|
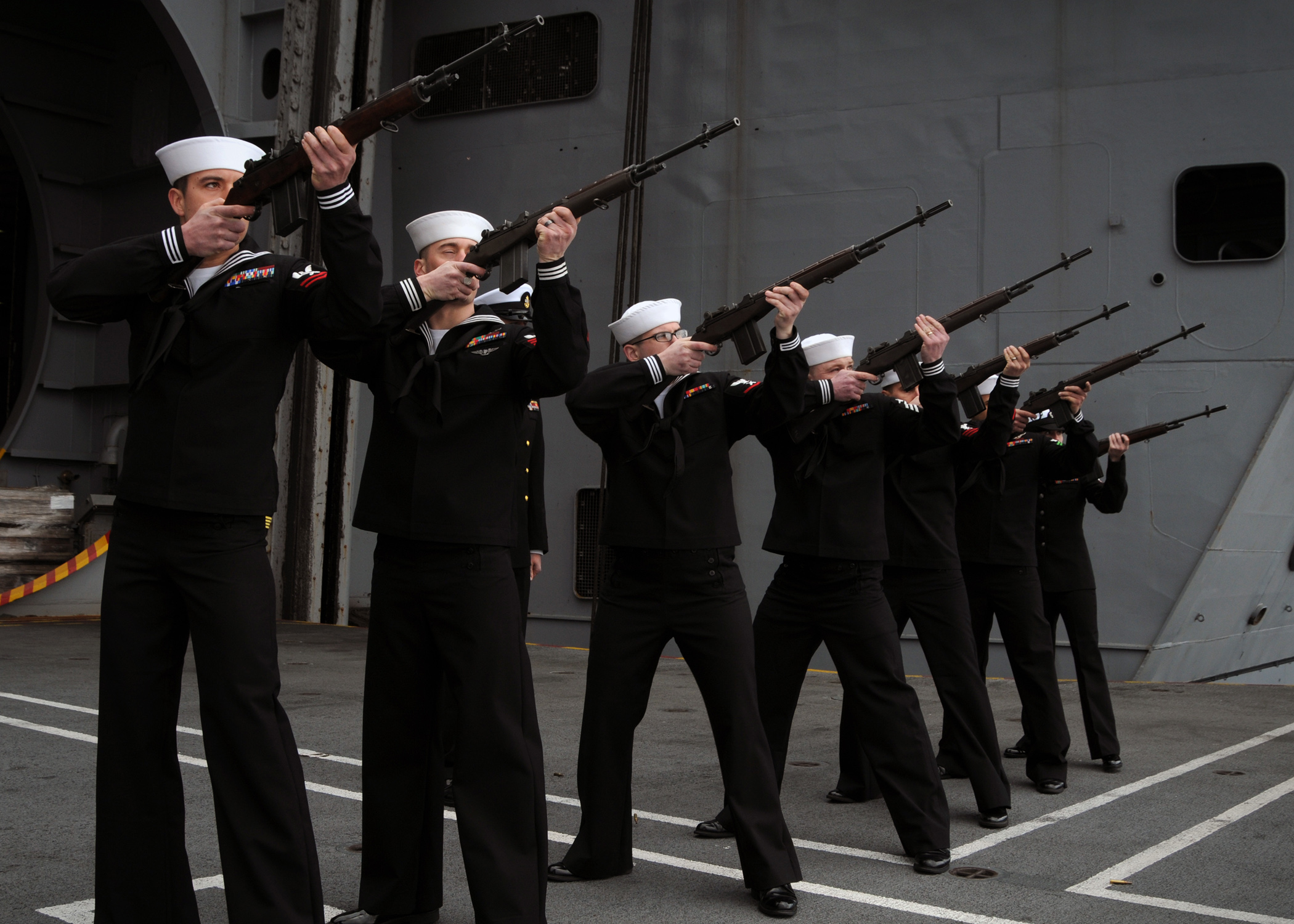
Three Volley Salute
The three-volley salute is a ceremonial act performed at military funerals and sometimes also police funerals. The custom likely originates with Roman funeral rites. Dirt would be cast on the body three times followed, and the ceremony was ended by the deceased's name being called three times. It was then customary for the friends and relatives of the deceased to repeat the word 'vale' (meaning farewell or goodbye) three times. In more recent history three volleys were fired to signify the end of a funeral and that the burial detail was to be ready for battle. It should not be confused with the 21-gun salute (or 19-gun or 17-gun, etc.) which is fired by a battery of artillery pieces. United States In the United States it is part of the drill and ceremony of the Honor Guard. It consists of a rifle party firing blank cartridges into the air three times. A rifle party usually has an odd number of members, from three to seven. The firearm used is typically a rifle, but at some p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
090410-N-0774H-210 - USS Abraham Lincoln Rifle Salute
9 (nine) is the natural number following and preceding . Evolution of the Hindu–Arabic digit Circa 300 BC, as part of the Brahmi numerals, various Indians wrote a digit 9 similar in shape to the modern closing question mark without the bottom dot. The Kshatrapa, Andhra and Gupta started curving the bottom vertical line coming up with a -look-alike. How the numbers got to their Gupta form is open to considerable debate. The Nagari continued the bottom stroke to make a circle and enclose the 3-look-alike, in much the same way that the sign @ encircles a lowercase ''a''. As time went on, the enclosing circle became bigger and its line continued beyond the circle downwards, as the 3-look-alike became smaller. Soon, all that was left of the 3-look-alike was a squiggle. The Arabs simply connected that squiggle to the downward stroke at the middle and subsequent European change was purely cosmetic. While the shape of the glyph for the digit 9 has an ascender in most modern typefa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Half-mast
Half-mast or half-staff (American English) refers to a flag flying below the summit of a ship mast, a pole on land, or a pole on a building. In many countries this is seen as a symbol of respect, mourning, distress, or, in some cases, a salute. The tradition of flying the flag at half-mast began in the 17th century. According to some sources, the flag is lowered to make room for an "invisible flag of death" flying above. However, there is disagreement about where on a flagpole a flag should be when it is at half-mast. It is often recommended that a flag at half-mast be lowered only as much as the hoist, or width, of the flag. British flag protocol is that a flag should be flown no less than two-thirds of the way up the flagpole, with at least the height of the flag between the top of the flag and the top of the pole. It is common for the phrase to be taken literally and for a flag to be flown only halfway up a flagpole, although some authorities deprecate that practice. Whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Guard
In Military, military organizations, a colour guard (or color guard) is a detachment of soldiers assigned to the protection of Colours, standards and guidons, regimental colours and the national flag. This duty is highly prestigious, and the military colour is generally carried by a young officer (Ensign (rank), ensign), while experienced non-commissioned officers (colour sergeants) are assigned to the protection of the national flag. These non-commissioned officers, accompanied in several countries by warrant officers, can be ceremonially armed with either sabres or rifles to protect the colour. Colour guards are generally dismounted, but there are also mounted colour guard formations as well. History As long as armies existed there was a need for soldiers to know where their comrades were. A solution to this problem was the carrying of colourful banners or other insignia. Such flags or banners either showed a personal symbol of the leader of said units or a symbol for the "st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Change Of Command
A change of command is a military tradition that represents a formal transfer of authority and responsibility for a unit from one commanding or flag officer to another. The passing of colors, standards, or ensigns from an outgoing commander to an incoming one ensures that the unit and its soldiers is never without official leadership, a continuation of trust, and also signifies an allegiance of soldiers to their unit's commander. Great symbolism is attached to the ceremonial aspects of a change of command. An inspection and review of soldiers, gun salutes, as well as a military band will often be incorporated into the ceremony. On the International Space Station, the new and old commanders ring a bell. For a Command Sergeant Major, the transferred item might be a saber during a Change of Responsibility, while for a Chaplain, the item might be the passing of a Clerical Stole. See also * 3-volley salute * 21-gun salute *Burial at sea *Casing of the Colors *Color guard *Half-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burial At Sea
Burial at sea is the disposal of Cadaver, human remains in the ocean, normally from a ship, boat or aircraft. It is regularly performed by navies, and is done by private citizens in many countries. Burial-at-sea services are conducted at many different locations and with many different customs, either by ship or by aircraft. Usually, either the Captain (nautical), captain of the ship or aircraft or a religious representative (of the deceased's religion or the state religion) performs the ceremony. The ceremony may include burial in a casket, burial sewn in sailcloth, burial in an urn, or scattering of the cremated remains from a ship. Burial at sea by aircraft is only done with cremated remains. Other types of burial at sea include the mixing of the ashes with concrete and dropping the concrete block to form an artificial reef such as the Atlantis Reef. Below is a list of religions that allow burial at sea, with some details of the burial. By religion Christianity In Christian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ten-bell Salute
In professional wrestling, a ten-bell salute is given to honor a wrestler who has died, especially when the wrestler is a current member of the professional wrestling promotion, promotion or a distinguished former member of the promotion. It is the professional wrestling equivalent of a three-volley salute. It is typically given at the beginning of a card (professional wrestling), card, with the current members of the promotion either in the entryway, in the ring, or around the ring. Both the wrestlers and audience observe a moment of silence while the bell is rung. In Japanese wrestling, ten-bell salutes (“ten-count gongs”) are held not only for deceased wrestlers but also for retiring wrestlers to mark the end of their careers. Retirement ten-count gongs are often preceded with a retirement ceremony for the retiree where they are presented with gifts, flowers and career memorabilia from the active roster, high-ranking officials of the promotion and special guests. Honorees ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volunteer (Irish Republican)
A volunteer is a member of various Irish republican paramilitary organisations. Among these have been the various forms of the Irish Republican Army (IRA), the Irish National Liberation Army (INLA), and the Irish People's Liberation Organization (IPLO). ' is the equivalent title in the Irish language. Background The Irish Volunteers were formed in 1913, in reaction to the formation of the Ulster Volunteer Force earlier that year, to protect the interests of Irish nationalists during the Home Rule Crisis. The Volunteers took part in the 1916 Easter Rising and—as the Irish Republican Army (IRA)—in the Irish War of Independence. The title "Volunteer" or "Vol." was used for members of the Volunteers who were involved in the 1916 Rising, and in the War of Independence. A number of witness statements given to the Bureau of Military History make frequent use of "Volunteer" as a title for members of the Volunteers and IRA during that period. The County Antrim Memorial in Milltown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish National Liberation Army
The Irish National Liberation Army (INLA, ) is an Irish republicanism, Irish republican Socialism, socialist paramilitary group formed on 8 December 1974, during the 30-year period of conflict known as "the Troubles". The group seeks to remove Northern Ireland from the United Kingdom and create a Socialist state, socialist republic encompassing United Ireland, all of Ireland. With membership estimated at 80–100 at their peak, it is the paramilitary wing of the Irish Republican Socialist Party (IRSP). The INLA was founded by former members of the Official Irish Republican Army who opposed that group's ceasefire. It was initially known as the People's Liberation Army. The INLA Timeline of Irish National Liberation Army actions, waged a paramilitary campaign against the British Army and Royal Ulster Constabulary (RUC) in Northern Ireland. It was also active to a lesser extent in the Republic of Ireland, Great Britain and mainland Europe. High-profile attacks carried out by the IN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
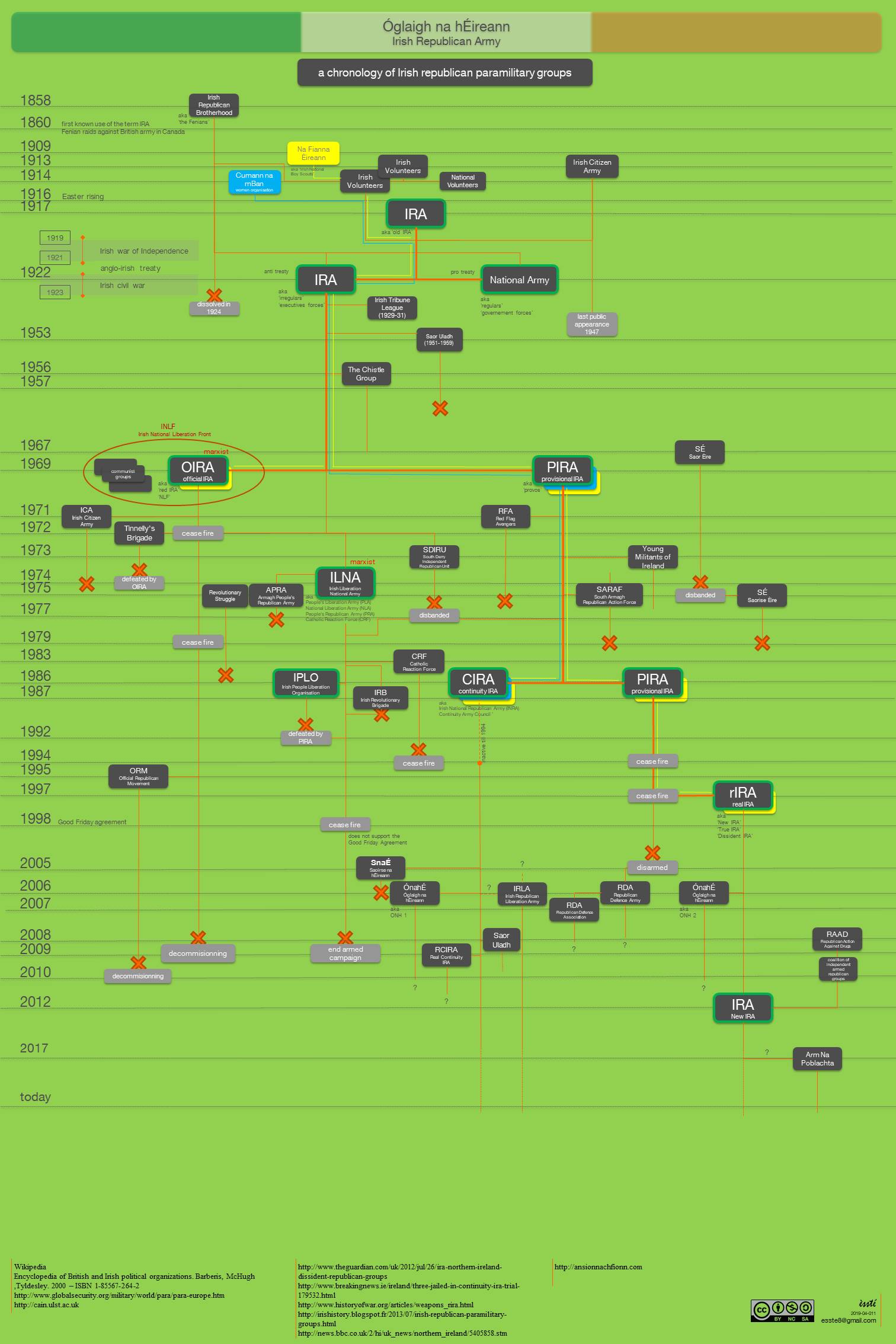
Irish Republican Army
The Irish Republican Army (IRA) is a name used by various Resistance movement, resistance organisations in Ireland throughout the 20th and 21st centuries. Organisations by this name have been dominantly Catholic and dedicated to anti-imperialism through Irish republicanism, the belief that all of Ireland should be an independent republic free from British colonial rule. The original Irish Republican Army (1919–1922), often now referred to as the "old IRA", was raised in 1917 from members of the Irish Volunteers and the Irish Citizen Army later reinforced by Irishmen formerly in the British Army in World War I, who returned to Ireland to fight against Britain in the Irish War of Independence. In Irish law, this IRA was the army of the revolutionary republic, revolutionary Irish Republic as declared by its parliament, Dáil Éireann (Irish Republic), Dáil Éireann, in 1919. In the century that followed, the original IRA was reorganised, changed and split on multiple occasions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Republicanism
Irish republicanism () is the political movement for an Irish Republic, Irish republic, void of any British rule in Ireland, British rule. Throughout its centuries of existence, it has encompassed various tactics and identities, simultaneously elective and militant and has been both widely supported and iconoclastic. The Modern era, modern emergence of nationalism, democracy, and Classical radicalism, radicalism provided a basis for the movement, with groups forming across the island in hopes of independence. Parliamentary defeats provoked uprisings and armed campaigns, quashed by British forces. The Easter Rising, an attempted coup that took place in the midst of the First World War, provided popular support for the movement. An Irish republic was declared in 1916 and officialized following the Irish War of Independence. The Irish Civil War, beginning in 1922 and spurred by the Partition of Ireland, partition of the island, then occurred. Republican action, including armed cam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, often referred to as the British Commonwealth or simply the Commonwealth, is an International organization, international association of member states of the Commonwealth of Nations, 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territorial evolution of the British Empire, territories of the British Empire from which it developed. They are connected through their English in the Commonwealth of Nations, use of the English language and cultural and historical ties. The chief institutions of the organisation are the Commonwealth Secretariat, which focuses on intergovernmental relations, and the Commonwealth Foundation, which focuses on non-governmental relations between member nations. Numerous List of Commonwealth organisations, organisations are associated with and operate within the Commonwealth. The Commonwealth dates back to the first half of the 20th century with the decolonisation of the British Empire through increased self-governance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |