|
Thiyl Radical
In chemistry, a thiyl radical has the formula RS, sometimes written RS• to emphasize that they are free radicals. R is typically an alkyl or aryl substituent. Because S–H bonds are about 20% weaker than C–H bonds, thiyl radicals are relatively easily generated from thiols RSH. Thiyl radicals are intermediates in the thiol-ene reaction, which is the basis of some polymeric coatings and adhesives. They are generated by hydrogen-atom abstraction from thiols using initiators such as AIBN: : RN=NR → 2 R• + N2 :R• + R′SH → R′S• + RH Thiyl radicals are also invoked as intermediates in some biochemical reactions. Thiyl radical in biology Reactivity of Thiyl Radicals The formation of thiyl radicals in vivo primarily occurs through the action of various radicals on the amino acid cysteine incorporated into proteins. The rate of radical formation is highest with the OH· radical (k = 6.8 x 109 M−1s−1) and decreases through the H· radical (k = 6.8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during chemical reaction, reactions with other chemical substance, substances. Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds. In the scope of its subject, chemistry occupies an intermediate position between physics and biology. It is sometimes called the central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both Basic research, basic and Applied science, applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level. For example, chemistry explains aspects of plant growth (botany), the formation of igneous rocks (geology), how atmospheric ozone is formed and how environmental pollutants are degraded (ecology), the prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caenorhabditis Elegans
''Caenorhabditis elegans'' () is a free-living transparent nematode about 1 mm in length that lives in temperate soil environments. It is the type species of its genus. The name is a Hybrid word, blend of the Greek ''caeno-'' (recent), ''rhabditis'' (rod-like) and Latin ''elegans'' (elegant). In 1900, Émile Maupas, Maupas initially named it ''Rhabditidae, Rhabditides elegans.'' Günther Osche, Osche placed it in the subgenus ''Caenorhabditis'' in 1952, and in 1955, Ellsworth Dougherty, Dougherty raised ''Caenorhabditis'' to the status of genus. ''C. elegans'' is an unsegmented pseudocoelomate and lacks respiratory or circulatory systems. Most of these nematodes are hermaphrodites and a few are males. Males have specialised tails for mating that include spicule (nematode), spicules. In 1963, Sydney Brenner proposed research into ''C. elegans,'' primarily in the area of neuronal development. In 1974, he began research into the molecular biology, molecular and developmental ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutathione
Glutathione (GSH, ) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an antioxidant in plants, animals, fungi, and some bacteria and archaea. Glutathione is capable of preventing damage to important cellular components caused by sources such as reactive oxygen species, free radicals, peroxides, lipid peroxides, and heavy metals. It is a tripeptide with a gamma peptide linkage between the carboxyl group of the glutamate side chain and cysteine. The carboxyl group of the cysteine residue is attached by normal peptide linkage to glycine. Biosynthesis and occurrence Glutathione biosynthesis involves two adenosine triphosphate-dependent steps: *First, γ-glutamylcysteine is synthesized from L-glutamate and L-cysteine. This conversion requires the enzyme glutamate–cysteine ligase (GCL, glutamate cysteine synthase). This reaction is the rate-limiting step in glutathione synthesis. *Second, glycine is added to the C-terminal of γ-glutamylcysteine. This condensation is ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascorbic Acid
Ascorbic acid is an organic compound with formula , originally called hexuronic acid. It is a white solid, but impure samples can appear yellowish. It dissolves freely in water to give mildly acidic solutions. It is a mild reducing agent. Ascorbic acid exists as two enantiomers (mirror-image isomers), commonly denoted "" (for "levo") and "" (for "dextro"). The isomer is the one most often encountered: it occurs naturally in many foods, and is one form (" vitamer") of vitamin C, an essential nutrient for humans and many animals. Deficiency of vitamin C causes scurvy, formerly a major disease of sailors in long sea voyages. It is used as a food additive and a dietary supplement for its antioxidant properties. The "" form ( erythorbic acid) can be made by chemical synthesis, but has no significant biological role. Etymology The term ''ascorbic'' means antiscruvy and denotes the ability to fight off scurvy. It is related to combating Vitamin C deficiency. History The antiscor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lycopene
Lycopene is an organic compound classified as a tetraterpene and a carotene. Lycopene (from the Neo-Latin '' Lycopersicon'', the name of a former tomato genus) is a bright red carotenoid hydrocarbon found in tomatoes and other red fruits and vegetables. Occurrence Aside from tomatoes or tomato products like ketchup, it is found in watermelons, grapefruits, red guavas, and baked beans. It has no vitamin A activity. In plants, algae, and other photosynthetic organisms, lycopene is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of many carotenoids, including beta-carotene, which is responsible for yellow, orange, or red pigmentation, photosynthesis, and photoprotection. Like all carotenoids, lycopene is a tetraterpene. It is soluble in fat, but insoluble in water. Eleven conjugated double bonds give lycopene its deep red color. Owing to the strong color, lycopene is used as a food coloring (registered as E160d) and is approved for use in the US, Australia and New Zealand (register ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antioxidant
Antioxidants are Chemical compound, compounds that inhibit Redox, oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce Radical (chemistry), free radicals. Autoxidation leads to degradation of organic compounds, including living matter. Antioxidants are frequently added to industrial products, such as polymers, fuels, and lubricants, to extend their usable lifetimes. Foods are also treated with antioxidants to prevent Food spoilage, spoilage, in particular the rancidification of Vegetable oil, oils and fats. In Cell (biology), cells, antioxidants such as glutathione, mycothiol, or bacillithiol, and enzyme systems like superoxide dismutase, inhibit damage from oxidative stress. Known diet (nutrition), dietary antioxidants are vitamins vitamin A, A, vitamin C, C, and vitamin E, E, but the term has also been applied to various compounds that exhibit antioxidant properties in vitro, having little evidence for antioxidant properties in vivo. Dietary supplements marketed as antioxidants hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyunsaturated Fat
In biochemistry and nutrition, a polyunsaturated fat is a fat that contains a polyunsaturated fatty acid (abbreviated PUFA), which is a subclass of fatty acid characterized by a backbone with two or more carbon–carbon double bonds. Some polyunsaturated fatty acids are essentials. Polyunsaturated fatty acids are precursors to and are derived from polyunsaturated fats, which include drying oils. Nomenclature The position of the carbon-carbon double bonds in carboxylic acid chains in fats is designated by Greek letters. The carbon atom closest to the carboxyl group is the ''alpha'' carbon, the next carbon is the ''beta'' carbon and so on. In fatty acids the carbon atom of the methyl group at the end of the hydrocarbon chain is called the ''omega'' carbon because ''omega'' is the last letter of the Greek alphabet. Omega-3 fatty acids have a double bond three carbons away from the methyl carbon, whereas omega-6 fatty acids have a double bond six carbons away from the methyl car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
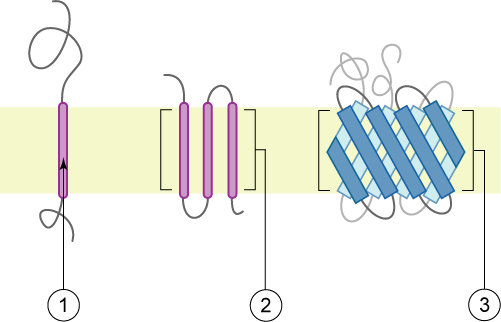
Membrane Protein
Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins are a permanent part of a cell membrane and can either penetrate the membrane (Transmembrane protein, transmembrane) or associate with one or the other side of a membrane (Integral monotopic protein, integral monotopic). Peripheral membrane proteins are transiently associated with the cell membrane. Membrane proteins are common, and medically important—about a third of all human proteins are membrane proteins, and these are targets for more than half of all drugs. Nonetheless, compared to other classes of proteins, determining membrane protein structures remains a challenge in large part due to the difficulty in establishing experimental conditions that can preserve the correct (Native state, native) Protein structure, conformation of the protein in isolation from its native ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monounsaturated Fat
In biochemistry and nutrition, a monounsaturated fat is a fat that contains a monounsaturated fatty acid (MUFA), a subclass of fatty acid characterized by having a double bond in the fatty acid chain with all of the remaining carbon atoms being single-bonded. By contrast, polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) have more than one double bond. Molecular description Monounsaturated fats are triglycerides containing one unsaturated fatty acid. Almost invariably that fatty acid is oleic acid (18:1 n−9). Palmitoleic acid (16:1 n−7) and cis-vaccenic acid (18:1 n−7) occur in small amounts in fats. Health Studies have shown that substituting dietary monounsaturated fat for saturated fat is associated with increased daily physical activity and resting energy expenditure. More physical activity was associated with a higher-oleic acid diet than one of a palmitic acid diet. From the study, it is shown that more monounsaturated fats lead to less anger and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Radical
A daughter category of ''Ageing'', this category deals only with the biological aspects of ageing. Ageing Biogerontology Biological processes Causes of death Cellular processes Gerontology Life extension Metabolic disorders Metabolism Old age Time in life {{CatAutoTOC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing energy, signaling, and acting as structural components of cell membranes. Lipids have applications in the cosmetic and food industries, and in nanotechnology. Lipids are broadly defined as hydrophobic or amphiphilic small molecules; the amphiphilic nature of some lipids allows them to form structures such as vesicles, multilamellar/ unilamellar liposomes, or membranes in an aqueous environment. Biological lipids originate entirely or in part from two distinct types of biochemical subunits or "building-blocks": ketoacyl and isoprene groups. Using this approach, lipids may be divided into eight categories: fatty acyls, glycerolipids, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids, saccharolipids, and polyketides (derived from condensatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |