|
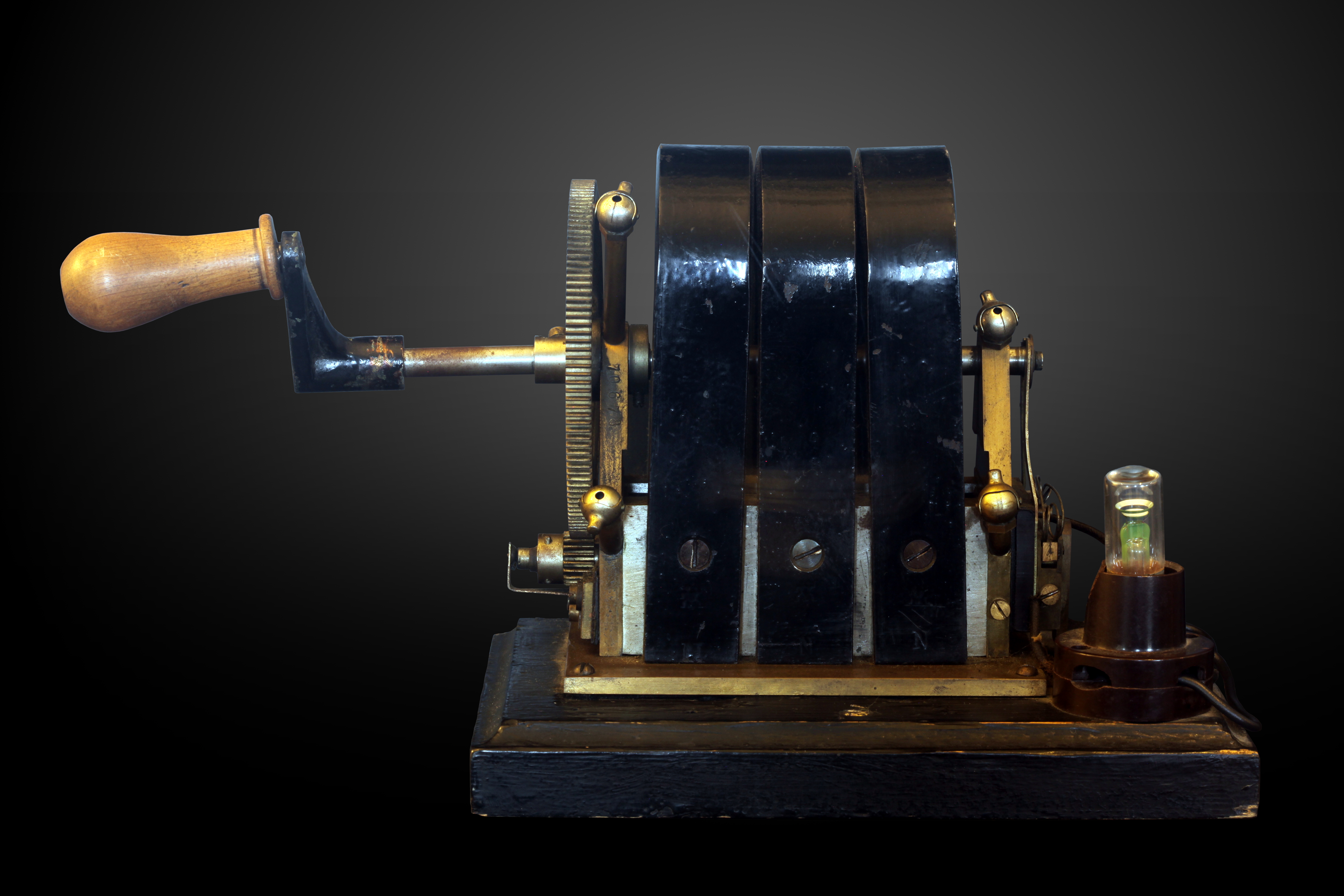
Telephone Magneto
A telephone magneto is a hand-cranked electrical generator that uses permanent magnets to produce alternating current from a rotating armature. In early telegraphy, magnetos were used to power instruments, while in telephony they were used to generate electrical current to drive electromechanical ringers in telephone sets and activate signals on operator consoles. Telegraphy Telegraphy pre-dated telephony and magnetos were used to drive some of the early printing telegraph instruments. Manual telegraphy with keys and reception by either a needle instrument or a syphon recorder could be powered by batteries. The later automatic and printing instruments, such as the Wheatstone ABC telegraph, required greater currents that could be delivered by a hand-cranked magneto. A hand-crank was used to rotate a belt drive that increases the rotational speed of an armature with a pair of coils between the poles of a stationary horseshoe magnet. Telephony Many early manual telephones h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telephone Magneto From Beneath
A telephone, colloquially referred to as a phone, is a telecommunications device that enables two or more users to conduct a conversation when they are too far apart to be easily heard directly. A telephone converts sound, typically and most efficiently the human voice, into electronic signals that are transmitted via Electrical cable, cables and other communication channels to another telephone which reproduces the sound to the receiving user. The term is derived from and (, ''voice''), together meaning ''distant voice''. In 1876, Alexander Graham Bell was the first to be granted a United States patent for a device that produced clearly intelligible replication of the human voice at a second device. This instrument was further developed by many others, and became rapidly indispensable in business, government, and in households. The essential elements of a telephone are a microphone (''transmitter'') to speak into and an earphone (''receiver'') which reproduces the voice a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
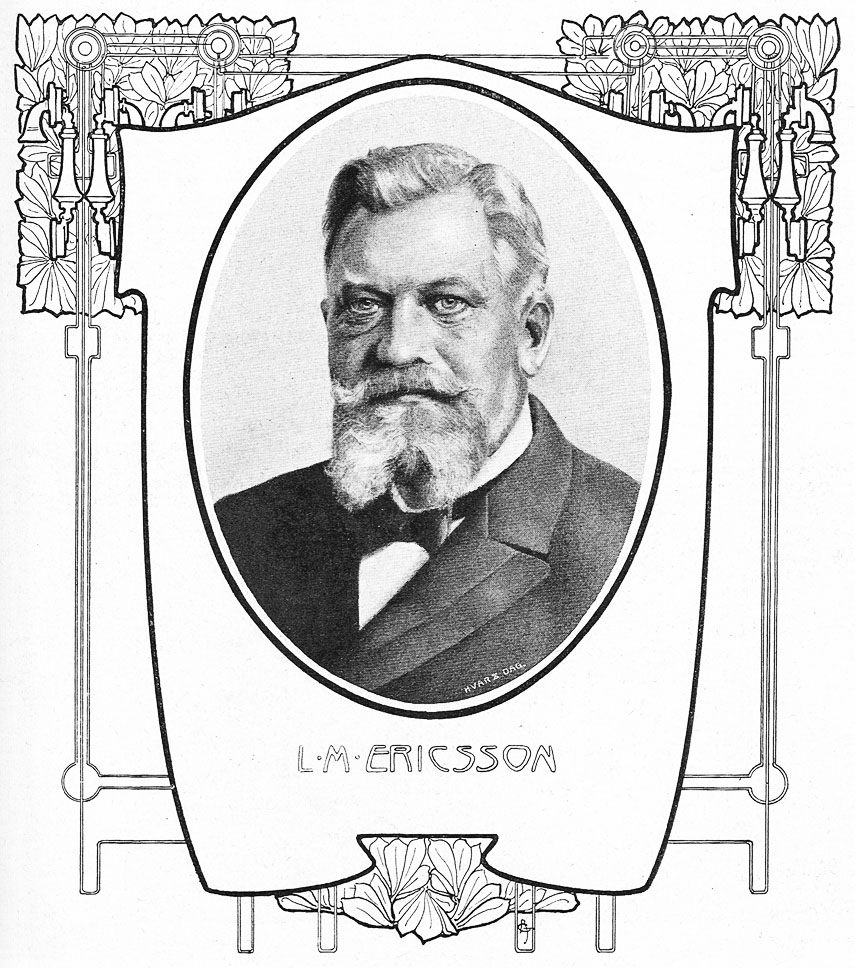
Ericsson Taxen (2)
(), commonly known as Ericsson (), is a Swedish multinational networking and telecommunications company headquartered in Stockholm, Sweden. Ericsson has been a major contributor to the development of the telecommunications industry and is one of the leaders in 5G. Ericsson has over 57,000 granted patents and it is the inventor of Bluetooth technology. The company sells infrastructure, software, and services in information and communications technology for telecommunications service providers and enterprises, including, among others, cellular 4G and 5G equipment, and Internet Protocol (IP) and optical transport systems. The company employs around 100,000 people and operates in more than 180 countries. The company is listed on the Nasdaq Stockholm under the ticker symbols ERIC.A and ERIC.B and on the American Nasdaq under the ticker symbol ERIC. The company was founded in 1876 by Lars Magnus Ericsson and is jointly controlled by the Wallenberg family through its holding comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ringer Box
A ringer box is a telephone signaling device, similar to a bell box. It usually contains an electromechanical gong and was used with most early desk stand telephones, such as candlestick telephones and the Western Electric type Western Electric hand telephone sets, which were too small to hold a ringer and other required electrical components. Many pay station telephones also used a separate ringer box. In telephony, ringer boxes and similar devices are often categorized as subscriber sets. The ringer contained in the ringer box alerts a call recipient to incoming calls by ringing one or more metallic bells emitting a ringtone. Ringers were commonly placed in the same housing as the subscriber set, which consisted of other electrical components, such as induction coils, capacitors, and, if required, a magneto generator. The subscriber set interfaced a telephone set to the telephone network, while magneto generators were used in a manual exchange to generate a remote ring si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magneto
A magneto is an electrical generator that uses permanent magnets to produce periodic pulses of alternating current. Unlike a dynamo, a magneto does not contain a commutator to produce direct current. It is categorized as a form of alternator, although it is usually considered distinct from most other alternators, which use field coils rather than permanent magnets. Hand-cranked magneto generators were used to provide ringing current in telephone systems. Magnetos were also adapted to produce pulses of high voltage in the ignition systems of some gasoline-powered internal combustion engines to provide power to the spark plugs. Use of such ignition magnetos for ignition is now limited mainly to engines without a low-voltage electrical system, such as lawnmowers and chainsaws, and to aircraft engines, in which keeping the ignition independent of the rest of the electrical system ensures that the engine continues running in the event of alternator or battery failure. For redund ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Switched Telephone Network
The public switched telephone network (PSTN) is the aggregate of the world's telephone networks that are operated by national, regional, or local telephony operators. It provides infrastructure and services for public telephony. The PSTN consists of telephone lines, fiber-optic cables, microwave transmission links, cellular networks, communications satellites, and undersea telephone cables interconnected by switching centers, such as central offices, network tandems, and international gateways, which allow telephone users to communicate with each other. Originally a network of fixed-line analog telephone systems, the PSTN is now predominantly digital in its core network and includes terrestrial cellular, satellite, and landline systems. These interconnected networks enable global communication, allowing calls to be made to and from nearly any telephone worldwide. Many of these networks are progressively transitioning to Internet Protocol to carry their telephony traffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
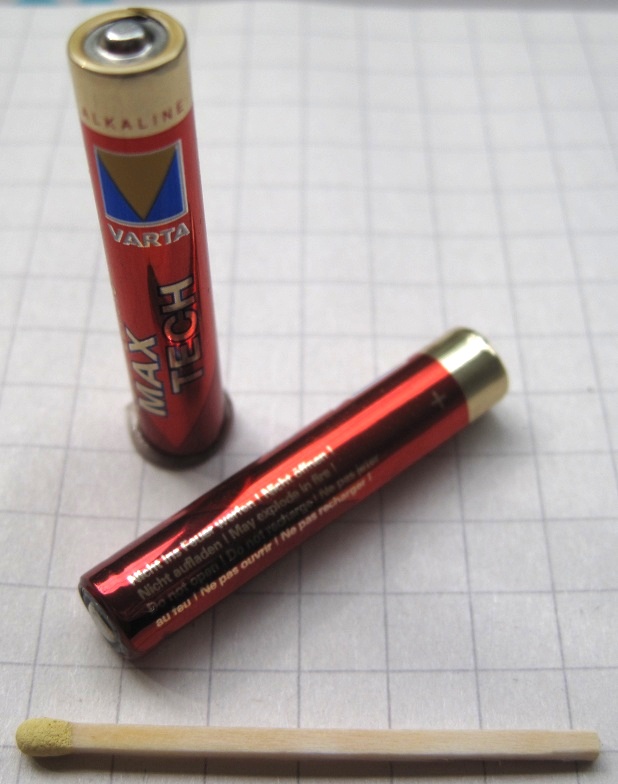
Zinc–carbon Battery
A zinc–carbon battery (or carbon zinc battery in U.S. English) is the generic “heavy duty” disposable battery. It has been overtaken in recent times by the longer-lasting alkaline battery. A zinc–carbon battery is a dry cell that provides direct electric current from the electrochemical reaction between zinc (Zn) and manganese dioxide (MnO2) in the presence of an ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) electrolyte. It produces a voltage of about 1.5 volts between the zinc anode, which is typically constructed as a cylindrical container for the battery cell, and a carbon rod surrounded by a compound with a higher Standard electrode potential (positive polarity), known as the cathode, that collects the current from the manganese dioxide electrode. The name "zinc–carbon" is slightly misleading as it implies that carbon is acting as the oxidizing agent rather than the manganese dioxide. General-purpose batteries may use an acidic aqueous paste of ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) as electro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Battery Sizes
This is a list of the sizes, shapes, and general characteristics of some common primary and secondary battery types in household, automotive and light industrial use. The complete nomenclature for a battery specifies size, chemistry, terminal arrangement, and special characteristics. The same physically interchangeable cell size or battery size may have widely different characteristics; physical interchangeability is not the sole factor in substituting a battery. The full battery designation identifies not only the size, shape and terminal layout of the battery but also the chemistry (and therefore the voltage per cell) and the number of cells in the battery. For example, a CR123 battery is always LiMnO2 ('Lithium') chemistry, in addition to its unique size. The following tables give the common battery chemistry types for the current common sizes of batteries. See Battery chemistry for a list of other electrochemical systems. Cylindrical batteries Rectangular batteries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telephone Exchange
A telephone exchange, telephone switch, or central office is a central component of a telecommunications system in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or in large enterprises. It facilitates the establishment of communication circuits, enabling telephone calls between subscribers. The term "central office" can also refer to a central location for fiber optic equipment for a fiber internet provider. In historical perspective, telecommunication terminology has evolved with time. The term ''telephone exchange'' is often used synonymously with ''central office'', a Bell System term. A central office is defined as the telephone switch controlling connections for one or more central office prefixes. However, it also often denotes the building used to house the inside plant equipment for multiple telephone exchange areas. In North America, the term ''wire center'' may be used to denote a central office location, indicating a facility that provides a telephone with a dial tone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telephone
A telephone, colloquially referred to as a phone, is a telecommunications device that enables two or more users to conduct a conversation when they are too far apart to be easily heard directly. A telephone converts sound, typically and most efficiently the human voice, into electronic signals that are transmitted via Electrical cable, cables and other communication channels to another telephone which reproduces the sound to the receiving user. The term is derived from and (, ''voice''), together meaning ''distant voice''. In 1876, Alexander Graham Bell was the first to be granted a United States patent for a device that produced clearly intelligible replication of the human voice at a second device. This instrument was further developed by many others, and became rapidly indispensable in business, government, and in households. The essential elements of a telephone are a microphone (''transmitter'') to speak into and an earphone (''receiver'') which reproduces the voice a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horseshoe Magnet
A horseshoe magnet is either a permanent magnet or an electromagnet made in the shape of a horseshoe (in other words, in a U-shape). The permanent kind has become the most widely recognized symbol for magnets. It is usually depicted as red and marked with 'North' and 'South' poles. Although rendered obsolete in the 1950s by squat, cylindrical magnets made of modern materials, horseshoe magnets are still regularly shown in elementary school textbooks. Historically, they were a solution to the problem of making a compact magnet that does not destroy itself in its own demagnetizing field. History In 1819, it was discovered that passing electric current through a piece of metal deflected a compass needle. Following this discovery, many other experiments surrounding magnetism were attempted. These experiments culminated in William Sturgeon wrapping wire around a horseshoe-shaped piece of iron and running electric current through the wires creating the first horseshoe magnet. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |