|
Tegmentum
The tegmentum (from Latin for "covering") is a general area within the brainstem. The tegmentum is the ventral part of the midbrain and the tectum is the dorsal part of the midbrain. It is located between the ventricular system and distinctive basal or ventral structures at each level. It forms the floor of the midbrain (mesencephalon) whereas the tectum forms the ceiling. It is a multisynaptic network of neurons that is involved in many subconscious homeostatic and reflexive pathways. It is a motor center that relays inhibitory signals to the thalamus and basal nuclei preventing unwanted body movement. The tegmentum area includes various different structures, such as the rostral end of the reticular formation, several nuclei controlling eye movements, the periaqueductal gray matter, the red nucleus, the substantia nigra, and the ventral tegmental area. The tegmentum is the location of several cranial nerve nuclei. The nuclei of CN III and IV are located in the tegmentum port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
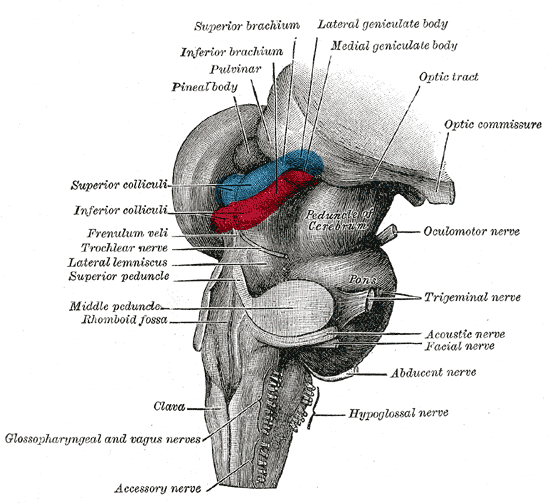
Mid-brain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the uppermost portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum. It is functionally associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal ( alertness), and temperature regulation.Breedlove, Watson, & Rosenzweig. Biological Psychology, 6th Edition, 2010, pp. 45-46 The name ''mesencephalon'' comes from the Greek ''mesos'', "middle", and ''enkephalos'', "brain". Structure The midbrain is the shortest segment of the brainstem, measuring less than 2cm in length. It is situated mostly in the posterior cranial fossa, with its superior part extending above the tentorial notch. The principal regions of the midbrain are the tectum, the cerebral aqueduct, tegmentum, and the cerebral peduncles. Rostrally the midbrain adjoins the diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, etc.), while caudally it adjoins the hindbrain (pon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the uppermost portion of the brainstem connecting the diencephalon and cerebrum with the pons. It consists of the cerebral peduncles, tegmentum, and tectum. It is functionally associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation.Breedlove, Watson, & Rosenzweig. Biological Psychology, 6th Edition, 2010, pp. 45-46 The name ''mesencephalon'' comes from the Greek ''mesos'', "middle", and ''enkephalos'', "brain". Structure The midbrain is the shortest segment of the brainstem, measuring less than 2cm in length. It is situated mostly in the posterior cranial fossa, with its superior part extending above the tentorial notch. The principal regions of the midbrain are the tectum, the cerebral aqueduct, tegmentum, and the cerebral peduncles. Rostral and caudal, Rostrally the midbrain adjoins the diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, etc.), while Rostral and caudal, cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Reticular Formation
The reticular formation is a set of interconnected nuclei in the brainstem that spans from the lower end of the medulla oblongata to the upper end of the midbrain. The neurons of the reticular formation make up a complex set of neural networks in the core of the brainstem. The reticular formation is made up of a diffuse net-like formation of reticular nuclei which is not well-defined. It may be seen as being made up of all the interspersed cells in the brainstem between the more compact and named structures. The reticular formation is functionally divided into the ascending reticular activating system (ARAS), ascending pathways to the cerebral cortex, and the descending reticular system, descending pathways ( reticulospinal tracts) to the spinal cord. Due to its extent along the brainstem it may be divided into different areas such as the midbrain reticular formation, the central mesencephalic reticular formation, the pontine reticular formation, the paramedian pontine reticul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ventral Tegmental Area
The ventral tegmental area (VTA) (tegmentum is Latin for ''covering''), also known as the ventral tegmental area of Tsai, or simply ventral tegmentum, is a group of neurons located close to the midline on the floor of the midbrain. The VTA is the origin of the dopaminergic cell bodies of the mesocorticolimbic dopamine system and other dopamine pathways; it is widely implicated in the drug and natural reward circuitry of the brain. The VTA plays an important role in a number of processes, including reward cognition ( motivational salience, associative learning, and positively-valenced emotions) and orgasm, among others, as well as several psychiatric disorders. Neurons in the VTA project to numerous areas of the brain, ranging from the prefrontal cortex to the caudal brainstem and several regions in between. Structure Neurobiologists have often had great difficulty distinguishing the VTA in humans and other primate brains from the substantia nigra (SN) and surrounding nuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Brainstem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is continuous with the thalamus of the diencephalon through the tentorial notch, and sometimes the diencephalon is included in the brainstem. The brainstem is very small, making up around only 2.6 percent of the brain's total weight. It has the critical roles of regulating heart and respiratory system, respiratory function, helping to control heart rate and breathing rate. It also provides the main motor and sensory nerve supply to the face and neck via the cranial nerves. Ten pairs of cranial nerves come from the brainstem. Other roles include the regulation of the central nervous system and the body's sleep cycle. It is also of prime importance in the conveyance of motor and sensory pathways from the rest of the brain to the body, and from the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Brain Stem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is continuous with the thalamus of the diencephalon through the tentorial notch, and sometimes the diencephalon is included in the brainstem. The brainstem is very small, making up around only 2.6 percent of the brain's total weight. It has the critical roles of regulating heart and respiratory function, helping to control heart rate and breathing rate. It also provides the main motor and sensory nerve supply to the face and neck via the cranial nerves. Ten pairs of cranial nerves come from the brainstem. Other roles include the regulation of the central nervous system and the body's sleep cycle. It is also of prime importance in the conveyance of motor and sensory pathways from the rest of the brain to the body, and from the body back ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Periaqueductal Gray
The periaqueductal gray (PAG), also known as the central gray, is a brain region that plays a critical role in autonomic function, motivated behavior and behavioural responses to threatening stimuli. PAG is also the primary control center for descending pain modulation. It has enkephalin-producing cells that suppress pain. The periaqueductal gray is the gray matter located around the cerebral aqueduct within the tegmentum of the midbrain. It projects to the nucleus raphe magnus, and also contains descending autonomic tracts. The ascending pain and temperature fibers of the spinothalamic tract send information to the PAG via the spinomesencephalic pathway (so-named because the fibers originate in the spine and terminate in the PAG, in the mesencephalon or midbrain). This region has been used as the target for brain-stimulating implants in patients with chronic pain. Role in analgesia Stimulation of the periaqueductal gray matter of the midbrain activates enkephalin-r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cerebral Aqueduct
The cerebral aqueduct (aqueduct of the midbrain, aqueduct of Sylvius, Sylvian aqueduct, mesencephalic duct) is a small, narrow tube connecting the third and fourth ventricles of the brain. The cerebral aqueduct is a midline structure that passes through the midbrain. It extends rostrocaudally through the entirety of the more posterior part of the midbrain. It is surrounded by the periaqueductal gray (central gray), a layer of gray matter. Congenital stenosis of the cerebral aqueduct is a cause of congenital hydrocephalus. It is named for Franciscus Sylvius. Anatomy The cerebral aqueduct is roughly circular in transverse section, and measures 1-2 mm in diameter. It is 15 mm long and is commonly subdivided into a pars anterior antrum, and pars posterior. Relations Rostrally, it is continuous with the third ventricle, commencing just inferior to the posterior commissure. Caudally, it is continuous with the fourth ventricle at the junction of the mesencephalon and pons. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pons
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other mammals, lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum. The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of Varolius"), after the Italian anatomist and surgeon Costanzo Varolio (1543–75). This region of the brainstem includes neural pathways and tracts that conduct signals from the brain down to the cerebellum and medulla, and tracts that carry the sensory signals up into the thalamus. Structure The pons in humans measures about in length. It is the part of the brainstem situated between the midbrain and the medulla oblongata. The horizontal ''medullopontine sulcus'' demarcates the boundary between the pons and medulla oblongata on the ventral aspect of the brainstem, and the roots of cranial nerves VI/VII/VIII emerge from the brainstem along this groove. The junction of pons, medulla oblongata, and cerebellum forms the cerebellopontine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Red Nucleus
The red nucleus or nucleus ruber is a structure in the rostral midbrain involved in motor coordination. The red nucleus is pale pink, which is believed to be due to the presence of iron in at least two different forms: hemoglobin and ferritin. The structure is located in the midbrain tegmentum next to the substantia nigra and comprises caudal magnocellular and rostral parvocellular components. The red nucleus and substantia nigra are subcortical centers of the extrapyramidal motor system. Function In a vertebrate without a significant corticospinal tract, gait is mainly controlled by the red nucleus. However, in primates, where the corticospinal tract is dominant, the rubrospinal tract may be regarded as vestigial in motor function. Therefore, the red nucleus is less important in primates than in many other mammals. Nevertheless, the crawling of babies is controlled by the red nucleus, as is arm swinging in typical walking. The red nucleus may play an additional role ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |