|
Thoracoscopes
Thoracoscopy is a medical procedure involving internal examination, biopsy and/or resection/drainage of disease or masses within the pleural cavity, usually with video assistance. Thoracoscopy may be performed either under general anaesthesia or under sedation with local anaesthetic. History Thoracoscopy was first performed by Sir Francis Cruise of the Mater Misericordiae Hospital in Dublin in conjunction with Dr Samuel Gordon in 1865. It was further developed by Hans Christian Jacobaeus, a Swedish internist in 1910 for the treatment of tuberculous intra-thoracic adhesions. He used a cystoscope to examine the thoracic cavity, developing his technique over the next twenty years. Today, thoracoscopy is performed using specialized thoracoscopes. These instruments include a light source and a lens for viewing and may have ports through which other instruments may be inserted for the purpose of tissue removal and manipulation. Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery Video-assisted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphangioma
Lymphatic malformations are benign slow-flow type of vascular malformation of the lymphatic system characterized by lymphatic vessels which do not connect to the normal lymphatic circulation. The term ''lymphangioma'' is outdated and newer research reference the term ''lymphatic malformation''. Lymphatic malformations can be macrocystic, microcystic, or a combination of the two. Macrocystic have cysts greater than , and microcystic lymphatic malformation have cysts that are smaller than . These malformations can occur at any age and may involve any part of the body, but 90% occur in children less than 2 years of age and involve the head and neck. These malformations are either congenital or acquired. Congenital lymphangiomas are often associated with chromosomal abnormalities such as Turner syndrome, although they can also exist in isolation. Lymphangiomas are commonly diagnosed before birth using fetal ultrasonography. Acquired lymphangiomas may result from trauma, inflammat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystoscope
Cystoscopy is endoscopy of the urinary bladder via the urethra. It is carried out with a cystoscope. The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. The cystoscope has lenses like a telescope or microscope. These lenses let the physician focus on the inner surfaces of the urinary tract. Some cystoscopes use optical fiber, optical fibres (flexible glass fibres) that carry an image from the tip of the instrument to a viewing piece at the other end. Cystoscopes range from pediatric to adult and from the thickness of a pencil up to approximately 9 mm and have a light at the tip. Many cystoscopes have extra tubes to guide other instruments for surgical procedures to treat urinary problems. There are two main types of cystoscopy—flexible and stiffness, rigid—differing in the flexibility of the cystoscope. Flexible cystoscopy is carried out with local anaesthesia on both sexes. Typically, a topical anesthetic, most often lidocaine, xyloc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VATS Lobectomy
Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) lobectomy is an approach to lung cancer surgery. Thoracotomy Anatomic lung resection, i.e. pulmonary lobectomy or pneumonectomy, in conjunction with removal of the lymph nodes from the mediastinum is the treatment modality that provides the greatest chance of long-term survival in patients with early stage non-small cell lung cancer. Anatomic lung resections require a dissection of the pulmonary hilum with individual ligation and division of the pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, and the bronchus where these enter the lung. In the setting of lung cancer, the rationale for anatomic lung resection is a complete removal of a lung tumor along with the lymphatics that drain that tumor to assure that any tumor cells present in the lymphatics will also be removed; lesser resections have been shown to be associated with a higher risk of local recurrence and diminished long-term survival. A cornerstone of surgical treatment of early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
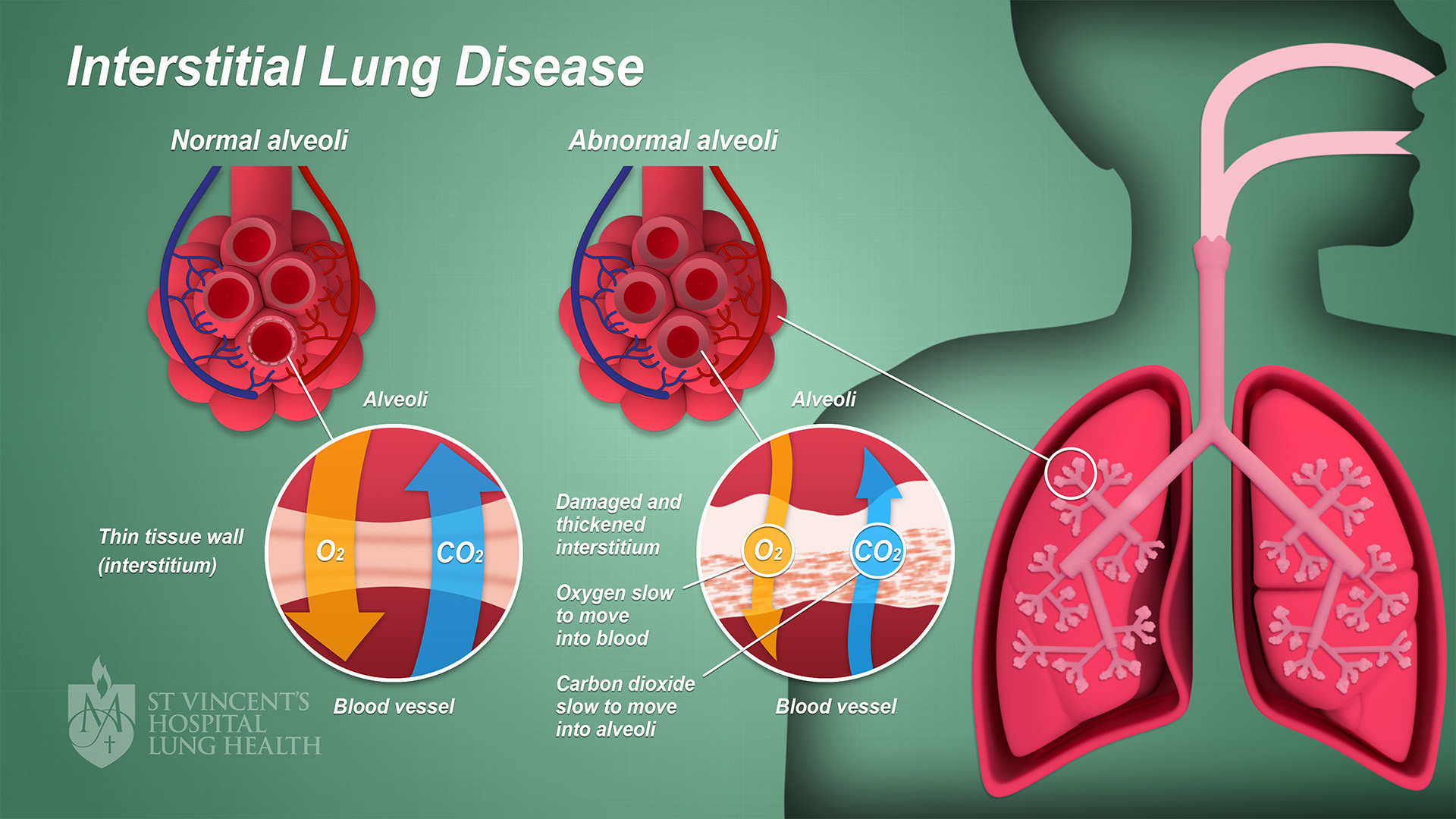
Interstitial Lung Disease
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD), is a group of respiratory diseases affecting the interstitium (the tissue) and space around the alveoli (air sacs) of the lungs. It concerns alveolar epithelium, pulmonary capillary endothelium, basement membrane, and perivascular and perilymphatic tissues. It may occur when an injury to the lungs triggers an abnormal healing response. Ordinarily, the body generates just the right amount of tissue to repair damage, but in interstitial lung disease, the repair process is disrupted, and the tissue around the air sacs (alveoli) becomes scarred and thickened. This makes it more difficult for oxygen to pass into the bloodstream. The disease presents itself with the following symptoms: shortness of breath, nonproductive coughing, fatigue, and weight loss, which tend to develop slowly, over several months. The average rate of survival for someone with this disease is between three and five years. The term IL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lobectomy (lung)
Lobectomy of the lung is a surgical operation where a lobe of the lung is removed. It is done to remove a portion of diseased lung, such as early stage lung cancer. Administration The most common type of lobectomy is known as a thoracotomy. When this type of surgery is done the chest is opened up. An incision will be made on the side of the chest where the affected area of the lung is located. The incision will be in between the two ribs located in that area. The surgeon will then be able to have access to the chest cavity once the two involved ribs have been pried open. The surgeon will then be able to remove the lobe where the problem is contained. Another less invasive lobectomy procedure can be performed through a video assisted surgery, where the surgeon does not need to pry the two ribs open in order to get access. A few small incisions are made and surgical tools are inserted into the chest cavity aided by a small video camera. The video images will be projected onto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgical Staple
Surgical staples are specialized Staple (fastener), staples used in surgery in place of surgical suture, sutures to close skin wounds or to resection (surgery), resect and/or anastomosis, connect parts of an Organ (biology), organ (e.g. bowels, stomach or lungs). The use of staples over sutures reduces the local inflammatory response, width of the wound, and time it takes to close a defect. A more recent development, from the 1990s, uses clips instead of staples for some applications; this does not require the staple to penetrate. History The technique was pioneered by "father of surgical stapling", Hungarian surgeon Hümér Hültl. Hultl's prototype stapler of 1908 weighed , and required two hours to assemble and load. The technology was refined in the 1950s in the Soviet Union, allowing for the first commercially produced re-usable stapling devices for creation of bowel and Surgical anastomosis, anastomoses. Mark M. Ravitch brought a sample of stapling device after attendin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endoscopes
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are inserted directly into the organ. There are many types of endoscopies. Depending on the site in the body and type of procedure, an endoscopy may be performed by a doctor or a surgeon. During the procedure, a patient may be fully conscious or anaesthetised. Most often, the term ''endoscopy'' is used to refer to an examination of the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract, known as an esophagogastroduodenoscopy. Similar instruments are called borescopes for nonmedical use. History Adolf Kussmaul was fascinated by sword swallowers who would insert a sword down their throat without gagging. This drew inspiration to insert a hollow tube for observation; the next problem to solve was how to shine light through the tube, as they were still relyin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgery
Surgery is a medical specialty that uses manual and instrumental techniques to diagnose or treat pathological conditions (e.g., trauma, disease, injury, malignancy), to alter bodily functions (e.g., malabsorption created by bariatric surgery such as gastric bypass), to reconstruct or alter aesthetics and appearance (cosmetic surgery), or to remove unwanted tissue (biology), tissues (body fat, glands, scars or skin tags) or foreign bodies. The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure or surgical operation, or simply "surgery" or "operation". In this context, the verb "operate" means to perform surgery. The adjective surgical means pertaining to surgery; e.g. surgical instruments, operating theater, surgical facility or surgical nurse. Most surgical procedures are performed by a pair of operators: a surgeon who is the main operator performing the surgery, and a surgical assistant who provides in-procedure manual assistance during surgery. Modern surgical opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video-assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery
Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) is a type of minimally invasive thoracic surgery performed using a small video camera mounted to a fiberoptic thoracoscope (either 5 mm or 10 mm caliber), with or without angulated visualization, which allows the surgeon to see inside the chest by viewing the video images relayed onto a television screen, and perform procedures using elongated surgical instruments. The camera and instruments are inserted into the patient's chest cavity through small incisions in the chest wall, usually via specially designed guiding tubes known as "ports". VATS procedures are done using either conventional surgical instruments or laparoscopic instruments. Unlike with laparoscopy, carbon dioxide insufflation is not generally required in VATS due to the inherent rigidity of the thoracic cage. However, lung deflation on the side of the operated chest is a must to be able to visualize and pass instruments into the thorax; this is usually e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |