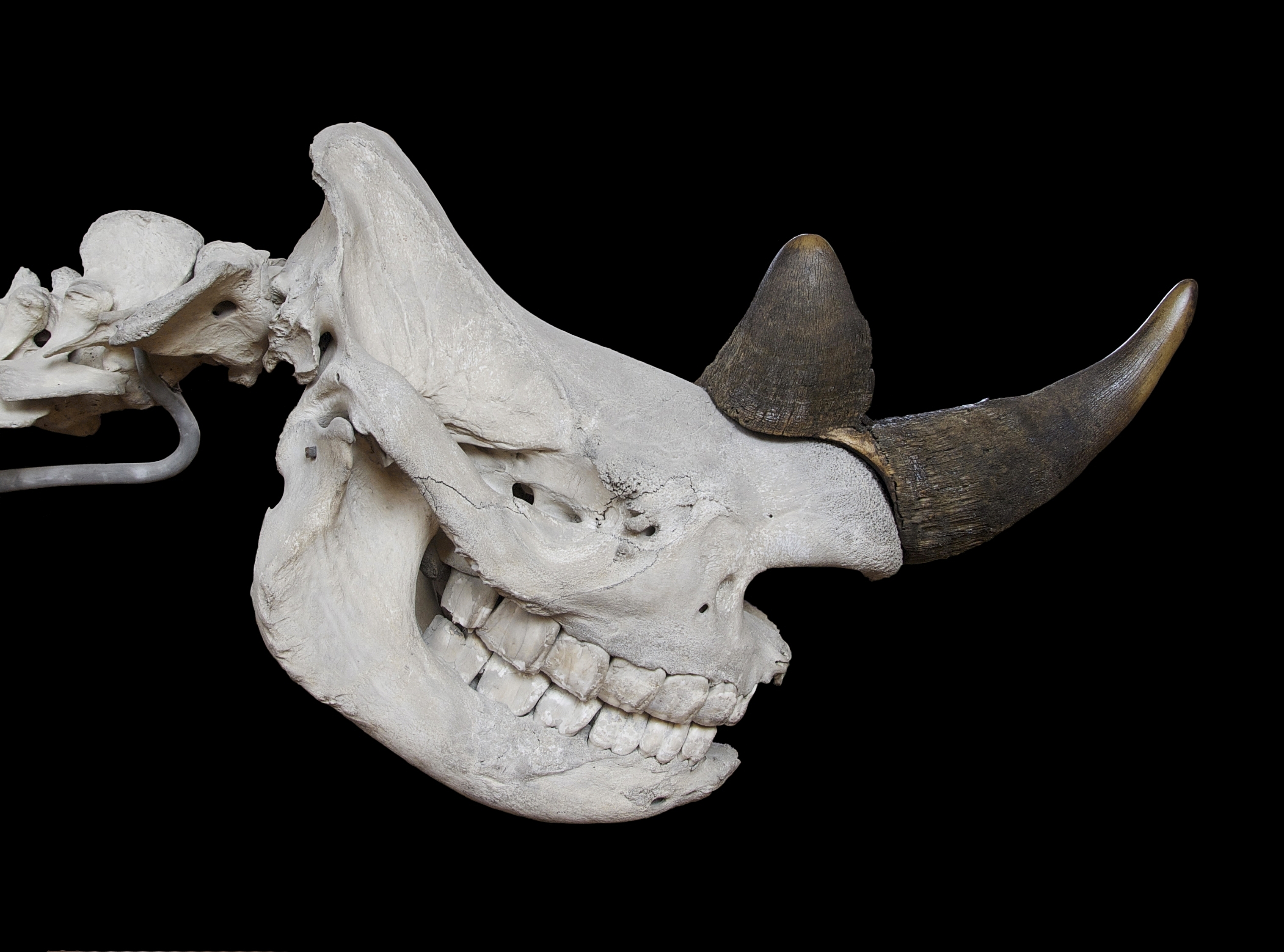
Black Rhinoceros
The black rhinoceros (''Diceros bicornis''), also called the black rhino or the hooked-lip rhinoceros, is a species of rhinoceros native to East Africa, East and Southern Africa, including Angola, Botswana, Eswatini, Kenya, Lesotho, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. Although the species is referred to as ''black'', its colours vary from brown to grey. It is the only extant species of the genus ''Diceros''. The other rhinoceros native to Africa is the white rhinoceros (''Ceratotherium simum''). The word "white" in the name "white rhinoceros" is often said to be a misinterpretation of the Afrikaans word ' (Dutch language, Dutch ') meaning wide, referring to its square upper lip, as opposed to the pointed or hooked lip of the black rhinoceros. These species are now sometimes referred to as the square-lipped (for white) or hook-lipped (for black) rhinoceros. The species overall is classified as critically endangered (even though the south-wes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Kilimanjaro Dec 2009 Edit1
Mount is often used as part of the name of specific mountains, e.g. Mount Everest. Mount or Mounts may also refer to: Places * Mount, Cornwall, a village in Warleggan parish, England * Mount, Perranzabuloe, a hamlet in Perranzabuloe parish, Cornwall, England People * Mount (surname) * William L. Mounts (1862–1929), American lawyer and politician Computing and software * Mount (computing), the process of making a file system accessible * Mount (Unix), the utility in Unix-like operating systems which mounts file systems Books * ''Mount!'', a 2016 novel by Jilly Cooper Displays and equipment * Mount, a fixed point for attaching equipment, such as a hardpoint on an airframe * Mounting board, in picture framing * Mount, a hanging scroll for mounting paintings * Mount, to display an item on a heavy backing such as foamcore, e.g.: ** To pin a biological specimen, on a heavy backing in a stretched stable position for ease of dissection or display ** To prepare dead animal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kitulo National Park
Kitulo National Park (''Hifadhi ya Taifa ya Kitulo'', in Swahili) is a national park of Tanzania, constituting a protected area of montane grassland and montane forest on the Kitulo Plateau in the southern highlands of Tanzania. The park is at an elevation of between the peaks of the Kipengere and Poroto mountains and covers an area of , The Ndumbi forest is also home to a 100-meter waterfall. References External links Kitulo National Park, Tanzania National Parks website {{authority control Geography of Njombe Region Geography of Mbeya Region National parks of Tanzania Protected areas established in 2005 Southern Highlands, Tanzania Southern Rift montane forest–grassland mosaic Tourist attractions in the Njombe Region Tourist attractions in the Mbeya Region 2005 establishments in Tanzania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanzania National Parks Authority
The Tanzania National Parks Authority () commonly known as TANAPA is responsible for the management and conservation of all national parks in the country, aiming to protect biodiversity and promote sustainable tourism.. TANAPA is a parastatal corporation and all its income is reinvested into the organization. It is governed by a number of instruments including the National Parks Act, Chapter 282 of the 2002 and the Wildlife Conservation Act No. 5 of 2009. TANAPA manages the nation's 23 National parks which covers approximately 15% of the land area and has the mandate to conserve and manage the wildlife in Tanzania, and to enforce the related laws and regulations in this industry. It manages the biodiversity of the country, protecting and conserving the flora and fauna. The organization does not have a mandate over the game reserves such as the Selous Game Reserve which is managed by the Tanzanian Wildlife Division and the Ngorongoro Conservation Area managed by the Ngorongoro C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
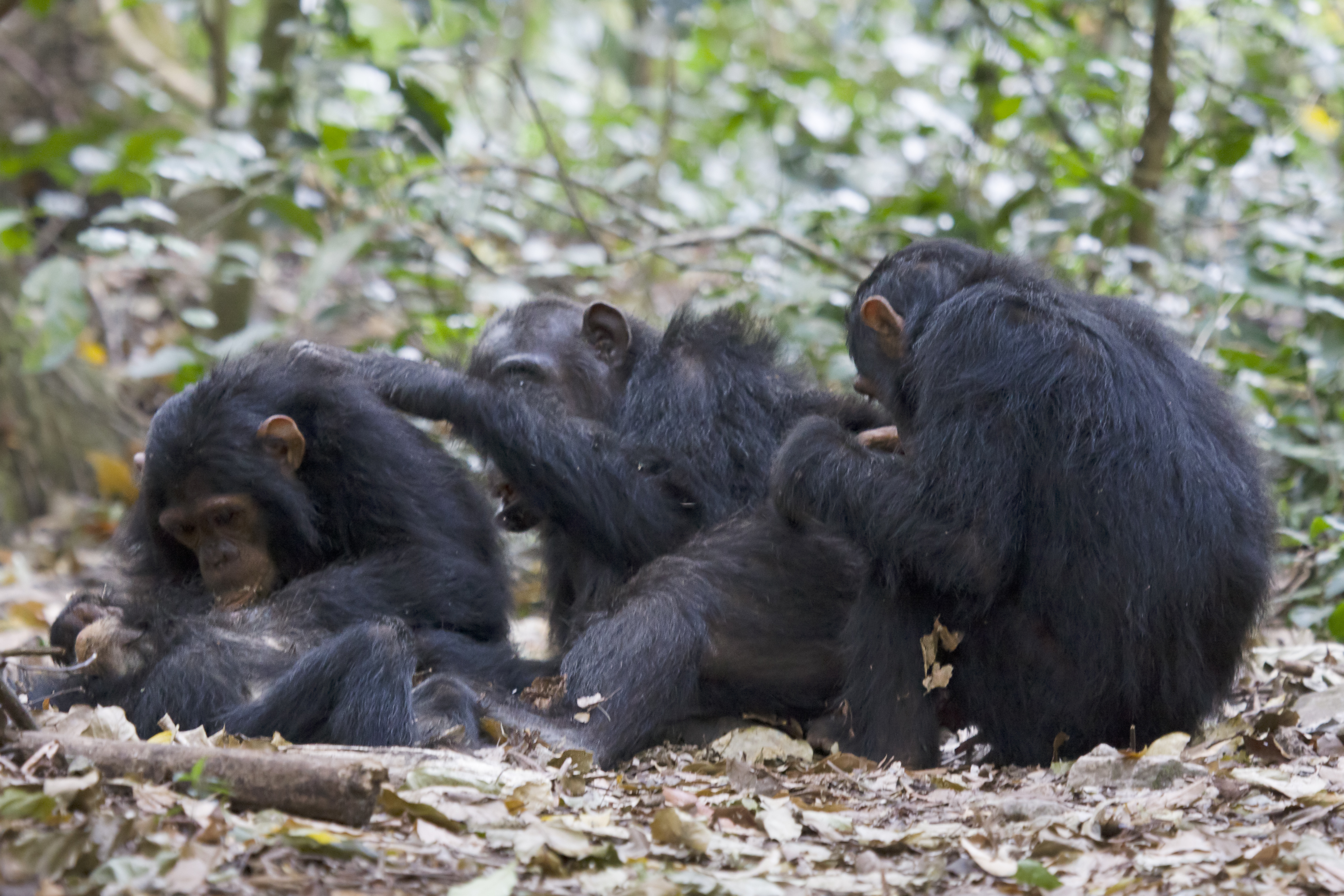
Common Chimpanzee
The chimpanzee (; ''Pan troglodytes''), also simply known as the chimp, is a species of great ape native to the forests and savannahs of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed one. When its close relative the bonobo was more commonly known as the pygmy chimpanzee, this species was often called the common chimpanzee or the robust chimpanzee. The chimpanzee and the bonobo are the only species in the genus ''Pan''. Evidence from fossils and DNA sequencing shows that ''Pan'' is a sister taxon to the human lineage and is thus humans' closest living relative. The chimpanzee is covered in coarse black hair but has a bare face, fingers, toes, palms of the hands, and soles of the feet. It is larger and more robust than the bonobo, weighing for males and for females and standing . The chimpanzee lives in groups that range in size from 15 to 150 members, although individuals travel and forage in much smaller groups during the day. The species lives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jane Goodall
Dame Jane Morris Goodall (; born Valerie Jane Morris-Goodall; 3 April 1934), formerly Baroness Jane van Lawick-Goodall, is an English zoologist, Primatology, primatologist and Anthropology, anthropologist. She is considered the world's foremost expert on chimpanzees, after 60 years' studying the social and family interactions of wild chimpanzees. Goodall first went to Gombe Stream National Park in Tanzania to observe its chimpanzees in 1960. She is the founder of the Jane Goodall Institute and the Roots & Shoots programme and has worked extensively on conservation and animal welfare issues. As of 2022, she is on the board of the Nonhuman Rights Project. In April 2002, she was named a United Nations Messengers of Peace, United Nations Messenger of Peace. Goodall is an honorary member of the World Future Council. Early life Valerie Jane Morris-Goodall was born in April 1934 in Hampstead, London, to businessman (1907–2001) and Margaret Myfanwe Joseph (1906–2000), a novelist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gombe Stream National Park
Gombe National Park () is a national park in Tanzania, located in the Kigoma District of the Kigoma Region. It was formerly called Gombe Stream National Park.Tanzania National Parks“Gombe Stream National Park”, 2008. Overview Established in 1968, it is one of the smallest List of protected areas of Tanzania, national parks in Tanzania, with only of protected land along the hills of the eastern shore of Lake Tanganyika.The Jane Goodall Institute“Gombe Stream Research Centre” 2008. The terrain is distinguished by steep Valley, valleys, and the vegetation ranges from grassland to woodland to tropical rainforest.PBS: Nature“Jane Goodall’s Wild Chimpanzees” 1996. Accessible only by boat, the park is most famous as the location where Jane Goodall pioneered her behavioural research on the common chimpanzee populations. The Kasakela chimpanzee community, featured in several books and documentaries, lives in Gombe National Park. Ecology The park is home to a rich tapestry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katavi National Park
Katavi National Park is a national park in Tanzania located within Mlele District and Nsimbo District of the Katavi Region. Overview Katavi National Park, located in the western region of Tanzania, was originally designated as a game reserve before being officially established as a national park in 1974. Initially covering an area of 1,823 square kilometers, the park was significantly expanded in 1997 to encompass 4,471 square kilometers. Situated approximately 40 kilometers south of Mpanda town, it ranks as Tanzania's third-largest national park, following the renowned Ruaha and Serengeti parks. The area is historically significant as it was originally home to the Rungwa, Manda, and Kimbu peoples, who were the first custodians of this land, contributing to the area's cultural heritage. It is a very remote park that is less frequently visited than other Tanzanian national parks. The park encompasses the Katuma River and the seasonal Lake Katavi and Lake Chada floodplains. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahale Mountains National Park
Mahale Mountains National Park (''Hifadhi ya Taifa ya Milima ya Mahale'', in Swahili) is a national park of Tanzania. The park is located on the eastern shore of Lake Tanganyika in Uvinza District of Kigoma Region. Named after the Mahale Mountains range that is within its borders, the park has several unusual characteristics. First, it is one of only two protected areas for chimpanzees in the country. (The other is nearby Gombe Stream National Park made famous by the researcher Jane Goodall.) Mahale Mountains National Park harbours the largest known population of eastern chimpanzees and due to its size and remoteness, the chimpanzees flourish. It also a place where chimpanzees and lions The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large cat of the genus ''Panthera'', native to Sub-Saharan Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; a short, rounded head; round ears; and a dark, hairy tuft at the tip of its tail. It is se ... co-exist. Another unusual feature of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paranthropus Boisei
''Paranthropus boisei'' is a species of australopithecine from the Early Pleistocene of East Africa about 2.5 to 1.15 million years ago. The holotype specimen, OH 5, was discovered by palaeoanthropologist Mary Leakey in 1959 at Olduvai Gorge, Tanzania and described by her husband Louis a month later. It was originally placed into its own genus as "''Zinjanthropus boisei''", but is now relegated to ''Paranthropus'' along with other robust australopithecines. However, it is also argued that ''Paranthropus'' is an invalid grouping and synonymous with ''Australopithecus'', so the species is also often classified as ''Australopithecus boisei''. Robust australopithecines are characterised by heavily built skulls capable of producing high stresses and bite forces, and some of the largest molars with the thickest enamel of any known ape. ''P. boisei'' is the most robust of this group. Brain size was about , similar to other australopithecines. Some skulls are markedly smaller than ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homo Habilis
''Homo habilis'' ( 'handy man') is an extinct species of archaic human from the Early Pleistocene of East and South Africa about 2.4 million years ago to 1.65 million years ago ( mya). Upon species description in 1964, ''H. habilis'' was highly contested, with many researchers recommending it be synonymised with ''Australopithecus africanus'', the only other early hominin known at the time, but ''H. habilis'' received more recognition as time went on and more relevant discoveries were made. By the 1980s, ''H. habilis'' was proposed to have been a human ancestor, directly evolving into ''Homo erectus'', which directly led to modern humans. This viewpoint is now debated. Several specimens with insecure species identification were assigned to ''H. habilis'', leading to arguments for splitting, namely into "'' H. rudolfensis''" and "'' H. gautengensis''" of which only the former has received wide support. Like contemporary ''Homo'', ''H. habilis'' brain size generally varied from . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |