|
Thermology
Non-contact thermography, thermographic imaging, or medical thermology is the field of thermography that uses infrared images of the Human anatomy, human skin to assist in the diagnosis and treatment of medical conditions. Medical thermology is sometimes referred to as medical infrared imaging or tele-thermology and utilizes thermographic cameras. According to the American Academy of Thermology, Medical Thermology practitioners are licensed health care practitioners who utilize IR imaging in consistent with medically established paradigms of care. Non-medically licensed alternative practitioners who are not held to the same standard may offer thermography services but that should not be confused with the field of medical thermology. Restated, medical thermology is the use of infrared (IR) imaging to assess skin temperature as an extension of the clinician's physical exam to aid in the formation of a medical diagnosis or treatment plan. Medical Thermology does not condone thos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
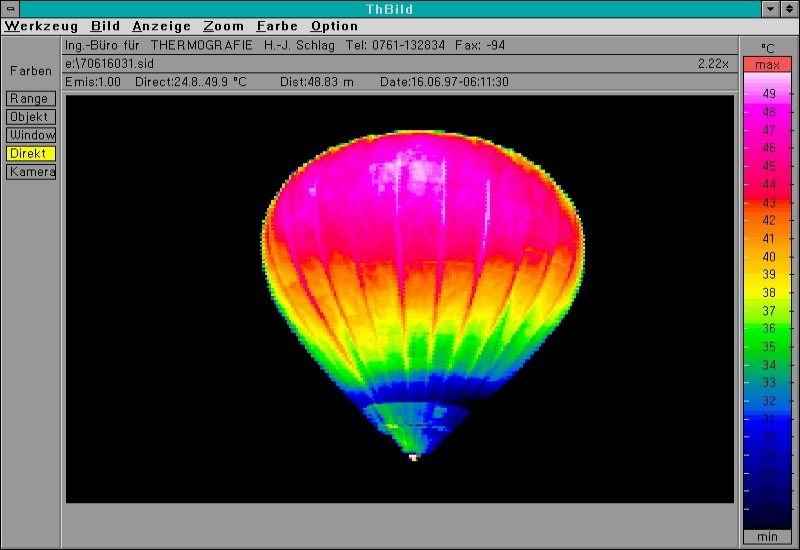
Thermography
Infrared thermography (IRT), thermal video or thermal imaging, is a process where a thermal camera captures and creates an image of an object by using infrared radiation emitted from the object in a process, which are examples of infrared imaging science. Thermographic cameras usually detect radiation in the long-infrared range of the electromagnetic spectrum (roughly 9,000–14,000 nanometers or 9–14 μm) and produce images of that radiation, called thermograms. Since infrared radiation is emitted by all objects with a temperature above absolute zero according to the black body radiation law, thermography makes it possible to see one's environment with or without visible illumination. The amount of radiation emitted by an object increases with temperature; therefore, thermography allows one to see variations in temperature. When viewed through a thermal imaging camera, warm objects stand out well against cooler backgrounds; humans and other warm-blooded animals becom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermography Of Electronics
Infrared thermography (IRT), thermal video or thermal imaging, is a process where a thermal camera captures and creates an image of an object by using infrared radiation emitted from the object in a process, which are examples of infrared imaging science. Thermographic cameras usually detect radiation in the long-infrared range of the electromagnetic spectrum (roughly 9,000–14,000 nanometers or 9–14 μm) and produce images of that radiation, called thermograms. Since infrared radiation is emitted by all objects with a temperature above absolute zero according to the black body radiation law, thermography makes it possible to see one's environment with or without visible illumination. The amount of radiation emitted by an object increases with temperature; therefore, thermography allows one to see variations in temperature. When viewed through a thermal imaging camera, warm objects stand out well against cooler backgrounds; humans and other warm-blooded animals become easil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
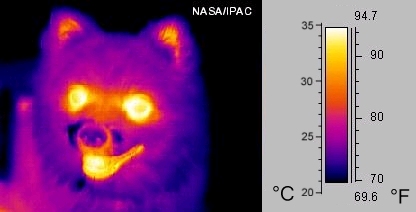
Infrared Imaging
Infrared thermography (IRT), thermal video or thermal imaging, is a process where a thermal camera captures and creates an image of an object by using infrared radiation emitted from the object in a process, which are examples of infrared imaging science. Thermographic cameras usually detect radiation in the long-infrared range of the electromagnetic spectrum (roughly 9,000–14,000 nanometers or 9–14 μm) and produce images of that radiation, called thermograms. Since infrared radiation is emitted by all objects with a temperature above absolute zero according to the black body Planck's law of black-body radiation, radiation law, thermography makes it possible to see one's environment with or without optical spectrum, visible illumination. The amount of radiation emitted by an object increases with temperature; therefore, thermography allows one to see variations in temperature. When viewed through a thermal imaging camera, warm objects stand out well against cooler backgr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermographic Camera
Infrared thermography (IRT), thermal video or thermal imaging, is a process where a Thermographic camera, thermal camera captures and creates an image of an object by using infrared radiation emitted from the object in a process, which are examples of infrared imaging science. Thermographic cameras usually detect electromagnetic radiation, radiation in the long-infrared range of the electromagnetic spectrum (roughly 9,000–14,000 nanometers or 9–14 μm) and produce images of that radiation, called thermograms. Since infrared radiation is emitted by all objects with a temperature above absolute zero according to the black body Planck's law of black-body radiation, radiation law, thermography makes it possible to see one's environment with or without optical spectrum, visible illumination. The amount of radiation emitted by an object increases with temperature; therefore, thermography allows one to see variations in temperature. When viewed through a thermal imaging camera, war ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared Imaging
Infrared thermography (IRT), thermal video or thermal imaging, is a process where a thermal camera captures and creates an image of an object by using infrared radiation emitted from the object in a process, which are examples of infrared imaging science. Thermographic cameras usually detect radiation in the long-infrared range of the electromagnetic spectrum (roughly 9,000–14,000 nanometers or 9–14 μm) and produce images of that radiation, called thermograms. Since infrared radiation is emitted by all objects with a temperature above absolute zero according to the black body Planck's law of black-body radiation, radiation law, thermography makes it possible to see one's environment with or without optical spectrum, visible illumination. The amount of radiation emitted by an object increases with temperature; therefore, thermography allows one to see variations in temperature. When viewed through a thermal imaging camera, warm objects stand out well against cooler backgr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to reveal internal structures hidden by the skin and bones, as well as to diagnose and treat disease. Medical imaging also establishes a database of normal anatomy and physiology to make it possible to identify abnormalities. Although imaging of removed organ (anatomy), organs and Tissue (biology), tissues can be performed for medical reasons, such procedures are usually considered part of pathology instead of medical imaging. Measurement and recording techniques that are not primarily designed to produce images, such as electroencephalography (EEG), magnetoencephalography (MEG), electrocardiography (ECG), and others, represent other technologies that produce data susceptible to representation as a parameter graph versus time or maps that contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adjunct Therapy
Adjuvant therapy, also known as adjunct therapy, adjuvant care, or augmentation therapy, is a therapy that is given in addition to the primary or initial therapy to maximize its effectiveness. The surgeries and complex treatment regimens used in cancer therapy have led the term to be used mainly to describe adjuvant cancer treatments. An example of such adjuvant therapy is the additional treatment usually given after surgery where all detectable disease has been removed, but where there remains a statistical risk of relapse due to the presence of undetected disease. If known disease is left behind following surgery, then further treatment is not technically adjuvant. An adjuvant used on its own specifically refers to an agent that improves the effect of a vaccine. Medications used to help primary medications are known as add-ons. History The term "adjuvant therapy," derived from the Latin term ''adjuvāre'', meaning "to help," was first coined by Paul Carbone and his team at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Mercola
Joseph Michael Mercola (; born July 8, 1954) is an American alternative medicine proponent, osteopathic physician, and Internet business personality. He markets largely unproven dietary supplements and medical devices. On his website, Mercola and colleagues advocate unproven and pseudoscientific alternative health notions including homeopathy and opposition to vaccination. These positions have received persistent criticism. Mercola is a member of several alternative medicine organizations as well as the political advocacy group Association of American Physicians and Surgeons, which promotes scientifically discredited views about medicine and disease. He is the author of two books. Mercola's medical claims have been criticized by the medical, scientific, regulatory, and business communities. A 2006 ''BusinessWeek'' editorial stated his marketing practices relied on "slick promotion, clever use of information, and scare tactics". In 2005, 2006, 2011, and 2021 the U.S. Food and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, caffeine products, dietary supplements, Prescription drug, prescription and Over-the-counter drug, over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, Animal feed, animal foods & feed and Veterinary medicine, veterinary products. The FDA's primary focus is enforcement of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C). However, the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act as well as associated regulations. Much of this regulatory-enforcement work is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
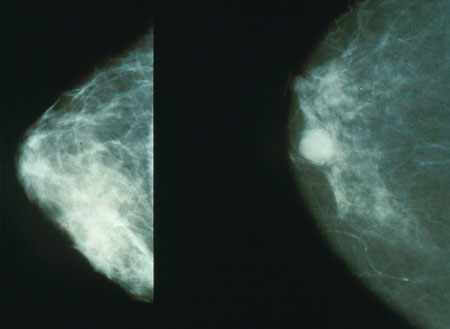
Mammography
Mammography (also called mastography; DICOM modality: MG) is the process of using low-energy X-rays (usually around 30 kVp) to examine the human breast for diagnosis and screening. The goal of mammography is the early detection of breast cancer, typically through detection of characteristic masses, microcalcifications, asymmetries, and distortions. As with all X-rays, mammograms use doses of ionizing radiation to create images. These images are then analyzed for abnormal findings. It is usual to employ lower-energy X-rays, typically Mo (K-shell X-ray energies of 17.5 and 19.6 keV) and Rh (20.2 and 22.7 keV) than those used for radiography of bones. Mammography may be 2D or 3D ( tomosynthesis), depending on the available equipment or purpose of the examination. Ultrasound, ductography, positron emission mammography (PEM), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are adjuncts to mammography. Ultrasound is typically used for further evaluation of masses found on mammography or palp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CBC News
CBC News is the division of the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation responsible for the news gathering and production of news programs on the corporation's English-language operations, namely CBC Television, CBC Radio, CBC News Network, and CBC.ca. Founded in 1941 by the public broadcaster, CBC News is the largest news broadcaster in Canada and has local, regional, and national broadcasts and stations. It frequently collaborates with its organizationally separate French-language counterpart, Radio-Canada Info. History The first CBC newscast was a bilingual radio report on November 2, 1936. The CBC News Service was inaugurated during World War II on January 1, 1941, when Dan McArthur, chief news editor, had Wells Ritchie prepare for the announcer Charles Jennings a national report at 8:00 pm. Previously, CBC relied on The Canadian Press to provide it with wire copy for its news bulletins. Readers who followed Jennings were Lorne Greene, Frank Herbert and Earl Cameron. '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |