|
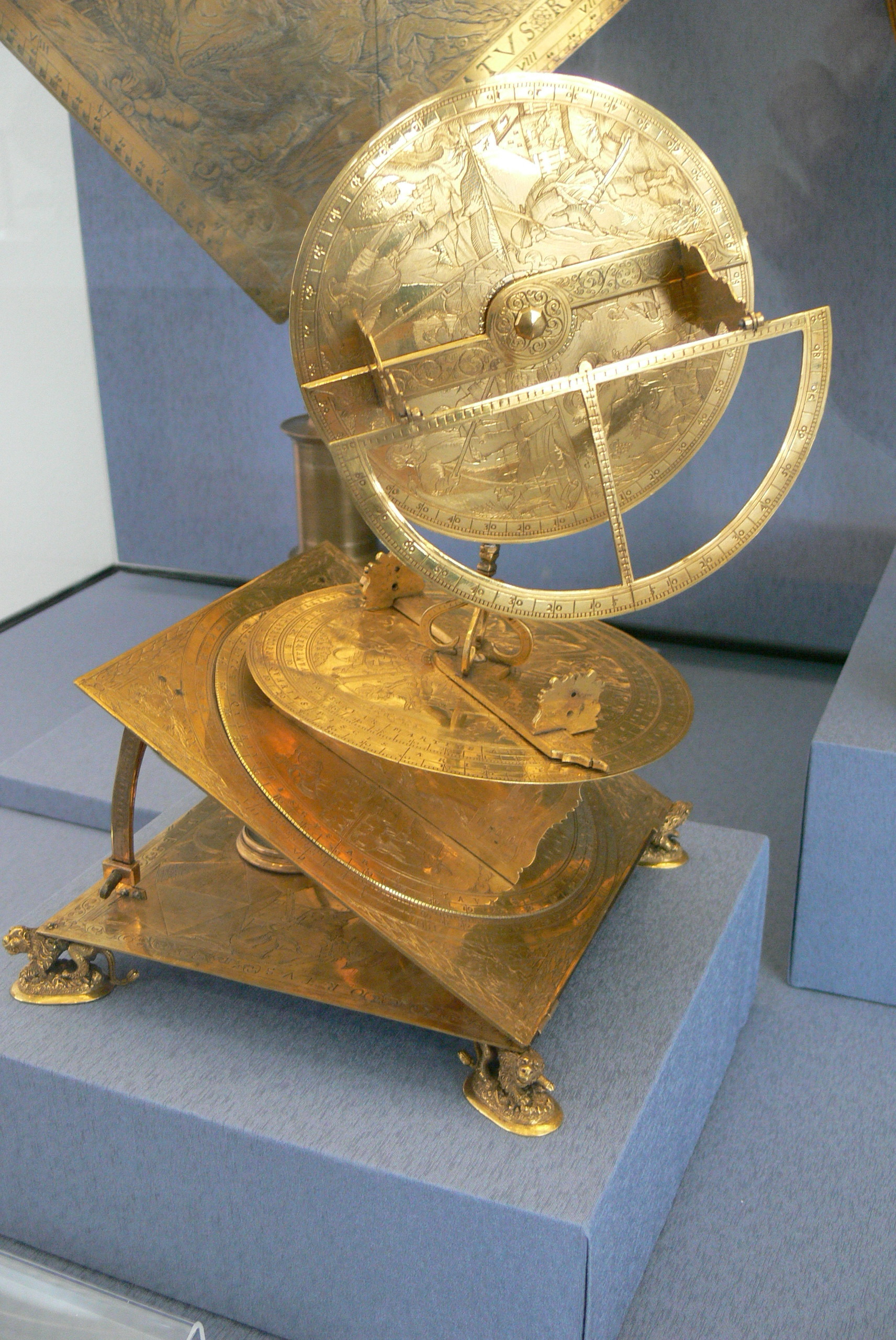
Torquetum
The ''torquetum'' or turquet is a medieval astronomical instrument designed by persons unknown to take and convert measurements made in three sets of coordinates: horizon, equatorial, and ecliptic. It is characterised by R. P. Lorch as a combination of Ptolemy's astrolabon () and the plane astrolabe. In a sense, the ''torquetum'' is an analog computer. Invention The origins of the ''torquetum'' are unclear. Its invention has been credited to multiple figures, including Jabir ibn Aflah, Bernard of Verdun and Franco of Poland. Jabir ibn Aflah of Al-Andalus in the early 12th century has been assumed by several historians to be the inventor of the ''torquetum'', based on a similar instrument he described in his ''Islah Almajisti''. However, while his device is similar in function, it has not been identified as a ''torquetum'', but evidence suggests it inspired the torquetum. The earliest explicit accounts of the ''torquetum'' appear in the 13th century writings of Bernard of Ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Ambassadors (Holbein)
''The Ambassadors'' is a 1533 painting by Hans Holbein the Younger. Also known as ''Jean de Dinteville and Georges de Selve'', after the two people it portrays, it was created in the Tudor period, in the same year Elizabeth I was born. Franny Moyle speculates that Elizabeth's mother, Anne Boleyn, then Queen of England, might have commissioned it as a gift for Jean de Dinteville, the French ambassador, portrayed on the left. De Selve was a Catholic Bishop. As well as being a double portrait, the painting contains a still life of meticulously rendered objects, the meaning of which is the cause of much debate. An array of expensive scientific objects, related to knowing the time and the cosmos are prominently displayed. Several refer to Rome, the seat of the Pope. A second shelf of objects shows a lute with a broken string, a symbol of discord, next to a hymnal composed by Martin Luther. It incorporates one of the best-known examples of anamorphosis in painting. While most scholars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jabir Ibn Aflah
Abū Muḥammad Jābir ibn Aflaḥ (, ; 1100–1150) was an Arab Muslim astronomer and mathematician from Seville, who was active in 12th century al-Andalus. His work ''Iṣlāḥ al-Majisṭi'' (Correction of the ''Almagest'') influenced Islamic, Jewish, and Christian astronomers. ''Iṣlāḥ al-Majisṭi (Correction of the Almagest)'' This work is a commentary and reworking of Ptolemy's ''Almagest'' and is the first criticism of it in the Islamic West. He particularly criticized the mathematical basis of the work. For example, he replaced the use of Menelaus' theorem with ones based on spherical trigonometry, in what seems to be an attempt to increase the mathematical precision of the work. These theorems had been developed by a group of 10th century Islamic mathematicians who included Abū al-Wafā' Būzjānī and then also by Abu Abd Allah Muhammad ibn Muadh Al-Jayyani who worked in al-Andalus during the 11th century. Jābir does not credit any of these authors and does n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Instruments
An astronomical instrument is a device for observing, measuring or recording astronomical data. They are used in the scientific field of astronomy, a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos, with the object of explaining their origin and evolution over time. Many are also used in navigation and surveying. Astronomical instruments include:Descriptions here are taken automatically from the linked articles or from items on Wikidata. * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Radio plate * * * * * * * * * * * * * See also *Astronomy * Outline of astronomy *Surveying instrument Instruments used in surveying include: * Alidade * Alidade table * Cosmolabe * Dioptra * Dumpy level * Engineer's chain * Geodimeter * Graphometer * Groma (surveying) * Laser scanning * Level * Level staff * Measuring tape * Plane table * ... * Measurement instrument Notes {{DEFAULTSORT:Astronomical instruments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Declination
In astronomy, declination (abbreviated dec; symbol ''δ'') is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system, the other being hour angle. The declination angle is measured north (positive) or south (negative) of the celestial equator, along the hour circle passing through the point in question. The root of the word ''declination'' (Latin, ''declinatio'') means "a bending away" or "a bending down". It comes from the same root as the words ''incline'' ("bend forward") and ''recline'' ("bend backward"). In some 18th and 19th century astronomical texts, declination is given as ''North Pole Distance'' (N.P.D.), which is equivalent to 90 – (declination). For instance an object marked as declination −5 would have an N.P.D. of 95, and a declination of −90 (the south celestial pole) would have an N.P.D. of 180. Explanation Declination in astronomy is comparable to geographic latitude, projected onto the celestial sphere, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Ascension
Right ascension (abbreviated RA; symbol ) is the angular distance of a particular point measured eastward along the celestial equator from the Sun at the equinox (celestial coordinates), March equinox to the (hour circle of the) point in question above the Earth. When paired with declination, these celestial coordinate system, astronomical coordinates specify the location of a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system. An old term, ''right ascension'' (), "''Ascensio recta'' Solis, stellæ, aut alterius cujusdam signi, est gradus æquatorus cum quo simul exoritur in sphæra recta"; roughly translated, "''Right ascension'' of the Sun, stars, or any other sign, is the degree of the equator that rises together in a right sphere" refers to the ''ascension'', or the point on the celestial equator that rises with any celestial object as seen from Earth's equator, where the celestial equator perpendicular, intersects the horizon at a right angle. It contrasts wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Computer
An analog computer or analogue computer is a type of computation machine (computer) that uses physical phenomena such as Electrical network, electrical, Mechanics, mechanical, or Hydraulics, hydraulic quantities behaving according to the mathematical principles in question (''analog signals'') to Scientific modelling, model the problem being solved. In contrast, digital computers represent varying quantities symbolically and by discrete values of both time and amplitude (digital signals). Analog computers can have a very wide range of complexity. Slide rules and nomograms are the simplest, while naval gunfire control computers and large hybrid digital/analog computers were among the most complicated. Complex mechanisms for process control and protective relays used analog computation to perform control and protective functions. Analog computers were widely used in scientific and industrial applications even after the advent of digital computers, because at the time they were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Astronomical Instruments
An astronomical instrument is a device for observing, measuring or recording astronomical data. They are used in the scientific field of astronomy, a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos, with the object of explaining their origin and evolution over time. Many are also used in navigation and surveying. Astronomical instruments include:Descriptions here are taken automatically from the linked articles or from items on Wikidata. * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Radio plate * * * * * * * * * * * * * See also *Astronomy Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest includ ... * Outline of astronomy * Surveying instrument * Measurement instrument Notes {{DEFAULTSORT:Astronomical instrumen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
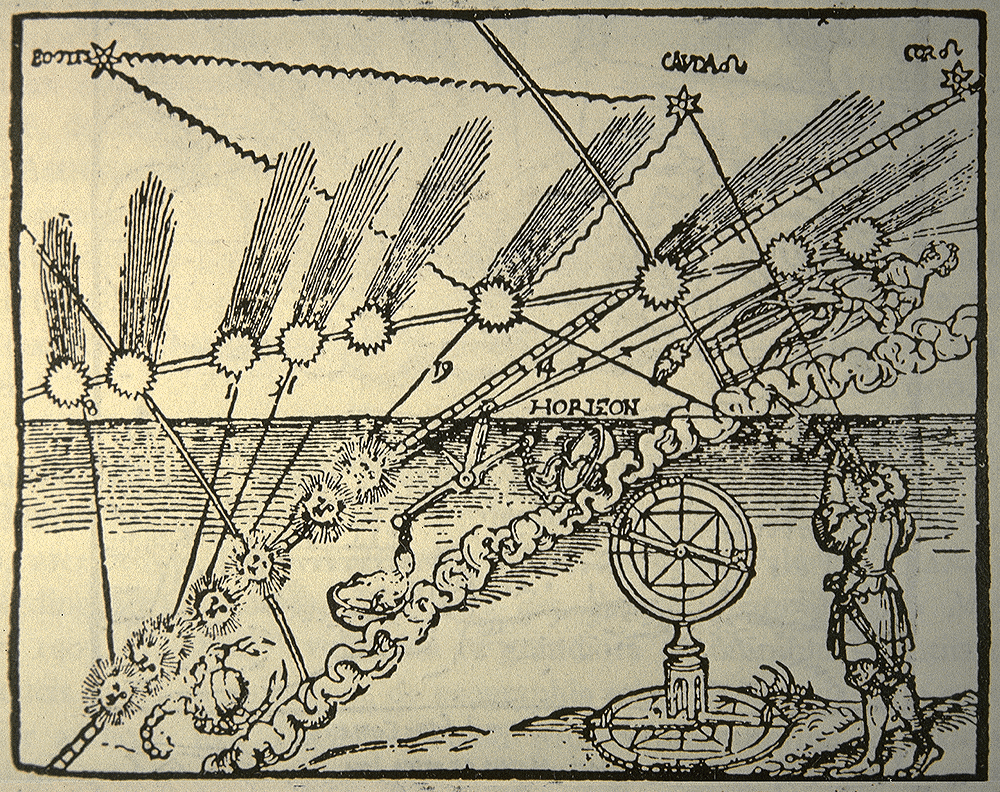
Comet 1532 Apian
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that warms and begins to release gases when passing close to the Sun, a process called outgassing. This produces an extended, gravitationally unbound atmosphere or Coma (cometary), coma surrounding the nucleus, and sometimes a Comet tail, tail of gas and dust gas blown out from the coma. These phenomena are due to the effects of solar radiation and the outstreaming solar wind plasma acting upon the nucleus of the comet. Comet nuclei range from a few hundred meters to tens of kilometers across and are composed of loose collections of ice, dust, and small rocky particles. The coma may be up to 15 times Earth's diameter, while the tail may stretch beyond one astronomical unit. If sufficiently close and bright, a comet may be seen from Earth without the aid of a telescope and can Subtended angle, subtend an arc of up to 30° (60 Moons) across the sky. Comets have been observed and recorded since ancient times by many cultures and religion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Scientific Instruments
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the Human history, human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some theorists categorize history as a social science, while others see it as part of the humanities or consider it a hybrid discipline. Similar debates surround the purpose of history—for example, whether its main aim is theoretical, to uncover the truth, or practical, to learn lessons from the past. In a more general sense, the term ''history'' refers not to an academic field but to the past itself, times in the past, or to individual texts about the past. Historical research relies on Primary source, primary and secondary sources to reconstruct past events and validate interpretations. Source criticism is used to evaluate these sources, assessing their authenticity, content, and reliability. Historians strive to integrate the perspectives o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navigational Equipment
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another.Bowditch, 2003:799. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navigation, marine navigation, aeronautic navigation, and space navigation. It is also the term of art used for the specialized knowledge used by navigators to perform navigation tasks. All navigational techniques involve locating the navigator's position compared to known locations or patterns. Navigation, in a broader sense, can refer to any skill or study that involves the determination of position and direction. In this sense, navigation includes orienteering and pedestrian navigation. For marine navigation, this involves the safe movement of ships, boats and other nautical craft either on or underneath the water using positions from navigation equipment with appropriate nautical charts (electronic and paper). Navigation equipment for ships is ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrolabe
An astrolabe (; ; ) is an astronomy, astronomical list of astronomical instruments, instrument dating to ancient times. It serves as a star chart and Model#Physical model, physical model of the visible celestial sphere, half-dome of the sky. Its various functions also make it an elaborate inclinometer and an analog computer, analog calculation device capable of working out several kinds of problems in astronomy. In its simplest form it is a metal disc with a pattern of wires, cutouts, and perforations that allows a user to calculate astronomical positions precisely. It is able to measure the horizontal coordinate system, altitude above the horizon of a celestial body, day or night; it can be used to identify stars or planets, to determine local latitude given local time (and vice versa), to survey, or to triangulation, triangulate. It was used in classical antiquity, the Islamic Golden Age, the European Middle Ages and the Age of Discovery for all these purposes. The astrolabe, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |