|
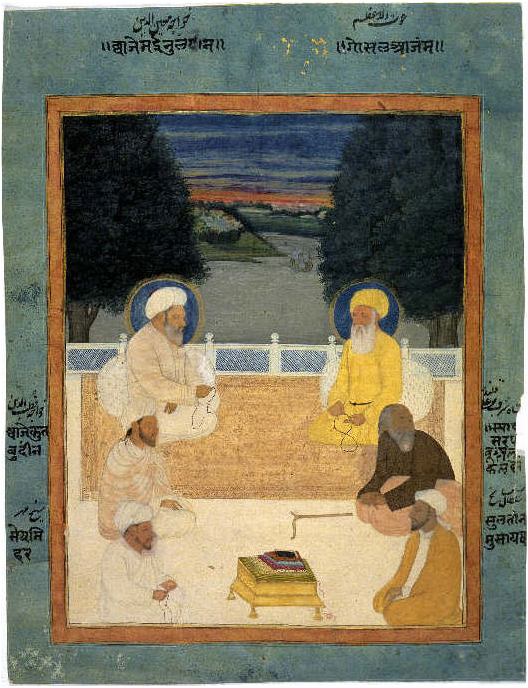
The Twelve Imams
The Twelve Imams (, '; , ') are the spiritual and political successors to the Islamic prophet Muhammad in the Twelver branch of Shia Islam, including that of the Alawite and Alevi. According to Twelver theology, the Twelve Imams are exemplary human individuals who not only rule over the community with justice, but also are able to keep and interpret ''sharia'' and the esoteric meaning of the Quran. The words and deeds of Muhammad and the imams are a guide and model for the community to follow; as a result, they must be free from error and sin (known as ''ismah'', or infallibility) and must be chosen by divine decree through Muhammad. Imamah It is believed in Twelver Shi’ism that the Islamic prophet Muhammad and his household are infallible, possessing '' Hikmah''. Their oppression and suffering served greater purposes and were a means of divine grace to their devotees. The Imams are also guided by preserved texts in their possession, such as al-Jafr, al-Jamia, and una ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world's Major religious groups, second-largest religious population after Christians. Muslims believe that Islam is the complete and universal version of a Fitra, primordial faith that was revealed many times through earlier Prophets and messengers in Islam, prophets and messengers, including Adam in Islam, Adam, Noah in Islam, Noah, Abraham in Islam, Abraham, Moses in Islam, Moses, and Jesus in Islam, Jesus. Muslims consider the Quran to be the verbatim word of God in Islam, God and the unaltered, final revelation. Alongside the Quran, Muslims also believe in previous Islamic holy books, revelations, such as the Torah in Islam, Tawrat (the Torah), the Zabur (Psalms), and the Gospel in Islam, Injil (Gospel). They believe that Muhammad in Islam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torah
The Torah ( , "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. The Torah is also known as the Pentateuch () or the Five Books of Moses. In Rabbinical Jewish tradition it is also known as the Written Torah (, ). If meant for liturgic purposes, it takes the form of a Torah scroll ( '' Sefer Torah''). If in bound book form, it is called '' Chumash'', and is usually printed with the rabbinic commentaries (). In rabbinic literature, the word ''Torah'' denotes both the five books ( "Torah that is written") and the Oral Torah (, "Torah that is spoken"). It has also been used, however, to designate the entire Hebrew Bible. The Oral Torah consists of interpretations and amplifications which according to rabbinic tradition have been handed down from generation to generation and are now embodied in the Talmud and Midrash. Rabbinic tradition's underst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sufism
Sufism ( or ) is a mysticism, mystic body of religious practice found within Islam which is characterized by a focus on Islamic Tazkiyah, purification, spirituality, ritualism, and Asceticism#Islam, asceticism. Practitioners of Sufism are referred to as "Sufis" (from , ), and historically typically belonged to "orders" known as (pl. ) — congregations formed around a grand (saint) who would be the last in a Silsilah, chain of successive teachers linking back to Muhammad, with the goal of undergoing (self purification) and the hope of reaching the Maqam (Sufism), spiritual station of . The ultimate aim of Sufis is to seek the pleasure of God by endeavoring to return to their original state of purity and natural disposition, known as . Sufism emerged early on in Islamic history, partly as a reaction against the expansion of the early Umayyad Caliphate (661–750) and mainly under the tutelage of Hasan al-Basri. Although Sufis were opposed to dry legalism, they strictly obs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadith Of The Twelve Successors
The hadith of the twelve successors () is a widely-reported prophecy, attributed to the Islamic prophet Muhammad, predicting that there would be twelve successors after him. As there were many more rulers after Muhammad, Sunni authors have variously identified these twelve successors with some of these rulers. In Twelver Shia, these successors are instead identified with their Twelve Imams. Their last imam, Muhammad al-Mahdi, is believed to miraculously remain in occultation since 874 CE, and is expected to return in the end of times to eradicate injustice and evil. Sunni sources Several variants of the hadith of twelve successors appear in Sunni sources, usually related on the authority of Jabir ibn Samura (), a companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, but also narrated from other companions, such as Abd Allah ibn Mas'ud (), Anas ibn Malik (), Umar (), Wasila ibn Asqa', Abd Allah ibn Umar (), Abu Huraira (), Salman the Persian (), Aisha (), and Uthman (). In particular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God in Abrahamic religions, God of Abraham (or ''Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the last Islamic prophet. Alongside the Quran, Muslims also believe in previous Islamic holy books, revelations, such as the Tawrat (Torah), the Zabur (Psalms), and the Injeel (Gospel). These earlier revelations are associated with Judaism and Christianity, which are regarded by Muslims as earlier versions of Islam. The majority of Muslims also follow the teachings and practices attributed to Muhammad (''sunnah'') as recorded in traditional accounts (hadith). With an estimated population of almost 2 billion followers, Muslims comprise around 26% of the world's total population. In descending order, the percentage of people who identify as Muslims on each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alevism
Alevism (; ; ) is a syncretic heterodox Islamic tradition, whose adherents follow the mystical Islamic teachings of Haji Bektash Veli, who taught the teachings of the Twelve Imams, whilst incorporating some traditions from shamanism. Differing from Sunni Islam and Usuli Twelver Shia Islam, Alevis have no binding religious dogmas, and teachings are passed on by a ''dede'' "spiritual leader" as with Sufi orders. They acknowledge the six articles of faith of Islam, but may differ regarding their interpretation. They have faced significant institutional stigma from the Ottoman and later Turkish state and academia, being described as heterodox to contrast them with the "orthodox" Sunni majority. The term “Alevi-Bektashi” is currently a widely and frequently used expression in the religious discourse of Turkey as an umbrella term for the two religious groups of Alevism and Bektashism. Adherents of Alevism are found primarily in Turkey and estimates of the percentage o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major Occultation
In Twelver Shia Islam, the Major Occultation (, ', 329 AH-present, 941 CE-present) is the second occultation of the Hidden Imam, Muhammad al-Mahdi, which is expected to continue until his rise at the end of time to establish peace and justice on earth. While various sects disagree about the identity of the eschatological Mahdi, the belief in him remains popular among all Muslims, possibly owing to numerous traditions to this effect in canonical Sunni and Shia sources. The Major Occultation began in 329 AH (941 CE) with the death of the fourth successive agent of the Hidden Imam, Abu al-Hasan al-Samarri, marking the end of the Minor Occultation (260-329 AH, 874-941 CE). According to Twelver sources, shortly before his death, al-Samarri received a letter from the Hidden Imam, which predicted his imminent death, ordered him not to designate a successor, and announced the beginning of the "complete occultation," in which there would be no agent of the Hidden Imam, though he is b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad Al-Mahdi
Muhammad al-Mahdi () is believed by the Twelver Shia to be the last of the Twelve Imams and the eschatological Mahdi, who will emerge in the end of time to establish peace and justice and redeem Islam. Hasan al-Askari, the eleventh Imam, died in 260 AH (873–874), possibly poisoned by the Abbasids. Immediately after his death, his main representative, Uthman ibn Sa'id al-Asadi, claimed that the eleventh Imam had an infant son named Muhammad, who was kept hidden from the public out of fear of Abbasid persecution. Uthman also claimed to represent Muhammad, who had entered a state of occultation. Other local representatives of al-Askari largely supported these assertions, while the Shia community fragmented into several sects over al-Askari's succession. All these sects, however, are said to have disappeared after a few decades except the Twelvers, who accept the son of al-Askari as the twelfth and final Imam in occultation. Uthman was followed by three more agents, col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hasan Ibn Ali
Hasan ibn Ali (; 2 April 670) was an Alids, Alid political and religious leader. The eldest son of Ali and Fatima and a grandson of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, Hasan briefly ruled as Rashidun caliphate, Rashidun caliph from January 661 until August 661. He is considered as the second Imamate in Shia doctrine, Imam in Shia Islam, succeeding Ali and preceding his brother Husayn ibn Ali, Husayn. As a grandson of the prophet, he is part of the and the , and also participated in the event of the mubahala. During the Ali as Caliph, caliphate of Ali (), Hasan accompanied him in the military campaigns of the First Fitna. Following Assassination of Ali, Ali's assassination in January 661, Hasan was acknowledged caliph in Kufa. His sovereignty was not recognized by Mu'awiya I, Mu'awiya ibn Abi Sufyan (), the governor of Syria, who led an army into Kufa while pressing Hasan for abdication in letters. In response, Hasan sent a vanguard under Ubayd Allah ibn al-Abbas to block Mu'awiya' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Husayn Ibn Ali
Husayn ibn Ali (; 11 January 626 – 10 October 680 Common Era, CE) was a social, political and religious leader in early medieval Arabia. The grandson of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and an Alids, Alid (the son of Ali ibn Abu Talib ibn Abd al-Muttalib, Abi Talib and Muhammad's daughter Fatima), as well as a younger brother of Hasan ibn Ali, Husayn is regarded as the third Imam in Shia Islam after his brother, Hasan, and before his son, Ali al-Sajjad. Husayn is a prominent member of the Ahl al-Bayt and is also considered to be a member of the Ahl al-Kisa and a participant in the event of the mubahala, event of the ''mubahala''. Muhammad described him and his brother, Hasan, as the leaders of the youth of Paradise in Islam, paradise. During the caliphate of Ali, Husayn accompanied him in wars. After the assassination of Ali, he obeyed his brother in recognizing the Hasan–Muawiya treaty, Hasan–Mu'awiya I treaty, despite it being suggested to do otherwise. In the nine-year pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatimah
Fatima bint Muhammad (; 605/15–632 CE), commonly known as Fatima al-Zahra' (), was the daughter of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and his wife Khadija bint Khuwaylid, Khadija. Fatima's husband was Ali, the fourth of the Rashidun caliphs and the first Twelve Imams, Shia imam. Fatima's sons were Hasan ibn Ali, Hasan and Husayn ibn Ali, Husayn, the second and third Shia imams, respectively. Fatima has been compared to Mary, mother of Jesus, Mary, mother of Jesus, especially in Shia Islam. Muhammad is said to have regarded her as the best of women and the dearest person to him. She is often viewed as an ultimate archetype for Muslim women and an example of compassion, generosity, and enduring suffering. It is through Fatima that Muhammad's family line has survived to this date. Her name and her epithets remain popular choices for Muslim girls. When Muhammad died in 632, Fatima and her husband Ali refused to acknowledge the authority of the first caliph, Abu Bakr. The couple and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharif
Sharīf or Sherif (, 'noble', 'highborn'), also spelled shareef, feminine sharīfa (), plural ashrāf (), shurafāʾ (), or (in the Maghreb) shurfāʾ, is a title used to designate a person descended, or claiming to be descended, from the family of the Islamic prophet Muhammad ( ). It may be used in three senses: #In the broadest sense, it refers to any descendant of Muhammad's great-grandfather Hashim (the Banu Hashim or Hashimites, already in Muhammad's day an established clan within the Meccan tribe of the Quraysh), including all descendants of Muhammad's paternal uncles Abu Talib (the Talibids) and al-Abbas (the Abbasids).. #More often, it refers to a descendant of Ali, a son of Abu Talib and a paternal cousin of Muhammad (the Alids), especially but not exclusively through Ali's marriage with Muhammad's daughter Fatima (the Fatimids). In the sense of descendants of Fatima and Ali (the most common one), the term effectively refers to all descendants of Muhammad. # ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |