|
Tokamak Sawtooth
A sawtooth is a relaxation that is commonly observed in the core of tokamak plasmas, first reported in 1974. The relaxations occur quasi-periodically and cause a sudden drop in the temperature and density in the center of the plasma. A soft-xray pinhole camera pointed toward the plasma core during sawtooth activity will produce a sawtooth-like signal. Sawteeth effectively limit the amplitude of the central current density. The Kadomtsev model of sawteeth is a classic example of magnetic reconnection. Other repeated relaxation oscillations occurring in tokamaks include the edge localized mode (ELM) which effectively limits the pressure gradient at the plasma edge and the fishbone instability which effectively limits the density and pressure of fast particles. Kadomtsev model An often cited description of the sawtooth relaxation is that by Kadomtsev. The Kadomtsev model uses a resistive magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) description of the plasma. If the amplitude of the current density ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sawtooth Reconnection
Sawtooth may refer to: Science and technology * Tooth of a saw blade (original meaning) * Sawtooth wave, a type of waveform * Sawtooth (cellular automaton) * Tokamak sawtooth, a phenomenon in plasma physics * Sawtooth, code name for the Power Mac G4 * Sawtooth coriander, a herb also called Culantro * Sawtooth eel * Sawtooth Software Arts and media * Sawtooth (film), a 2004 American thriller and drama film * ''Sawtooth'' (album), an album by British electronic musician Jonny L Places * The Sawtooth, between Mount Evans and Mount Bierstadt in Colorado, United States * Sawtooth Bridges, rail viaducts on Northeast Corridor in Kearny, New Jersey * Sawtooth City, Idaho, United States * Sawtooth National Forest, Idaho, United States * Sawtooth National Recreation Area, Idaho, United States * Sawtooth Wilderness, Idaho, United States See also * Sawtooth Range (other) Sawtooth Range, Sawtooth Ridge, and Sawtooth Mountains may refer to: *Sawtooth Range (Alaska) in Alaska, Unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokamak
A tokamak (; ) is a device which uses a powerful magnetic field generated by external magnets to confine plasma (physics), plasma in the shape of an axially symmetrical torus. The tokamak is one of several types of magnetic confinement fusion, magnetic confinement devices being developed to produce controlled thermonuclear fusion power. The tokamak concept is currently one of the leading candidates for a practical fusion reactor for providing minimally polluting electrical power. The proposal to use controlled thermonuclear fusion for industrial purposes and a specific scheme using thermal insulation of high-temperature plasma by an electric field was first formulated by the Soviet physicist Oleg Lavrentiev in a mid-1950 paper. In 1951, Andrei Sakharov and Igor Tamm modified the scheme by proposing a theoretical basis for a thermonuclear reactor, where the plasma would have the shape of a torus and be held by a magnetic field. The first tokamak was built in the Soviet Union ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
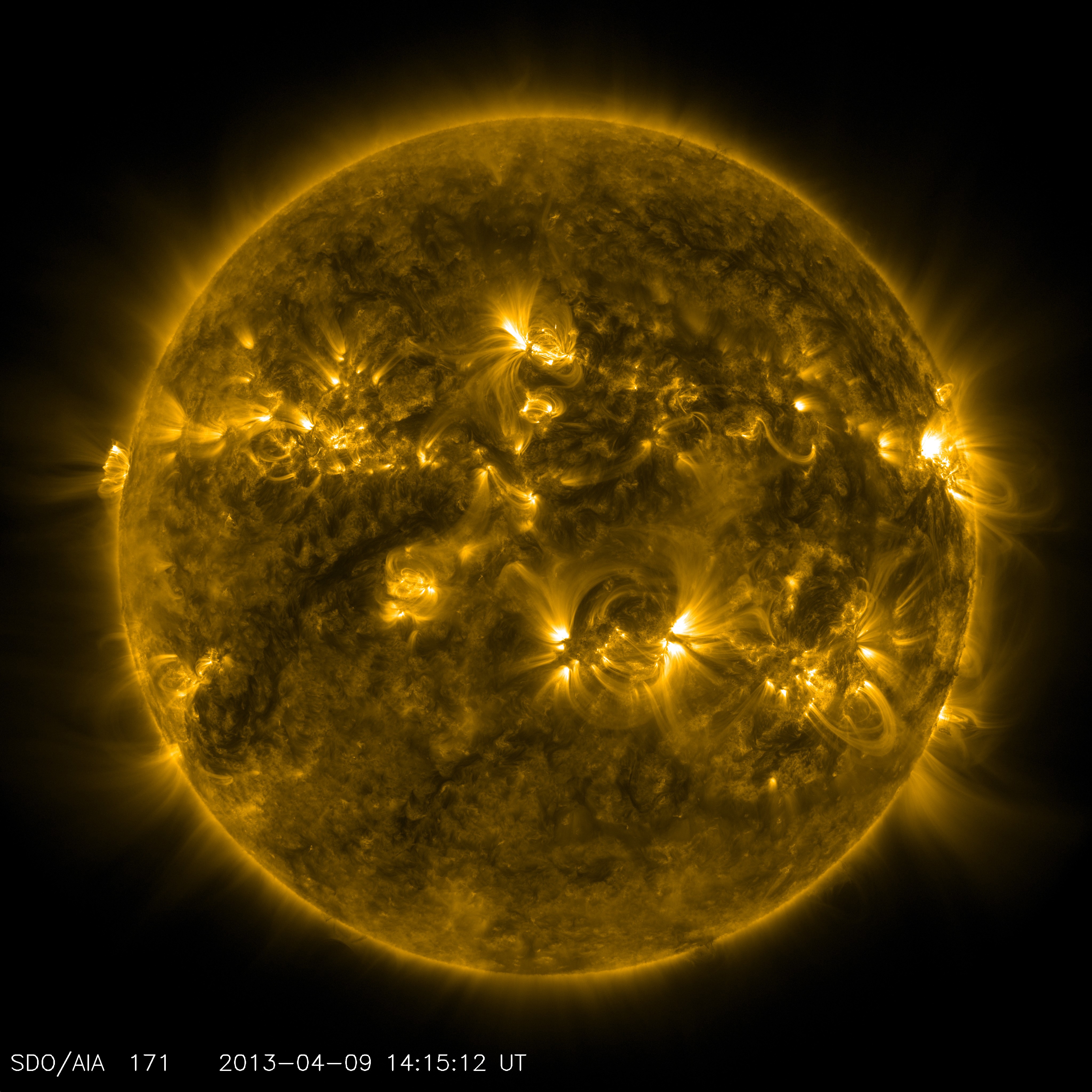
Plasma (physics)
Plasma () is a state of matter characterized by the presence of a significant portion of charged particles in any combination of ions or electrons. It is the most abundant form of ordinary matter in the universe, mostly in stars (including the Sun), but also dominating the rarefied intracluster medium and Outer space#Intergalactic space, intergalactic medium. Plasma can be artificially generated, for example, by heating a neutral gas or subjecting it to a strong electromagnetic field. The presence of charged particles makes plasma electrically conductive, with the dynamics of individual particles and macroscopic plasma motion governed by collective electromagnetic fields and very sensitive to externally applied fields. The response of plasma to electromagnetic fields is used in many modern devices and technologies, such as plasma display, plasma televisions or plasma etching. Depending on temperature and density, a certain number of neutral particles may also be present, in wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sawtooth Wave
The sawtooth wave (or saw wave) is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform. It is so named based on its resemblance to the teeth of a plain-toothed saw with a zero rake angle. A single sawtooth, or an intermittently triggered sawtooth, is called a ramp waveform. The convention is that a sawtooth wave ramps upward and then sharply drops. In a reverse (or inverse) sawtooth wave, the wave ramps downward and then sharply rises. It can also be considered the extreme case of an asymmetric triangle wave. The equivalent piecewise linear functions x(t) = t - \lfloor t \rfloor x(t) = t \bmod 1 based on the floor function of time ''t'' is an example of a sawtooth wave with period 1. A more general form, in the range −1 to 1, and with period ''p'', is 2\left( - \left\lfloor + \right\rfloor\right) This sawtooth function has the same phase as the sine function. While a square wave is constructed from only odd harmonics, a sawtooth wave's sound is harsh and clear and its spectrum cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Reconnection
Magnetic reconnection is a physical process occurring in electrically conducting Plasma (physics), plasmas, in which the magnetic topology is rearranged and magnetic energy is converted to kinetic energy, thermal energy, and particle acceleration. Magnetic reconnection involves plasma flows at a substantial fraction of the Alfvén wave speed, which is the fundamental speed for mechanical information flow in a magnetized plasma. The concept of magnetic reconnection was developed in parallel by researchers working in solar physics and in the interaction between the solar wind and magnetized planets. This reflects the bidirectional nature of reconnection, which can either disconnect formerly connected magnetic fields or connect formerly disconnected magnetic fields, depending on the circumstances. Ron Giovanelli is credited with the first publication invoking magnetic energy release as a potential mechanism for particle acceleration in Solar flare, solar flares. Giovanelli propose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edge-localized Mode
An edge-localized mode (ELM) is a plasma instability occurring in the edge region of a tokamak plasma due to periodic relaxations of the edge transport barrier in high-confinement mode. Each ELM burst is associated with expulsion of particles and energy from the confined plasma into the scrape-off layer. This phenomenon was first observed in the ASDEX tokamak in 1981. Diamagnetic effects in the model equations expand the size of the parameter space in which solutions of repeated sawteeth can be recovered compared to a resistive MHD model. An ELM can expel up to 20 percent of the reactor's energy. Issues ELM is a major challenge in magnetic fusion research with tokamaks, as these instabilities can: * Damage wall components (in particular divertor plates) by ablating them away due to their extremely high energy transfer rate (GW/m2); * Potentially couple or trigger other instabilities, such as the resistive wall mode (RWM) or the neoclassical tearing mode (NTM). Prevention a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetohydrodynamics
In physics and engineering, magnetohydrodynamics (MHD; also called magneto-fluid dynamics or hydromagnetics) is a model of electrically conducting fluids that treats all interpenetrating particle species together as a single Continuum mechanics, continuous medium. It is primarily concerned with the low-frequency, large-scale, magnetic behavior in Plasma (physics), plasmas and liquid metals and has applications in multiple fields including space physics, geophysics, astrophysics, and engineering. The word ''magnetohydrodynamics'' is derived from ' meaning magnetic field, ' meaning water, and ' meaning movement. The field of MHD was initiated by Hannes Alfvén, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1970. History The MHD description of electrically conducting fluids was first developed by Hannes Alfvén in a 1942 paper published in Nature (journal), ''Nature'' titled "Existence of Electromagnetic–Hydrodynamic Waves" which outlined his discovery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safety Factor (plasma Physics)
In a toroidal fusion power reactor, the magnetic fields confining the plasma (physics), plasma are formed in a helical shape, winding around the interior of the reactor. The safety factor, labeled q or q(r), is the ratio of the times a particular magnetic field line travels around a toroidal confinement area's "long way" (toroidally) to the "short way" (poloidally). The term "safety" refers to the resulting stability of the plasma; plasmas that rotate around the torus poloidally about the same number of times as toroidally are inherently less susceptible to certain instabilities. The term is most commonly used when referring to tokamak devices. Although the same considerations apply in stellarators, by convention the inverse value is used, the rotational transform, or i. The concept was first developed by Martin David Kruskal and Vitaly Shafranov, who noticed that the plasma in pinch effect reactors would be stable if q was larger than 1. Macroscopically, this implies that the wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Stability
In plasma physics, plasma stability concerns the stability properties of a plasma in equilibrium and its behavior under small perturbations. The stability of the system determines if the perturbations will grow, oscillate, or be damped out. It is an important consideration in topics such as nuclear fusion and astrophysical plasma. In many cases, a plasma can be treated as a fluid and analyzed with the theory of magnetohydrodynamics (MHD). MHD stability is necessary for stable operation of magnetic confinement fusion devices and places certain operational limits. The beta limit, for example, sets the maximum achievable plasma beta in tokamaks. On the other hand, small-scale plasma instabilities (typically described by kinetic theory), such as the drift wave instability, are believed to be the driving mechanism of turbulent transport in tokamaks, which leads to high rate of particle and energy transport across the confining magnetic fields. Plasma instabilities described by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Reconnection
Magnetic reconnection is a physical process occurring in electrically conducting Plasma (physics), plasmas, in which the magnetic topology is rearranged and magnetic energy is converted to kinetic energy, thermal energy, and particle acceleration. Magnetic reconnection involves plasma flows at a substantial fraction of the Alfvén wave speed, which is the fundamental speed for mechanical information flow in a magnetized plasma. The concept of magnetic reconnection was developed in parallel by researchers working in solar physics and in the interaction between the solar wind and magnetized planets. This reflects the bidirectional nature of reconnection, which can either disconnect formerly connected magnetic fields or connect formerly disconnected magnetic fields, depending on the circumstances. Ron Giovanelli is credited with the first publication invoking magnetic energy release as a potential mechanism for particle acceleration in Solar flare, solar flares. Giovanelli propose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lundquist Number
In plasma physics, the Lundquist number (denoted by S) is a dimensionless ratio which compares the timescale of an Alfvén wave crossing to the timescale of resistive diffusion. It is a special case of the magnetic Reynolds number when the Alfvén velocity is the typical velocity scale of the system, and is given by :S = \frac , where L is the typical length scale of the system, \eta is the magnetic diffusivity and v_A is the Alfvén velocity of the plasma. High Lundquist numbers indicate highly conducting plasmas, while low Lundquist numbers indicate more resistive plasmas. Laboratory plasma experiments typically have Lundquist numbers between 10^2-10^8, while in astrophysical situations the Lundquist number can be greater than 10^. Considerations of Lundquist number are especially important in magnetic reconnection Magnetic reconnection is a physical process occurring in electrically conducting Plasma (physics), plasmas, in which the magnetic topology is rearranged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |