|
Tomistominae
Tomistominae is a subfamily of crocodylians that includes one living species, the false gharial. Many more extinct species are known, extending the range of the subfamily back to the Eocene epoch. In contrast to the false gharial, which is a freshwater species that lives only in southeast Asia, extinct tomistomines had a global distribution and lived in estuaries and along coastlines. The classification of tomistomines among Crocodylia has been in flux; while traditionally thought to be within Crocodyloidea, molecular evidence indicates that they are more closely related to true gharials as members of Gavialoidea. Description Tomistomines have narrow or longirostrine snouts like gharials. The living false gharial lives in fresh water and uses its long snout and sharp teeth to catch fish, although true gharials are more adapted toward piscivory, or fish-eating. Despite the similarity with gharials, the shapes of bones in tomistomine skulls link them with crocodiles. For example, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toyotamaphimeia
''Toyotamaphimeia machikanensis'' (Toyotama-hime from Mountain Machikane ( :ja:待兼山)) is an extinct gavialid crocodylian which lived in Japan during the Pleistocene. A specimen recovered in 1964 at Osaka University during the construction of a new science building has been dated to around 430–380 thousand years old based on the stratum in which it was found. Unassigned species from same genus is also known from Taiwan. ''T. machikanensis'' was a fairly large crocodylian with a 1 m (3.3 ft) skull and a total length up to 7.7 m (25 ft). It was originally described as a member of the genus ''Tomistoma''. History and naming The first bones belonging to ''Toyotamaphimeia'' were discovered on May 3rd 1964 during the construction of a new school building on the grounds of Ôsaka University. A field survey was conducted shortly afterwards, confirming the presence of more fossils, however not yet identifying their crocodilian nature. Following the survey seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
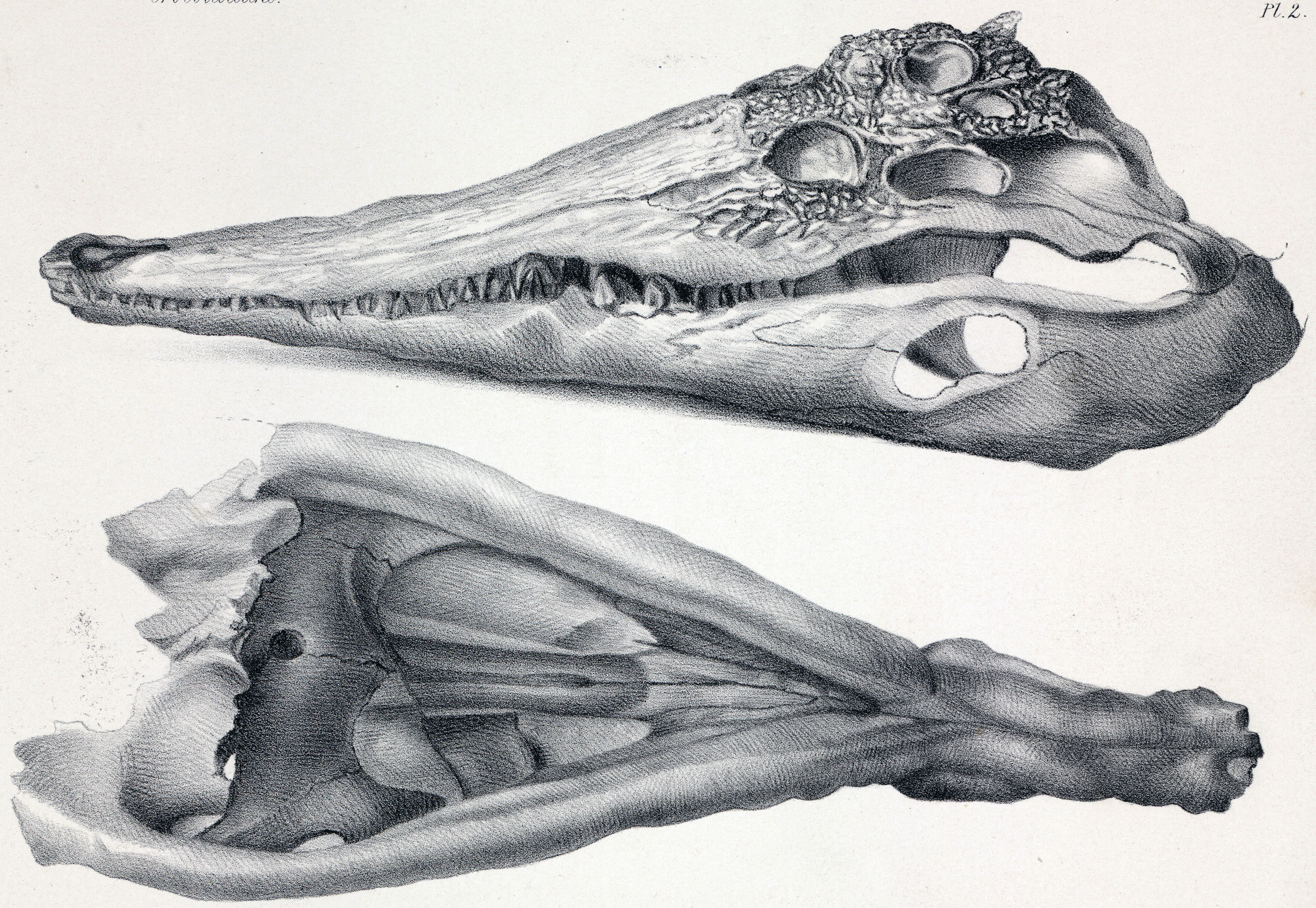
Gavialosuchus
''Gavialosuchus'' is an extinct genus of gavialid crocodylian from the early Miocene of Europe. Currently only one species is recognized, as a few other species of ''Gavialosuchus'' have since been reclassified to other genera. Taxonomy The type species, ''G. eggenburgensis'', is known from the early Miocene of Austria. Two other species - ''G. americanus'' and ''G. carolinensis'' - have since been reclassified to other genera. Myrick Jr. (2001) proposed synonymizing ''Gavialosuchus americanus'' with ''Thecachampsa antiqua''. Piras ''et al.'' (2007) advocated transferring both ''G. americanus'' and ''G. carolinensis'' to ''Thecachampsa'' as distinct species of the latter genus, however. Jouve ''et al.'' (2008) retained ''G. americanus'' in ''Gavialosuchus'' and found it to be the sister group of ''G. eggenburgensis'' (''G. carolinensis'' was not discussed). However, Jouve ''et al.'' (2008) didn't test ''Thecachampsa antiqua'' in their phylogenetic analysis. Shan ''et al.'' (200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penghusuchus
''Penghusuchus'' is an extinct genus of gavialid crocodylian. It is known from a skeleton found in Upper Miocene rocks of Penghu Island, off Taiwan. It may be related to two other fossil Asian gavialids: '' Maomingosuchus petrolica'' of southeastern China and '' Toyotamaphimeia machikanensis'' of Japan. The taxon was described in 2009 by Shan and colleagues; the type species is ''P. pani''. Below is a cladogram based morphological studies comparing skeletal features that shows ''Penghusuchus'' as a member of Tomistominae, related to the false gharial: Based on morphological studies of extinct taxa, the tomistomines (including the living false gharial) were long thought to be classified as crocodiles and not closely related to gavialoids. However, recent molecular studies using DNA sequencing have consistently indicated that the false gharial (''Tomistoma'') (and by inference other related extinct forms in Tomistominae) actually belong to Gavialoidea (and Gavialidae). Bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunggamarandu
''Gunggamarandu'' (meaning "river boss" in Barunggam and Wakka Wakka) is an extinct monospecific genus of tomistomine crocodilian from Pliocene-Pleistocene aged deposits in the Darling Downs (possibly the Riversleigh lagerstätte) of Australia. ''Gunggamarandu'' represents the first tomistomine known from Oceania and it is also the southernmost known tomistomine to date. The type, and only known, species is ''Gunggamarandu maunala'' (meaning "head hole", after the Barunggam words for such), which was described by Jorgo Ristevski ''et al.'' in 2021. Discovery and naming The holotype of ''Gunggamarandu'', QMF14.548 (a partial cranium), was discovered no later than the 1870s, probably around 1875, and it was part of the "old collection" at the Queensland Museum in Brisbane and QMF14.548 was later accessioned into the Queensland Museum collection on January 8, 1914. In 1995, Salisbury ''et al.'' suggested that QMF14.548 may have been a gavialoid.Salisbury, S. W., Molnar, R. E. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dollosuchoides
''Dollosuchoides'', colloquially known as the Crocodile of Maransart, is an extinct monospecific genus of gavialoid crocodilian, traditionally regarded as a member of the subfamily Tomistominae. Fossils have been found in the Brussel Formation of Maransart, Belgium and date back to the middle Eocene. The holotype, IRScNB 482, was discovered in 1915 and it was prepared during 1926–1927 by M. Hubert, J. Mehschaert and M. Jean de Kleermaeker, and also in 1927, Louis Dollo had the holotype put on display in the Museum of Natural Sciences and he intended to describe the specimen but he died in 1931 before he was able to describe it and the specimen was eventually referred to '' Dollosuchus'' by Swinton (1937)Swinton, W. E. (1937)The Crocodile of Maransart (Dollosuchus dixoni [Owen]).''Mémoire'' 80: 3–46 until it was moved to its own genus by Brochu (2007). It is currently housed in the Gand Museum in Belgium. Phylogeny Below is a cladogram based morphological studie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe by the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south. The country covers five-eighths of the island of Great Britain, which lies in the North Atlantic, and includes over 100 smaller islands, such as the Isles of Scilly and the Isle of Wight. The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic period, but takes its name from the Angles, a Germanic tribe deriving its name from the Anglia peninsula, who settled during the 5th and 6th centuries. England became a unified state in the 10th century and has had a significant cultural and legal impact on the wider world since the Age of Discovery, which began during the 15th century. The English language, the Anglican Church, and Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in the west, to Egypt's Suez Canal. Varying sources limit it to the countries of Algeria, Libya, Morocco, and Tunisia, a region that was known by the French during colonial times as "''Afrique du Nord''" and is known by Arabs as the Maghreb ("West", ''The western part of Arab World''). The United Nations definition includes Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, Egypt, Sudan, and the Western Sahara, the territory disputed between Morocco and the Sahrawi Republic. The African Union definition includes the Western Sahara and Mauritania but not Sudan. When used in the term Middle East and North Africa ( MENA), it often refers only to the countries of the Maghreb. North Africa includes the Spanish cities of Ceuta and Melilla, and plazas de so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''palaiós'' meaning "old" and the Eocene Epoch (which succeeds the Paleocene), translating to "the old part of the Eocene". The epoch is bracketed by two major events in Earth's history. The K–Pg extinction event, brought on by an asteroid impact and possibly volcanism, marked the beginning of the Paleocene and killed off 75% of living species, most famously the non-avian dinosaurs. The end of the epoch was marked by the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), which was a major climatic event wherein about 2,500–4,500 gigatons of carbon were released into the atmosphere and ocean systems, causing a spike in global temperatures and ocean acidification. In the Paleocene, the continents of the Northern Hemisphere were still connected v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crocodylia
Crocodilia (or Crocodylia, both ) is an order of mostly large, predatory, semiaquatic reptiles, known as crocodilians. They first appeared 95 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous period (Cenomanian stage) and are the closest living relatives of birds, as the two groups are the only known survivors of the Archosauria. Members of the order's total group, the clade Pseudosuchia, appeared about 250 million years ago in the Early Triassic period, and diversified during the Mesozoic era. The order Crocodilia includes the true crocodiles (family Crocodylidae), the alligators and caimans (family Alligatoridae), and the gharial and false gharial (family Gavialidae). Although the term 'crocodiles' is sometimes used to refer to all of these, crocodilians is a less ambiguous vernacular term for members of this group. Large, solidly built, lizard-like reptiles, crocodilians have long flattened snouts, laterally compressed tails, and eyes, ears, and nostrils at the top of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. Comprising the westernmost peninsulas of Eurasia, it shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south and Asia to the east. Europe is commonly considered to be separated from Asia by the watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea and the waterways of the Turkish Straits. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and Europe ... is formed by the Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountains, and the Blac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splenial
The splenial is a small bone in the lower jaw of reptiles, amphibians and birds, usually located on the lingual side (closest to the tongue) between the angular and surangular The suprangular or surangular is a jaw bone found in most land vertebrates, except mammals. Usually in the back of the jaw, on the upper edge, it is connected to all other jaw bones: dentary, angular, splenial and articular The articular bone ....Watson, D. M. S. (1912). LXVII.—On some reptilian lower jaws. Journal of Natural History, 10(60), 573-587. References Vertebrate anatomy {{Vertebrate anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piscivory
A piscivore () is a carnivorous animal that eats primarily fish. The name ''piscivore'' is derived . Piscivore is equivalent to the Greek-derived word ichthyophage, both of which mean "fish eater". Fish were the diet of early tetrapod evolution (via water-bound amphibians during the Devonian period); insectivory came next; then in time, the more terrestrially adapted reptiles and synapsids evolved herbivory. Almost all predatory fishes (most sharks, tuna, billfishes, pikes etc.) are obligated piscivores. Some non-piscine aquatic animals, such as whales, sea lion and crocodilians, are not completely piscivorous, often also preying on invertebrates, marine mammals, waterbirds and even wading land animals in addition to fish; while others, such as the bulldog bat and gharial, are strictly dependent on fish for food. Some creatures, including cnidarians, octopuses, squid, spiders, cetaceans, grizzly bears, jaguars, wolves, snake Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |