|
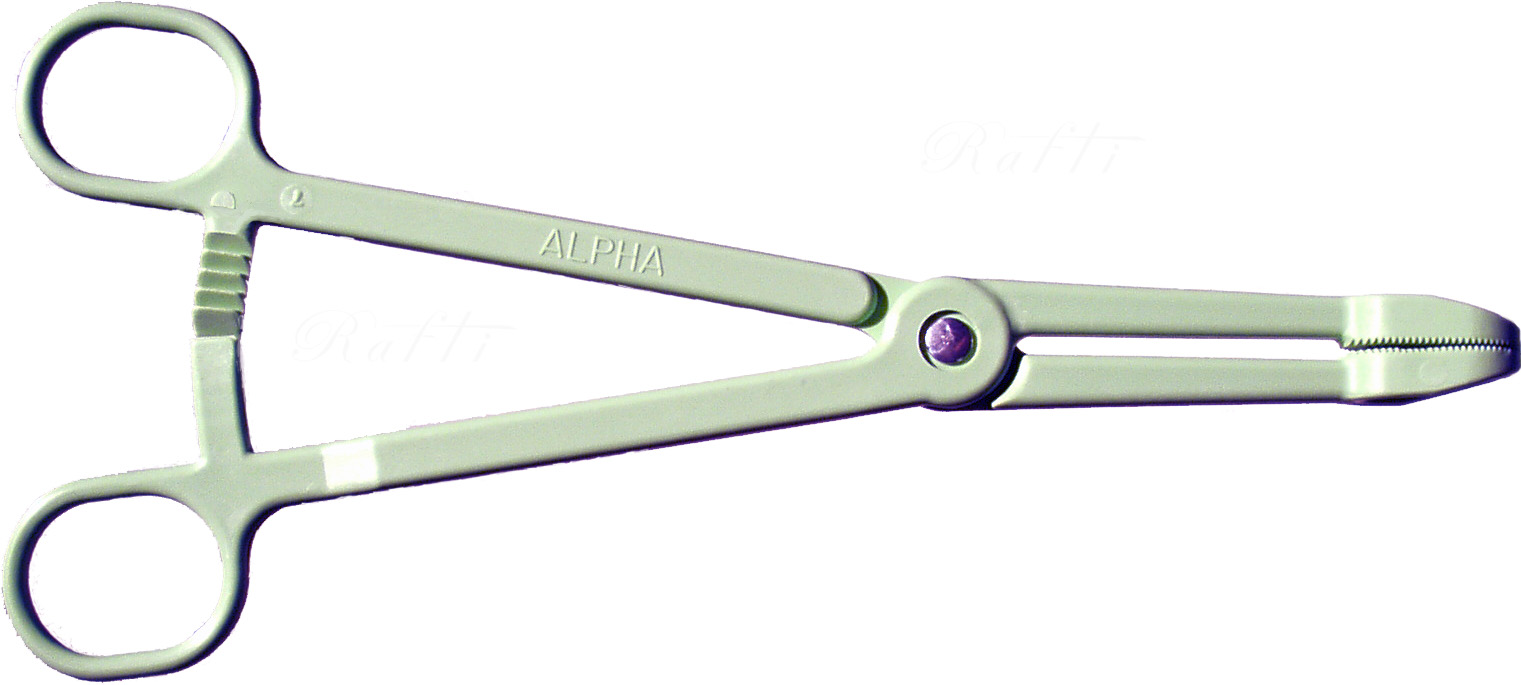
Tenaculum
A tenaculum is a surgical instrument, usually classified as a type of forceps. It consists of a slender sharp-pointed hook attached to a handle and is used mainly in surgery for seizing and holding parts, such as blood vessels.> tenaculumRetrieved August 2010 Uses include: *Steadying the cervix and uterus, as is done during insertion of an intrauterine device or during a surgical abortionBirth Control Intrauterine Devices (IUDs) Author: Omnia M Samra. Last Editorial Review: 5/18/2006 (although recent research indicates that an may be better suited for those tasks, as it is less likely to cause bleeding complications). *Seizing and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forceps
Forceps (: forceps or considered a plural noun without a singular, often a pair of forceps; the Latin plural ''forcipes'' is no longer recorded in most dictionaries) are a handheld, hinged instrument used for grasping and holding objects. Forceps are used when fingers are too large to grasp small objects or when many objects need to be held at one time while the hands are used to perform a task. The term "forceps" is used almost exclusively in the fields of biology and medicine. Outside biology and medicine, people usually refer to forceps as tweezers, tongs, pliers, clips or clamps. Mechanically, forceps employ the principle of the lever to grasp and apply pressure. Depending on their function, basic surgical forceps can be categorized into the following groups: # Non-disposable forceps. They should withstand various kinds of physical and chemical effects of body fluids, secretions, cleaning agents, and sterilization methods. # Disposable forceps. They are usually made of lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
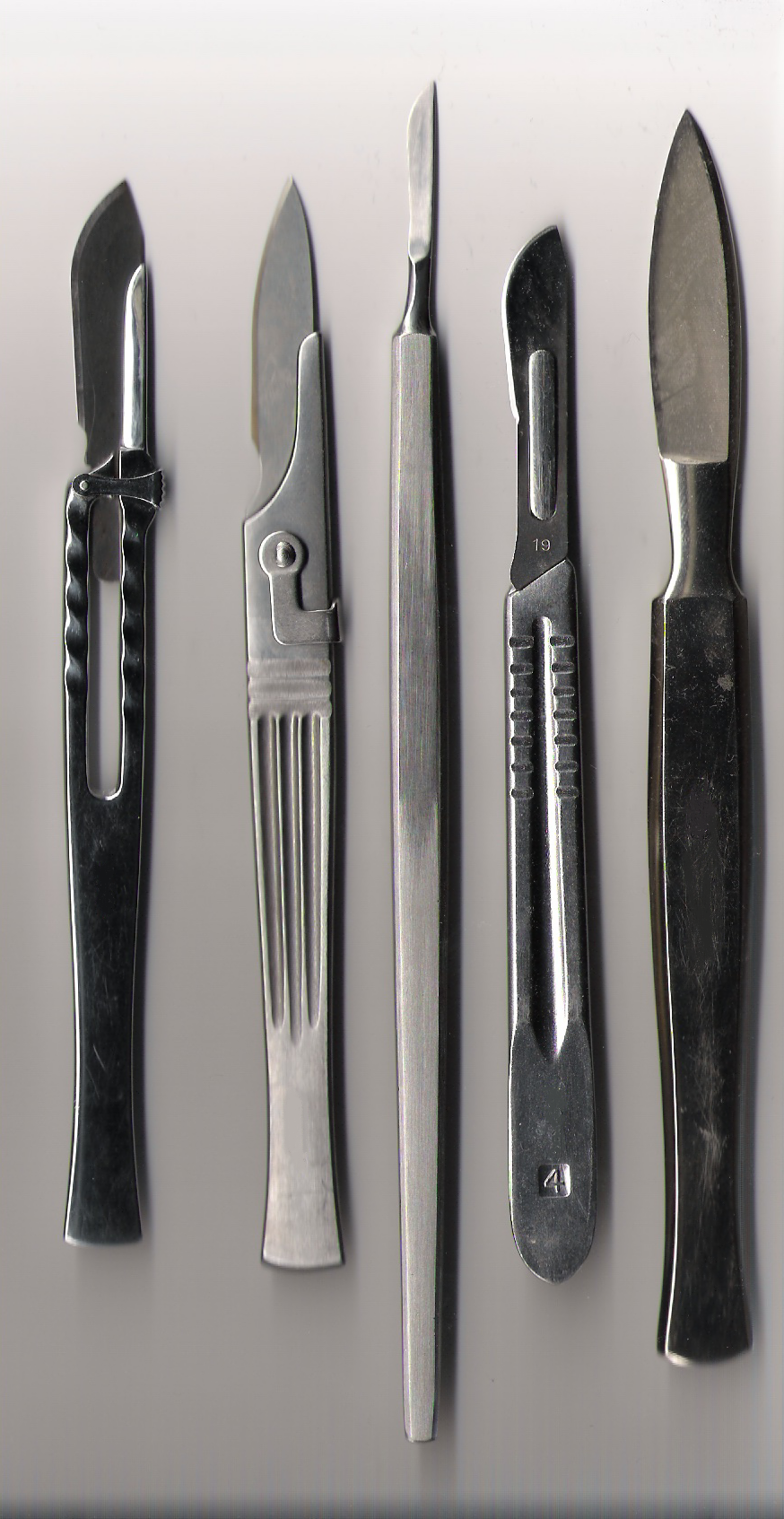
Surgical Instrument
A surgical instrument is a medical device for performing specific actions or carrying out desired effects during a surgery or operation, such as modifying biological tissue, or to provide access for viewing it. Over time, many different kinds of surgical instruments and tools have been invented. Some surgical instruments are designed for general use in all sorts of surgeries, while others are designed for only certain specialties or specific procedures. Classification of surgical instruments helps surgeons to understand the functions and purposes of the instruments. With the goal of optimizing surgical results and performing more difficult operations, more instruments continue to be invented in the modern era. History Many different kinds of surgical instruments and tools have been invented and some have been repurposed as medical knowledge and surgical practices have developed. As surgery practice diversified, some tools are advanced for higher accuracy and stability while so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervix
The cervix (: cervices) or cervix uteri is a dynamic fibromuscular sexual organ of the female reproductive system that connects the vagina with the uterine cavity. The human female cervix has been documented anatomically since at least the time of Hippocrates, over 2,000 years ago. The cervix is approximately 4 cm long with a diameter of approximately 3 cm and tends to be described as a cylindrical shape, although the front and back walls of the cervix are contiguous. The size of the cervix changes throughout a woman's life cycle. For example, women in the fertile years of their reproductive cycle tend to have larger cervixes than postmenopausal women; likewise, women who have produced offspring have a larger cervix than those who have not. In relation to the vagina, the part of the cervix that opens to the uterus is called the ''internal os'' and the opening of the cervix in the vagina is called the ''external os''. Between them is a conduit commonly called the cervic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', : uteri or uteruses) or womb () is the hollow organ, organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic development, embryonic and prenatal development, fetal development of one or more Fertilized egg, fertilized eggs until birth. The uterus is a hormone-responsive sex organ that contains uterine gland, glands in its endometrium, lining that secrete uterine milk for embryonic nourishment. (The term ''uterus'' is also applied to analogous structures in some non-mammalian animals.) In humans, the lower end of the uterus is a narrow part known as the Uterine isthmus, isthmus that connects to the cervix, the anterior gateway leading to the vagina. The upper end, the body of the uterus, is connected to the fallopian tubes at the uterine horns; the rounded part, the fundus, is above the openings to the fallopian tubes. The connection of the uterine cavity with a fallopian tube is called the utero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intrauterine Device
An intrauterine device (IUD), also known as an intrauterine contraceptive device (IUCD or ICD) or coil, is a small, often T-shaped birth control device that is inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. IUDs are a form of long-acting reversible contraception (LARC). The use of IUDs as a form of birth control dates from the 1800s. A previous model known as the Dalkon shield was associated with an increased risk of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). However, current models do not affect PID risk in women without sexually transmitted infections during the time of insertion. Although copper IUDs may increase menstrual bleeding and result in painful cramps, hormonal IUDs may reduce menstrual bleeding or stop menstruation altogether. However, women can have daily spotting for several months after insertion, and it can take up to three months for there to be a 90% decrease in bleeding with hormonal IUDs. Cramping can be treated with NSAIDs. More serious potential complications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abortion
Abortion is the early termination of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus. Abortions that occur without intervention are known as miscarriages or "spontaneous abortions", and occur in roughly 30–40% of all pregnancies. Deliberate actions to end a pregnancy are called induced abortion, or less frequently "induced miscarriage". The unmodified word ''abortion'' generally refers to induced abortion. Common reasons for having an abortion are birth-timing and limiting family size. Other reasons include maternal health, an inability to afford a child, domestic violence, lack of support, feelings of being too young, wishing to complete an education or advance a career, or not being able or willing to raise a child conceived as a result of rape or incest. When done legally in industrialized societies, induced abortion is one of the safest procedures in medicine. Modern methods use medication or surgery for abortions. The drug mifepristone (aka RU-4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allis Clamp
Allis may refer to: People * Allis (surname) Places * Allis Township, Michigan * North Allis Township, Michigan * West Allis, Wisconsin Other * Allis-Chalmers, a former manufacturer of farm equipment based in Milwaukee, Wisconsin * Big Allis, a giant generator in Queens, New York, commissioned by Consolidated Edison and built by Allis-Chalmers in 1965 * Allis-Chalmers Model B, popular tractor manufactured by Allis-Chalmers * Charles Allis Art Museum, in Milwaukee, Wisconsin * Allis shad, ''Alosa alosa'', species of fish found in Europe and North Africa * Fiat Allis, manufacturer of construction equipment * Allis clamp, a vital surgical instrument used in many surgical procedures See also * Alliss * Alis (other) * Alice (other) {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gynaecology
Gynaecology or gynecology (see American and British English spelling differences) is the area of medicine concerned with conditions affecting the female reproductive system. It is often paired with the field of obstetrics, which focuses on pregnancy and childbirth, thereby forming the combined area of obstetrics and gynaecology (OB-GYN). Gynaecology encompasses both primary and preventative care of issues related to female reproduction and sexual health, such as the uterus, vagina, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and breasts; subspecialties include family planning; minimally invasive surgery; pediatric and adolescent gynecology; and pelvic medicine and reconstructive surgery. While gynaecology has traditionally centered on cisgender women, it increasingly encompasses anyone with female organs, including transgender, intersex, and nonbinary individuals; however, many non-cis women face accessibility issues due to stigma, bias, and systemic exclusion in healthcare. Etymology Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of America, Confederacy ("the South"), which was formed in 1861 by U.S. state, states that had Secession in the United States, seceded from the Union. The Origins of the American Civil War, central conflict leading to war was a dispute over whether Slavery in the United States, slavery should be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prohibited from doing so, which many believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction. Timeline of events leading to the American Civil War, Decades of controversy over slavery came to a head when Abraham Lincoln, who opposed slavery's expansion, won the 1860 presidential election. Seven Southern slave states responded to Lincoln's victory by seceding f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Jean Pozzi
Samuel Jean Pozzi (3 October 1846 – 13 June 1918) was a French surgeon and gynecologist. He was also interested in anthropology and neurology. He is remembered today for John Singer Sargent's portrait of him. After studying medicine in Paris, Pozzi volunteered to be a medic during the Franco-Prussian War. He later specialized in gynecological and abdominal surgery, establishing the first Chair of Gynecology in Paris in 1884, and performing the first gastroenterostomy in France. Pozzi was elected to the French Academy of Medicine in 1896, and co-founded the Revue de gynécologie et de chirurgie abdominale in 1897. His personal life was marked by a tumultuous marriage, multiple affairs, and cultural interests, including friendships with notable figures such as Sarah Bernhardt and Marcel Proust. In the political arena, Pozzi served as a senator for his hometown, Bergerac, and supported Alfred Dreyfus during his trial. He died in 1918, when a disgruntled patient fatally shot him. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicines And Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency
The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) is an executive agency of the Department of Health and Social Care in the United Kingdom which is responsible for ensuring that medicines and medical devices work and are acceptably safe. The MHRA was formed in 2003 with the merger of the Medicines Control Agency (MCA) and the Medical Devices Agency (MDA). In April 2013, it merged with the National Institute for Biological Standards and Control (NIBSC) and was rebranded, with the MHRA identity being used solely for the regulatory centre within the group. The agency employs more than 1,200 people in London, York and South Mimms, Hertfordshire. Structure The MHRA is divided into three main centres: * MHRA Regulatory – the regulator for the pharmaceutical and medical devices industries * Clinical Practice Research Datalink – licences anonymised health care data to pharmaceutical companies, academics and other regulators for research * National Institute for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |