|
Thrombocytopenic
In hematology, thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of platelets (also known as thrombocytes) in the blood. Low levels of platelets in turn may lead to prolonged or excessive bleeding. It is the most common coagulation disorder among intensive care patients and is seen in a fifth of medical patients and a third of surgical patients. A normal human platelet count ranges from 150,000 to 450,000 platelets/microliter (μL) of blood. Values outside this range do not necessarily indicate disease. One common definition of thrombocytopenia requiring emergency treatment is a platelet count below 50,000/μL. Thrombocytopenia can be contrasted with the conditions associated with an abnormally ''high'' level of platelets in the blood – thrombocythemia (when the cause is unknown), and thrombocytosis (when the cause is known). Signs and symptoms Thrombocytopenia usually has no symptoms and is picked up on a routine complete blood count. Some individual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platelet
Platelets or thrombocytes () are a part of blood whose function (along with the coagulation#Coagulation factors, coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping to form a thrombus, blood clot. Platelets have no cell nucleus; they are fragments of cytoplasm from megakaryocytes which reside in bone marrow or Lung, lung tissue, and then enter the circulation. Platelets are found only in mammals, whereas in other vertebrates (e.g. birds, amphibians), thrombocytes circulate as intact agranulocyte, mononuclear cells. One major function of platelets is to contribute to hemostasis: the process of stopping bleeding at the site where the lining of vessels (endothelium) has been interrupted. Platelets gather at the site and, unless the interruption is physically too large, they plug the hole. First, platelets attach to substances outside the interrupted endothelium: ''adhesion (medicine), adhesion''. Second, they change shape, turn on receptors and secret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purpura
Purpura () is a condition of red or purple discolored spots on the skin that do not blanch on applying pressure. The spots are caused by bleeding underneath the skin secondary to platelet disorders, vascular disorders, coagulation disorders, or other causes. They measure 3–10 mm, whereas petechiae measure less than 3 mm, and ecchymoses greater than 1 cm. Purpura is common with typhus and can be present with meningitis caused by meningococci or septicaemia. In particular, meningococcus ('' Neisseria meningitidis''), a Gram-negative diplococcus organism, releases endotoxin when it lyses. Endotoxin activates the Hageman factor (clotting factor XII), which causes disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). The DIC is what appears as a rash on the affected individual. Classification Purpura are a common and nonspecific medical sign; however, the underlying mechanism commonly involves one of: * Platelet disorders ( thrombocytopenic purpura) ** Primary throm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petechia
A petechia (; : petechiae) is a small red or purple spot ( 1 cm in diameter) and purpura (3 to 10 mm in diameter). The term is typically used in the plural (petechiae), since a single petechia is seldom noticed or significant. Causes Physical trauma The most common cause of petechiae is through physical trauma such as a hard bout of coughing, holding breath, vomiting, or crying, which can result in facial petechiae, especially around the eyes. Excessive scratching and friction, especially on thin and poorly circulated parts of the body may also cause petechiae. Such instances are generally considered harmless and usually disappear within a few days, but depending on severity and frequency may be indicative of an underlying medical condition. * Constriction, asphyxiation – petechiae, especially in the eyes, may also occur when excessive pressure is applied to tissue (e.g., when a tourniquet is applied to an extremity or with excessive coughing or vomiting). * Sunburn, childbir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
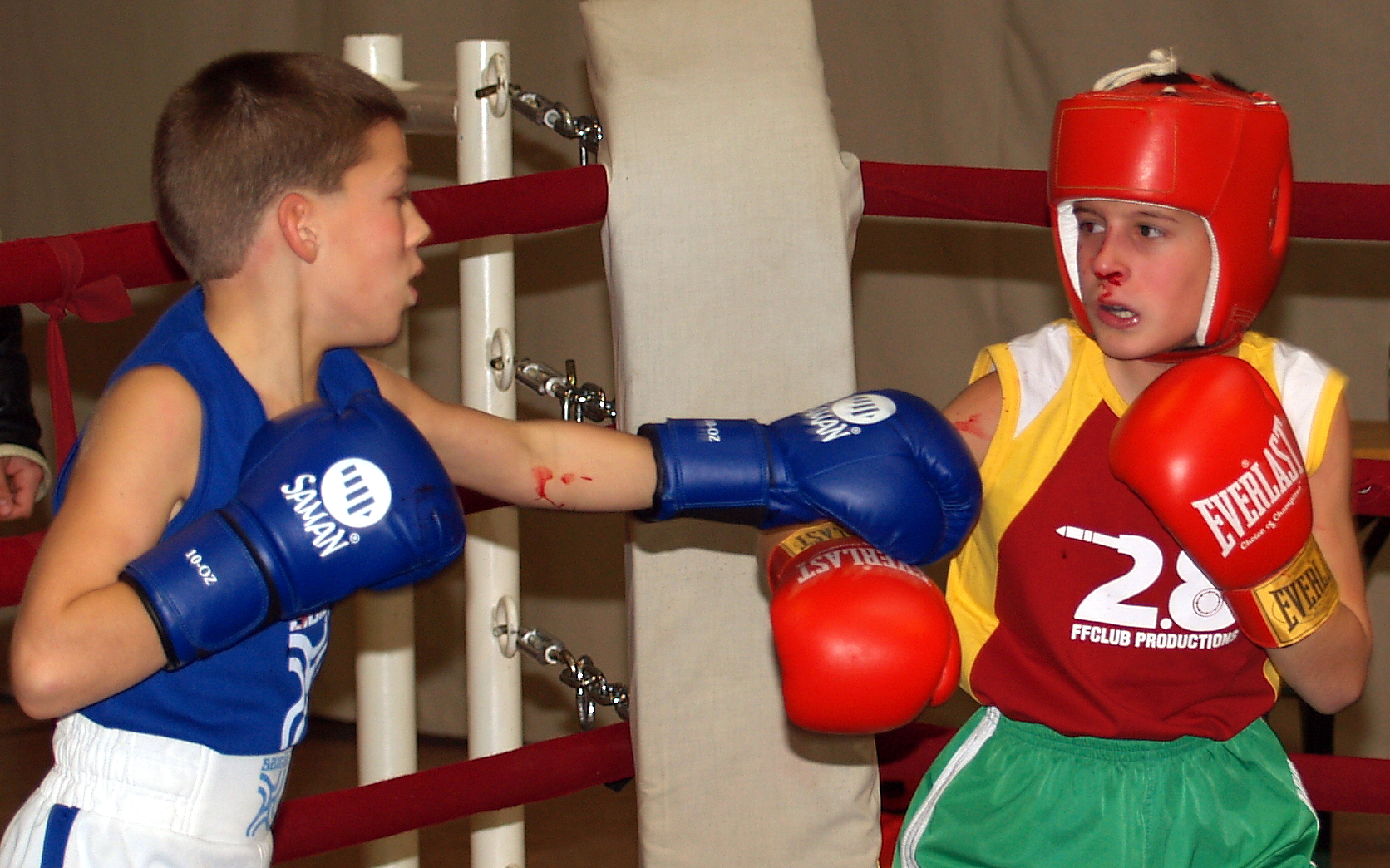
Nosebleed
A nosebleed, also known as epistaxis, is an instance of bleeding from the nose. Blood can flow down into the stomach, and cause nausea and vomiting. In more severe cases, blood may come out of both nostrils. Rarely, bleeding may be so significant that low blood pressure occurs. Blood may also be forced to flow up and through the nasolacrimal duct and out of the eye, producing bloody tears. Risk factors include trauma, including putting the finger in the nose, blood thinners, high blood pressure, alcoholism, seasonal allergies, dry weather, and inhaled corticosteroids. There are two types: anterior, which is more common; and posterior, which is less common but more serious. Anterior nosebleeds generally occur from Kiesselbach's plexus while posterior bleeds generally occur from the sphenopalatine artery or Woodruff's plexus. The diagnosis is by direct observation. Prevention may include the use of petroleum jelly in the nose. Initially, treatment is generally the appli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematology
Hematology (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, spelled haematology in British English) is the branch of medicine concerned with the study of the cause, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to blood. It involves treating diseases that affect the production of blood and its components, such as blood cells, hemoglobin, blood proteins, bone marrow, platelets, blood vessels, spleen, and the mechanism of coagulation. Such diseases might include hemophilia, sickle cell anemia, blood clots (thrombus), other bleeding disorders, and blood cancers such as leukemia, multiple myeloma, and lymphoma. The laboratory analysis of blood is frequently performed by a medical technologist or medical laboratory scientist. Specialization Physicians specialized in hematology are known as hematologists or haematologists. Their routine work mainly includes the care and treatment of patients with hematological diseases, although some may also work at the hema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bleeding
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vagina, or anus, or through a puncture in the skin. Hypovolemia is a massive decrease in blood volume, and death by excessive loss of blood is referred to as exsanguination. Typically, a healthy person can endure a loss of 10–15% of the total blood volume without serious medical difficulties (by comparison, blood donation typically takes 8–10% of the donor's blood volume). The stopping or controlling of bleeding is called hemostasis and is an important part of both first aid and surgery. Types * Upper head ** Intracranial hemorrhage — bleeding in the skull. ** Cerebral hemorrhage — a type of intracranial hemorrhage, bleeding within the brain tissue itself. ** Intracerebral hemorrhage — bleeding in the brain caused by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Blood Cells
White blood cells (scientific name leukocytes), also called immune cells or immunocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign entities. White blood cells are generally larger than red blood cells. They include three main subtypes: granulocytes, lymphocytes and monocytes. All white blood cells are produced and derived from multipotent cells in the bone marrow known as hematopoietic stem cells. Leukocytes are found throughout the body, including the blood and lymphatic system. All white blood cells have nuclei, which distinguishes them from the other blood cells, the anucleated red blood cells (RBCs) and platelets. The different white blood cells are usually classified by cell lineage ( myeloid cells or lymphoid cells). White blood cells are part of the body's immune system. They help the body fight infection and other diseases. Types of white blood cells are granulocytes (neutrophils, eosino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splenectomy
A splenectomy is the surgical procedure that partially or completely removes the spleen. The spleen is an important organ in regard to immunological function due to its ability to efficiently destroy encapsulated bacteria. Therefore, removal of the spleen runs the risk of overwhelming post-splenectomy infection, a medical emergency and rapidly fatal disease caused by the inability of the body's immune system to properly fight infection following splenectomy or asplenia. Common indications for splenectomy include trauma, tumors, splenomegaly or for hematological disease such as sickle cell anemia or thalassemia. Indications The spleen is an organ located in the abdomen next to the stomach. It is composed of red pulp which filters the blood, removing foreign material, damaged and worn out red blood cells. It also functions as a storage site for iron, red blood cells and platelets. The rest (~25%) of the spleen is known as the white pulp and functions like a large lymph n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymptomatic
Asymptomatic (or clinically silent) is an adjective categorising the medical conditions (i.e., injuries or diseases) that patients carry but without experiencing their symptoms, despite an explicit diagnosis (e.g., a positive medical test). Pre-symptomatic is the adjective categorising the time periods during which the medical conditions are asymptomatic. Subclinical and paucisymptomatic are other adjectives categorising either the asymptomatic infections (i.e., subclinical infections), or the psychosomatic illnesses and mental disorders expressing a subset of symptoms but not the entire set an explicit medical diagnosis requires. Examples An example of an asymptomatic disease is cytomegalovirus (CMV) which is a member of the herpes virus family. "It is estimated that 1% of all newborns are infected with CMV, but the majority of infections are asymptomatic." (Knox, 1983; Kumar et al. 1984) In some diseases, the proportion of asymptomatic cases can be important. For exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatigue
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a signs and symptoms, symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself. Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated with medical conditions including autoimmune disease, organ failure, chronic pain conditions, mood disorders, heart disease, infectious diseases, and post-infectious-disease states. However, fatigue is complex and in up to a third of primary care cases no medical or psychiatric diagnosis is found. Fatigue (in the general usage sense of normal tiredness) often follows prolonged physical or mental activity. Physical fatigue results from muscle fatigue brought about by intense physical activity. Mental fatigue results from prolonged periods of Cognition, cognitive activity which impairs cognitive ability, can manifest as sleepiness, lethargy, or directed attention fatigue, and can also impair physical performance. Definition Fatigue in a medica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |