|
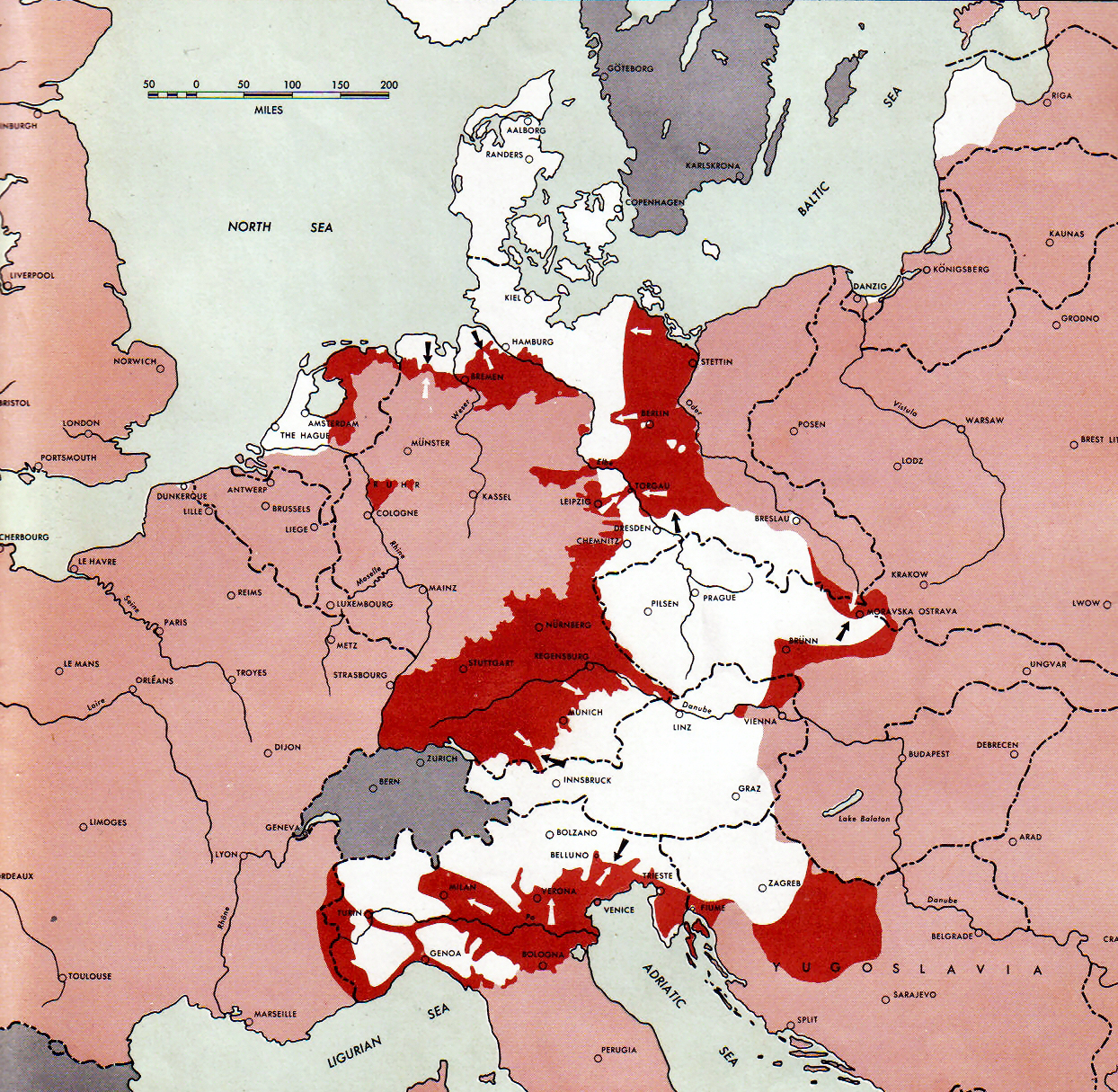
The End Of World War II In Europe
The end of World War II in Europe occurred in May 1945. Following the suicide of Adolf Hitler on 30 April, leadership of Nazi Germany passed to Grand Admiral Karl Dönitz and the Flensburg Government. Soviet troops conquered Berlin on 2 May, and a number of German military forces surrendered over the next few days. On 8 May, Field Marshal Wilhelm Keitel signed the German Instrument of Surrender, an unconditional surrender to the Allies, in Karlshorst, Berlin. This is celebrated as Victory in Europe Day, while in Russia 9 May is celebrated as Victory Day. Some fighting continued after the German surrender. Some battles continued on the Eastern Front such as the Courland Pocket in western Latvia surrendering on 10 May, and the Prague offensive in Czechoslovakia ending on 11 May. On 25 May 1945, the Battle of Odžak ended in a Yugoslav Partisan victory. Following the conclusion in the European theatre, the war continued in the Pacific theatre. Final events before the end of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Instrument Of Surrender (May 8, 1945) - Page 3
The German Instrument of Surrender was a legal document effecting the unconditional surrender of the remaining German armed forces to the Allies, ending World War II in Europe. It was signed at 22:43 CET on 8 May 1945 and took effect at 23:01 CET on the same day. The day before, Germany had signed another surrender document with the Allies in Reims in France, but it was not recognized by the Soviet Union, which demanded among other things that the act of surrender should take place at the seat of government of Nazi Germany from where German aggression had been initiated. Therefore, another document needed to be signed. In addition, immediately after signing the first document, the German forces were ordered to cease fire in the west and continue fighting in the east. Germany under the Flensburg Government led by the head of state, Grand-Admiral Karl Dönitz, also accepted the Allied suggestion to sign a new document. The document was signed at the seat of the Soviet Military ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courland Pocket
The Courland Pocket was a Pocket (military), pocket located on the Courland Peninsula in Latvia on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front of World War II from 9 October 1944 to 10 May 1945. Army Group North of the ''Wehrmacht'' were surrounded in western Latvia by the Red Army after the Baltic Offensive, when forces of the 1st Baltic Front reached the Baltic Sea near Klaipėda, Memel (Klaipėda) after the collapse of Army Group Centre during Operation Bagration. Army Group North retreated to the Courland Pocket and was renamed Army Group Courland on 25 January, holding off six Red Army Offensive (military), offensives until the German Instrument of Surrender was signed on 8 May 1945. Army Group Courland were in a communication "Blackout (broadcasting), blackout" and did not get the official order until 10 May, becoming one of the last German groups to European theatre of World War II, surrender in Europe. Background In June 1941, Nazi Germany launched Operation Bar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geneva Convention On Prisoners Of War (1929)
The Geneva Convention on Prisoners of War was signed at Geneva, July 27, 1929. Its official name is the Convention relative to the Treatment of Prisoners of War. It entered into force 19 June 1931. It is this version of the Geneva Conventions which covered the treatment of prisoners of war during World War II. It is the predecessor of the Third Geneva Convention signed in 1949. On their web site, the International Committee of the Red Cross states that: General provisions Article 1 makes explicit reference to Articles 1, 2, and 3 of ''Hague Convention respecting the laws and customs of war on land ( Hague IV), of October 18, 1907'', to define who are lawful combatants and so qualify as prisoners of war (POW) on capture. In addition to combatants covered by Hague IV, some civilians are also covered in the section of this Convention called the " Application of the Convention to certain classes of civilians". Articles 2, 3, and 4 specifies that POWs are prisoners of the Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legal Fiction
A legal fiction is a construct used in the law where a thing is taken to be true, which is not in fact true, in order to achieve an outcome. Legal fictions can be employed by the courts or found in legislation. Legal fictions are different from Presumption, legal presumptions which assume a certain state of facts until the opposite is proved, such as the presumption of legitimacy. The term ''legal fiction'' is sometimes used in a pejorative way. Jeremy Bentham was a famous historical critic of legal fictions. Proponents of legal fictions, particularly of their use historically, identify legal fictions as "scaffolding around a building under construction". Common law examples Adoption Adoption, Child adoption is a legal fiction in that the adoptive parents become the legal parents, notwithstanding the lack of a biological relationship. Once an order or judgment of adoption is entered, the biological parents become legal strangers to the child, legally no longer related nor with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prisoner Of War
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610. Belligerents hold prisoners of war for a range of legitimate and illegitimate reasons. These may include isolating them from enemy combatants still in the field (releasing and Repatriation, repatriating them in an orderly manner after hostilities), demonstrating military victory, punishment, prosecution of war crimes, labour exploitation, recruiting or even conscripting them as combatants, extracting collecting military and political intelligence, and political or religious indoctrination. Ancient times For much of history, prisoners of war would often be slaughtered or enslaved. Early Roman gladiators could be prisoners of war, categorised according to their ethnic roots as Samnites, Thracians, and Gauls (''Galli''). Homer's ''Iliad'' describes Trojan and Greek soldiers offeri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disarmed Enemy Forces
Disarmed Enemy Forces (DEF, less commonly, Surrendered Enemy Forces) is a US designation for soldiers who surrender to an adversary after hostilities end, and for those POWs who had already surrendered and were held in camps in occupied German territory at the time. It was General Dwight D. Eisenhower's designation of German prisoners in post–World War II occupied Germany. Because of the logistical difficulties of feeding all of the nearly two million of surrendered German soldiers at the levels required by the Geneva Convention during the food crisis of 1945, the purpose of the designation, along with the British designation of Surrendered Enemy Personnel (SEP), was to prevent categorization of the prisoners as prisoners of war (POW) under the 1929 Geneva Convention. Germany at the end of the war Food and agriculture in Nazi Germany had declined greatly in 1944 and 1945. Germany had mobilized for total war, and food for the troops and war workers was vital to the war. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supreme Headquarters Allied Expeditionary Force
Supreme Headquarters Allied Expeditionary Force (SHAEF; ) was the headquarters of the Commander of Allies of World War II, Allied forces in northwest Europe, from late 1943 until the end of World War II. US General Dwight D. Eisenhower was the commander in SHAEF throughout its existence. The position itself shares a common lineage with Supreme Allied Commander Europe and Supreme Allied Commander Atlantic, Atlantic, but they are different titles. History Eisenhower transferred from command of the Mediterranean Theater of Operations, United States Army, Mediterranean Theater of Operations to command SHAEF, which was formed in Camp Griffiss, Bushy Park, Teddington, London, from December 1943; an adjacent street named Shaef Way, and a gate into the park called Shaef Gate, remain to this day. Southwick House was used as an alternative headquarters near Portsmouth. Its staff took the outline plan for Operation Overlord created by Lieutenant General Sir Frederick E. Morgan, Chief of St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axis Powers
The Axis powers, originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis and also Rome–Berlin–Tokyo Axis, was the military coalition which initiated World War II and fought against the Allies of World War II, Allies. Its principal members were Nazi Germany, Fascist Italy, Kingdom of Italy and the Empire of Japan. The Axis were united in their far-right positions and general opposition to the Allies, but otherwise lacked comparable coordination and ideological cohesion. The Axis grew out of successive diplomatic efforts by Germany, Italy, and Japan to secure their own specific expansionist interests in the mid-1930s. The first step was the Italo-German protocol of 23 October 1936, protocol signed by Germany and Italy in October 1936, after which Italian leader Benito Mussolini declared that all other European countries would thereafter rotate on the Rome–Berlin axis, thus creating the term "Axis". The following November saw the ratification of the Anti-Comintern Pact, an anti-communis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheinwiesenlager
The ''Rheinwiesenlager'' (, ''Rhine meadow camps'') were a group of 19 camps built in the Allied-occupied part of Germany by the U.S. Army to hold captured German soldiers at the close of the Second World War. Officially named Prisoner of War Temporary Enclosures (PWTE), they held between one and almost two million surrendered ''Wehrmacht'' personnel from April until September 1945. Prisoners held in the camps were designated ''disarmed enemy forces'', not ''prisoners of war''. This decision was made in March 1945 by SHAEF commander in chief Dwight D. Eisenhower: by not classifying the hundreds of thousands of captured troops as POWs, the logistical problems associated with accommodating so many prisoners of war mandated by the Geneva Convention governing their treatment were negated. Background By early 1945 half of almost all German soldiers taken prisoner in the West were held by U.S. forces, while the other half were taken by the British. But in late March 1945, as Allie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific War
The Pacific War, sometimes called the Asia–Pacific War or the Pacific Theatre, was the Theater (warfare), theatre of World War II fought between the Empire of Japan and the Allies of World War II, Allies in East Asia, East and Southeast Asia, the Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans, and Oceania. It was geographically the largest theatre of the war, including the Pacific Ocean theater of World War II, Pacific Ocean theatre, the South West Pacific theater of World War II, South West Pacific theatre, the Second Sino-Japanese War, and the brief Soviet–Japanese War, and included some of the Largest naval battle in history, largest naval battles in history. War between Japan and the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China had begun in 1937, with hostilities dating back to Japanese invasion of Manchuria, Japan's invasion of Manchuria in 1931, but the Pacific War is more widely accepted to have started in 1941, when the United States and United Kingdom entered the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Theatre Of World War II
The European theatre of World War II was one of the two main theatres of combat during World War II, taking place from September 1939 to May 1945. The Allied powers (including the United Kingdom, the United States, the Soviet Union and France) fought the Axis powers (including Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy) on both sides of the continent in the Western and Eastern fronts. There was also conflict in the Scandinavian, Mediterranean and Balkan regions. It was an intense conflict that led to at least 39 million deaths and a dramatic change in the balance of power in the continent. During the 1930s, Adolf Hitler, the leader of Nazi Germany, expanded German territory by annexing all of Austria and the Sudetenland region of Czechoslovakia in 1938. This was motivated in part by Germany's racial policy that believed the country needed to expand for the pseudoscientific "Aryan race" to survive. They were aided by Italy, another fascist state which was led by Benito Mussolini. Wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Odžak
The Battle of Odžak was the last battle of World War II in Europe Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east .... The battle began on 19 April 1945 and lasted until 25 May 1945, 17 days after the end of the war in Europe. The combatants were the Croatian Armed Forces (Independent State of Croatia) (NDH) commanded by Petar Rajkovačić and the Yugoslav Army commanded by Miloš Zekić. The battle took place in the Bosnian town of Odžak. The battle was a victory for the Partisans. The battle is thoroughly described in a number of books, for example, in a 1969 book on 53rd Division, 1981 book on 16th Muslim Brigade, 1983 book on 27th East Bosnian Division, and 1983 book on 14th Central Bosnian Brigade. File:"Vlaška Mala" from 23rd to 28th of April 1945.jpg, alt=, Operation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |